Final ID: MP2457
Advanced Complementary Imaging Analysis of Single Ventricle Patients Using Cardiac Magnetic Resonance and Echocardiography
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: The hemodynamic efficiency in patients with single ventricle (SV)-type anatomy is critical for their long-term outcomes. Conventional and novel metrics of SV function such as cardiac index, flow energy loss (FEL) and kinetic energy (KE) can be quantified by non-invasive parameters (CMR) and 4D flow, although echocardiography (echo) remains the front-line modality for serial measurement. There is recent development in echo-based intracardiac flow analysis using novel Doppler velocity reconstruction (DoVeR). This study utilizes both 4D flow and DoVeR to analyze flow parameters in SV patients.
Methods: SV patients with Pre-Fontan and Fontan anatomy with both echo and CMR imaging within 1 year apart were identified from institutional electronic medical records. 4D flow datasets were analyzed using ITFlow (CardioFlowDesign) to measure FEL/KE (indexed against body surface area) in the SV through the cardiac cycle. Conventional color flow echo from the apical view were post-processed via DoVeR to also obtain FEL and KE (indexed against the ventricular cavity area on the imaging plane). Post processed data was analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficient analysis to evaluate the relationships between echo/4D flow parameters as well as conventional CMR metrics such as cardiac index.
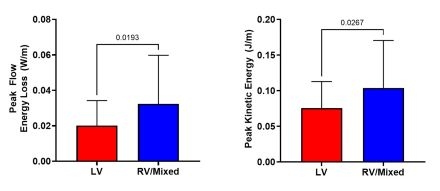
Results: 4D flow and DoVeR was successfully post-processed in 86 SV patients (13.6±9.8 years, 21 female, 1.3±0.5m2, indexed end diastolic volume 116 ± 34 mL/m2, cardiac index 4.2±1.6L/min/m2). By DoVeR, left ventricular dominant morphology (n = 53) was associated with lower FEL/KE compared to right/mixed ventricular dominant morphology. DoVeR KE and FEL both correlated with cardiac index (r=0.330, p=0.0003 and r=0.494, p<0.0001 respectively). Finally, there was moderate correlation of FEL/KE measurements between DoVeR and 4D Flow (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Echo can provide concordant measures of intracardiac flow via DoVeR. While CMR/4D flow remains the gold standard in flow/functional assessment, complementary use of DoVeR may provide insight into the longitudinal progression of intracardiac flow and hemodynamic efficiency in SV patients.
Methods: SV patients with Pre-Fontan and Fontan anatomy with both echo and CMR imaging within 1 year apart were identified from institutional electronic medical records. 4D flow datasets were analyzed using ITFlow (CardioFlowDesign) to measure FEL/KE (indexed against body surface area) in the SV through the cardiac cycle. Conventional color flow echo from the apical view were post-processed via DoVeR to also obtain FEL and KE (indexed against the ventricular cavity area on the imaging plane). Post processed data was analyzed by Pearson correlation coefficient analysis to evaluate the relationships between echo/4D flow parameters as well as conventional CMR metrics such as cardiac index.
Results: 4D flow and DoVeR was successfully post-processed in 86 SV patients (13.6±9.8 years, 21 female, 1.3±0.5m2, indexed end diastolic volume 116 ± 34 mL/m2, cardiac index 4.2±1.6L/min/m2). By DoVeR, left ventricular dominant morphology (n = 53) was associated with lower FEL/KE compared to right/mixed ventricular dominant morphology. DoVeR KE and FEL both correlated with cardiac index (r=0.330, p=0.0003 and r=0.494, p<0.0001 respectively). Finally, there was moderate correlation of FEL/KE measurements between DoVeR and 4D Flow (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Echo can provide concordant measures of intracardiac flow via DoVeR. While CMR/4D flow remains the gold standard in flow/functional assessment, complementary use of DoVeR may provide insight into the longitudinal progression of intracardiac flow and hemodynamic efficiency in SV patients.
More abstracts on this topic:
Are Discharge Barriers Responsible for Insurance-Based Differences in Length of Stay After Congenital Heart Surgery?
Laternser Christina, Zdanowicz Zofia, Lay Amy, Woo Joyce
A 10 Year Report on Fontan CandidacyAdamson Marissa, John Mohan, Nayi Pranay, Deshpande Shriprasad, Ferguson Matthew, Maher Kevin, Chai Paul, Beshish Asaad