Final ID: MP1533
Association of County-Level School Expenditure per Student During Childhood with Cardiovascular Health in Young Adulthood
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: There is a well-established link between educational attainment and health outcomes. Area-level investment in education is an upstream contributor to individual-level educational attainment and is a policy-level factor that may broadly represent area-level socioeconomic status. We evaluated whether county-level public school expenditure per student during childhood is associated with cardiovascular health (CVH) during young adulthood.
Research Question: Is county-level school expenditure per student during childhood associated with CVH in young adulthood?
Methods: We analyzed data from the Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study, which is a birth cohort study that includes information on county-level measures of annual school expenditure per student across childhood and CVH outcomes at study year 22. Multivariable linear regression models evaluated the associations of county-level school expenditure per student at birth (low [z-score ≤-0.5], intermediate [z-score -0.5 to 0.5], and high [z-score ≥0.5]) with CVH factors (systolic blood pressure [SBP], non-HDL cholesterol (non-HDL-C), hemoglobin A1c, body mass index (BMI)] and Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) CVH score at year 22, adjusted for child’s sex, family income in childhood, primary caregiver’s educational attainment, mother’s age at baseline.
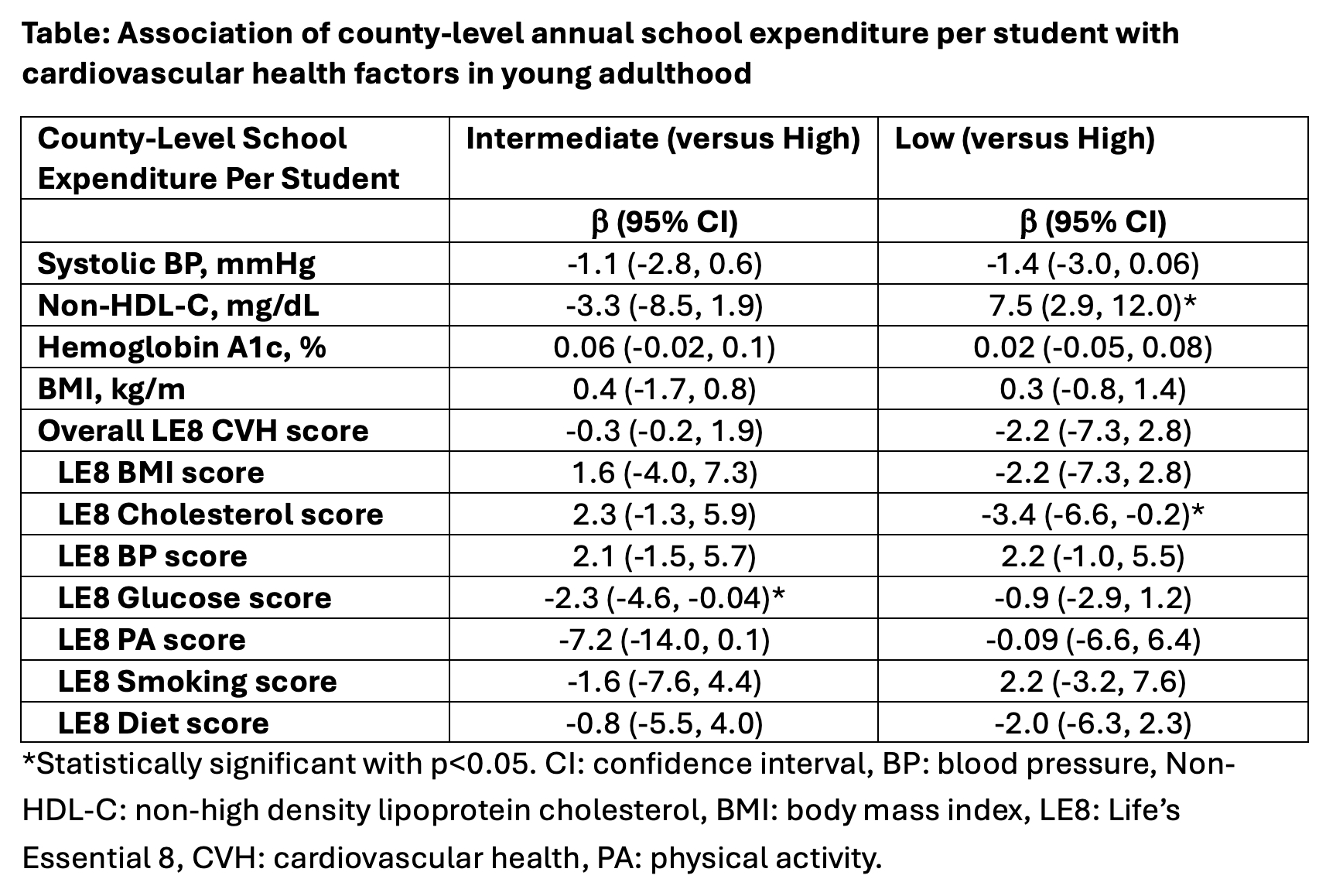
Results: Of 1,183 participants, 54% were female, 52% were Black, 26% were Hispanic, and 17% were White. The range of annual expenditure per student was: low, $4,020-6,245; intermediate, $6,317-7,392; high, $7,561-9,902. By study year 22, 21% graduated college, 22% had some college education, and 41% graduated high school. Mean LE8 score was 68 (SD 14). Compared with living in a county with high expenditure per student at baseline, living in a county with low school expenditure per student in childhood was associated with 7.5 mg/dL higher non-HDL-C levels (95% CI 2.9,12.0) and a 3.4-point lower LE8 cholesterol score (95% CI -6.6,-0.23) in young adulthood; and living in a county with intermediate school expenditure per student was associated with a 2.3-point lower LE8 glucose score in young adulthood (95% CI -4.6,-0.04).
Conclusions: Living in a county with lower school expenditure per student during childhood is associated with modestly but significantly worse CVH factors in young adulthood. Policies that influence area-level educational investment and socioeconomic position during childhood may influence CVH in young adulthood.
Research Question: Is county-level school expenditure per student during childhood associated with CVH in young adulthood?
Methods: We analyzed data from the Future of Families and Child Wellbeing Study, which is a birth cohort study that includes information on county-level measures of annual school expenditure per student across childhood and CVH outcomes at study year 22. Multivariable linear regression models evaluated the associations of county-level school expenditure per student at birth (low [z-score ≤-0.5], intermediate [z-score -0.5 to 0.5], and high [z-score ≥0.5]) with CVH factors (systolic blood pressure [SBP], non-HDL cholesterol (non-HDL-C), hemoglobin A1c, body mass index (BMI)] and Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) CVH score at year 22, adjusted for child’s sex, family income in childhood, primary caregiver’s educational attainment, mother’s age at baseline.
Results: Of 1,183 participants, 54% were female, 52% were Black, 26% were Hispanic, and 17% were White. The range of annual expenditure per student was: low, $4,020-6,245; intermediate, $6,317-7,392; high, $7,561-9,902. By study year 22, 21% graduated college, 22% had some college education, and 41% graduated high school. Mean LE8 score was 68 (SD 14). Compared with living in a county with high expenditure per student at baseline, living in a county with low school expenditure per student in childhood was associated with 7.5 mg/dL higher non-HDL-C levels (95% CI 2.9,12.0) and a 3.4-point lower LE8 cholesterol score (95% CI -6.6,-0.23) in young adulthood; and living in a county with intermediate school expenditure per student was associated with a 2.3-point lower LE8 glucose score in young adulthood (95% CI -4.6,-0.04).
Conclusions: Living in a county with lower school expenditure per student during childhood is associated with modestly but significantly worse CVH factors in young adulthood. Policies that influence area-level educational investment and socioeconomic position during childhood may influence CVH in young adulthood.
More abstracts on this topic:
Acceptability and Effectiveness of a Novel, Video-Based CPR and AED Education Program in Canadian Schools
Allan Katherine, Dhillon Santokh, Mcculloch Holly, Ruether Kim, Zotzman Jeanine, Blanchard Ian, Janczyszyn Mike, Wong Natalie, Oneil Emma, Sapp John
A Finding of Unique Peak Exercise Level in Respiratory Exchange Ratio during Bicycle Ergometric Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing in Healthy SubjectsNakayama Atsuko, Sakuma Hiroki, Iwata Tomoharu, Kashino Kunio, Isobe Mitsuaki, Tomoike Hitonobu