Final ID: MP1375
Diagnostic Performance of Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging versus Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography for Cardiac Sarcoidosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiac sarcoidosis (CS) is a rare, but potentially life-threatening manifestation of systemic sarcoidosis. While both cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMRI) and fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) are widely used as non-invasive imaging modalities, their relative diagnostic accuracy remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of CMRI compared to FDG-PET for detecting CS.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL through May 2025 to identify studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of CMRI and/or FDG-PET for CS. Studies were included if they reported sufficient data to calculate diagnostic accuracy metrics against a clinical or histological reference standard. A bivariate random-effects model was used to estimate pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratios (DOR) along with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). The positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative likelihood ratio (LR-) and Youden Index were also calculated. A summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) diagnostic model was used to calculate the area under curve (AUC) and evaluate overall diagnostic performance. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant in all cases.
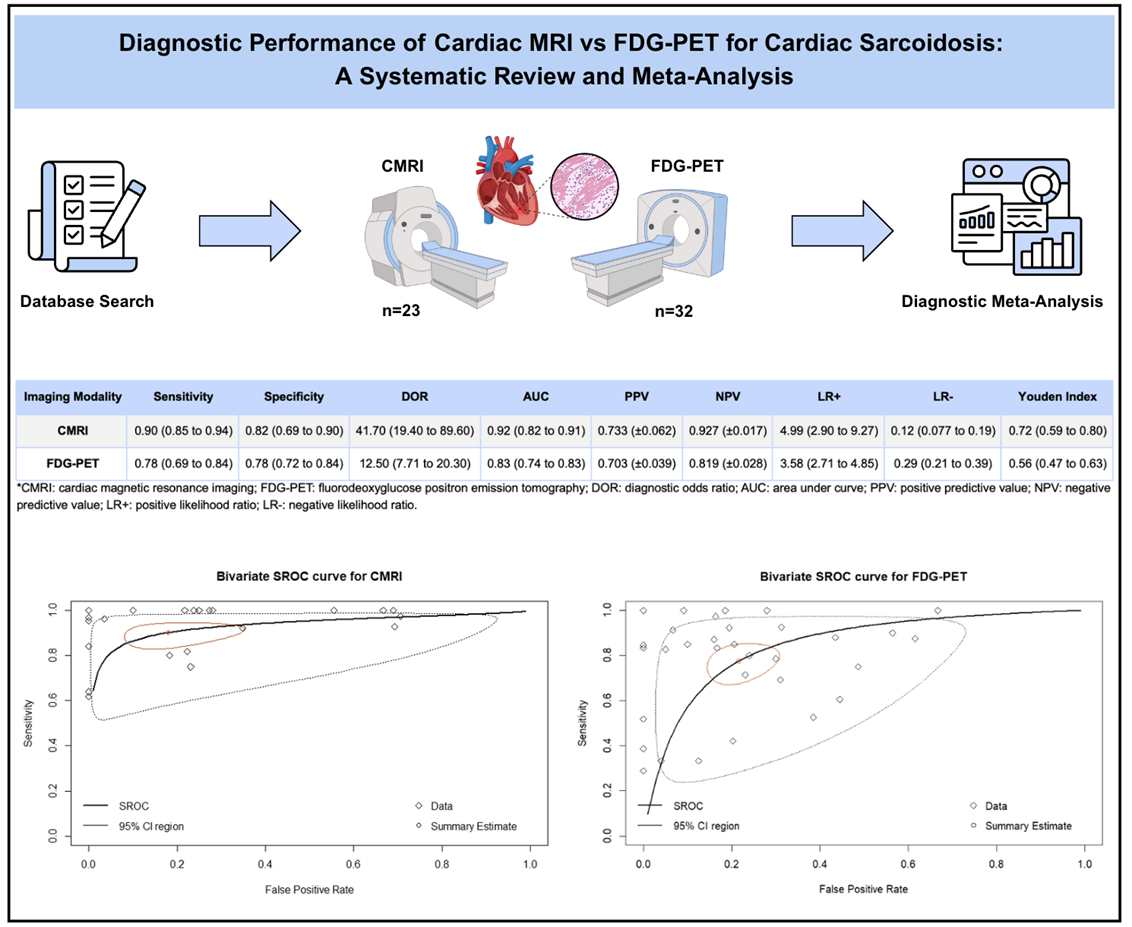
Results: A total of 41 studies were included, out of which 23 reported data for CMRI and 32 for FDG-PET. CMRI demonstrated significantly superior overall diagnostic performance compared to FDG-PET (p = 0.013 for AUC comparison) for the detection of cardiac sarcoidosis. Pooled sensitivity and specificity for CMRI were 0.90 (95% CI: 0.85-0.94) and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.69-0.90) respectively, both higher than FDG-PET, which showed a sensitivity of 0.78 (95% CI: 0.69-0.84) and specificity of 0.78 (0.72-0.84). CMRI also yielded a greater DOR of 41.7 (95% CI: 19.40-89.6) versus 12.50 (95% CI: 7.71-20.30), AUC of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.82-0.91) versus 0.83 (0.74-0.83) and YI of 0.72 (95% CI: 0.59-0.80) versus 0.56 (95% CI: 0.47-0.63) compared to FDG-PET.
Conclusion: CMRI demonstrated a significantly greater diagnostic performance for detection of CS compared to FDG-PET with a superior sensitivity, specificity, DOR, AUC and YI, highlighting CMRI as a more robust imaging modality for CS. However, direct comparative studies and standardized diagnostic criteria remain essential to confirm these findings and guide clinical imaging strategies.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted across PubMed, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL through May 2025 to identify studies evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of CMRI and/or FDG-PET for CS. Studies were included if they reported sufficient data to calculate diagnostic accuracy metrics against a clinical or histological reference standard. A bivariate random-effects model was used to estimate pooled sensitivity, specificity, diagnostic odds ratios (DOR) along with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). The positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative likelihood ratio (LR-) and Youden Index were also calculated. A summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) diagnostic model was used to calculate the area under curve (AUC) and evaluate overall diagnostic performance. A p-value <0.05 was considered significant in all cases.
Results: A total of 41 studies were included, out of which 23 reported data for CMRI and 32 for FDG-PET. CMRI demonstrated significantly superior overall diagnostic performance compared to FDG-PET (p = 0.013 for AUC comparison) for the detection of cardiac sarcoidosis. Pooled sensitivity and specificity for CMRI were 0.90 (95% CI: 0.85-0.94) and 0.82 (95% CI: 0.69-0.90) respectively, both higher than FDG-PET, which showed a sensitivity of 0.78 (95% CI: 0.69-0.84) and specificity of 0.78 (0.72-0.84). CMRI also yielded a greater DOR of 41.7 (95% CI: 19.40-89.6) versus 12.50 (95% CI: 7.71-20.30), AUC of 0.92 (95% CI: 0.82-0.91) versus 0.83 (0.74-0.83) and YI of 0.72 (95% CI: 0.59-0.80) versus 0.56 (95% CI: 0.47-0.63) compared to FDG-PET.
Conclusion: CMRI demonstrated a significantly greater diagnostic performance for detection of CS compared to FDG-PET with a superior sensitivity, specificity, DOR, AUC and YI, highlighting CMRI as a more robust imaging modality for CS. However, direct comparative studies and standardized diagnostic criteria remain essential to confirm these findings and guide clinical imaging strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Stepwise Approach to Identifying and Assessing the Content Validity of Patient-Reported Outcome (PRO) Measures for Use with Adults with Acute Heart Failure
O'connor Meaghan, Loughlin Anita, Waldman Laura, Rucker Sloan, Vaghela Shailja, Kwon Namhee, Sikirica Vanja
Brain and Cardiovascular Connection in Recovery: Coupling Neurovascular Regulation to Vascular and Non-cardiac Inflammation in the Individual Patient Post Acute Myocardial InfarctionLopez Javier, Chung Kevin, Atsina Kwame, Abdelhafez Yasser, Chaudhari Abhijit, Schaefer Saul, Badawi Ramsey, Wang Guobao