Final ID: Mo2018
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Models Effectively Detect Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction (CTRCD): a Diagnostic Test Accuracy (DTA) Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Significant advances in cancer diagnosis and treatment, have yielded improved survival among cancer patients. This predisposes patients to cardiovascular compromise, which have become a major cause of mortality in cancer survivors. Thus, effective, non-invasive screening procedures for early detection of cardiovascular dysfunction in high-risk patients are needed. Several AI models incorporating clinical and radiologic parameters have been developed to detect cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) in cancer patients or survivors.
Aim & Hypothesis
We sought to investigate the pooled diagnostic performance of these models for CTRCD detection in oncology patients. We hypothesized that AI models would be effective for and would outperform clinical comparators including non-AI nomograms and cardiologist’s assessment in CTRCD detection among cancer patients and survivors.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane from inception till May 2025 was performed to identify studies investigating the use of an AI model for CTRCD detection (defined as post-treatment LVEF<50% or >10% LVEF drop from baseline). For meta-analysis inclusion, studies either (a) provided complete AI model confusion matrix data; or (b) provided area-under-the-curve (AUC) mean and 95% confidence interval (CI) for both AI model and a clinical comparator. Inverse variance random effects model meta-analysis was performed. Pooled performance estimates with corresponding 95% CIs are presented in forest plots and a summary receiver operating characteristics (sROC) curve.
Results
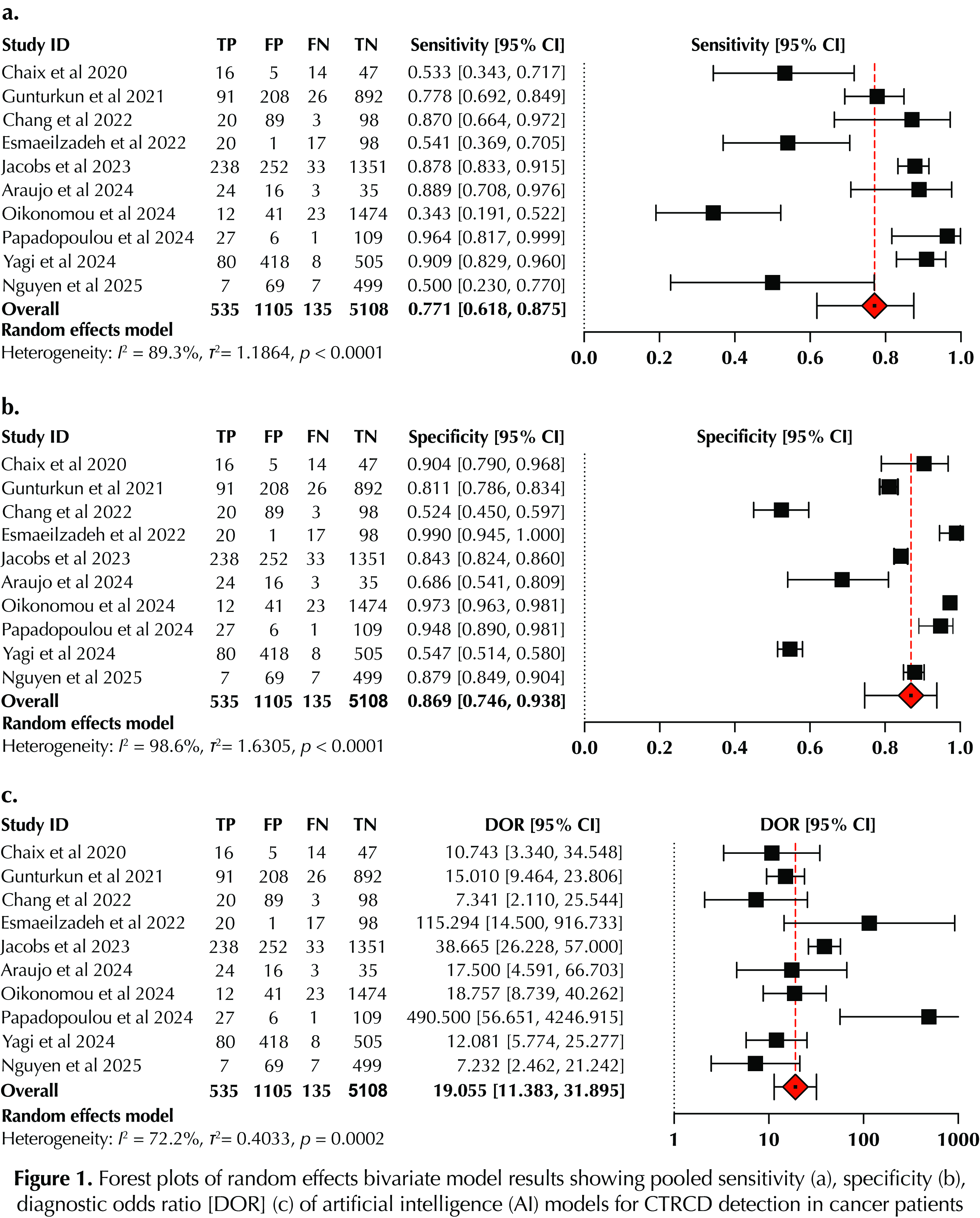
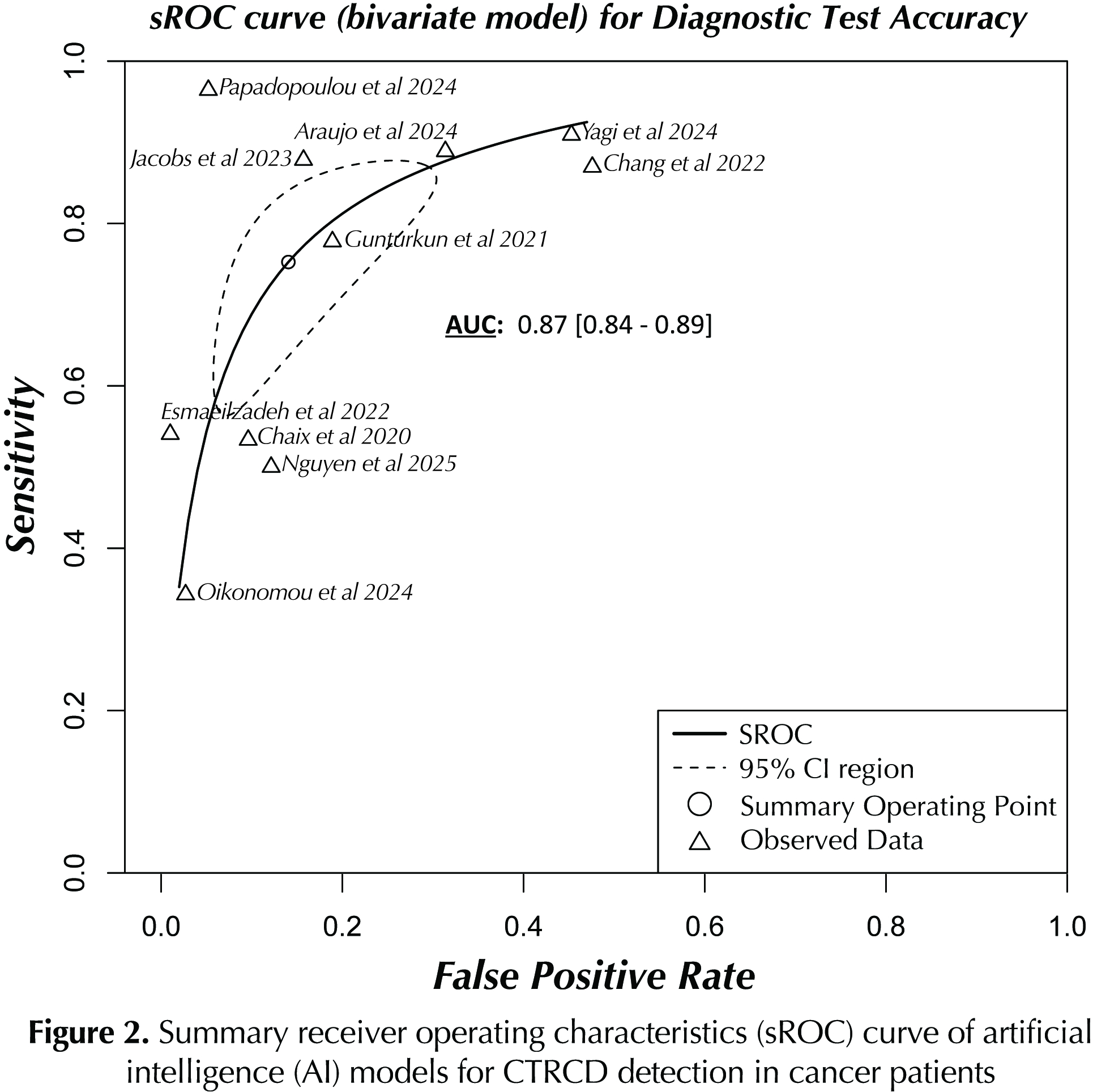
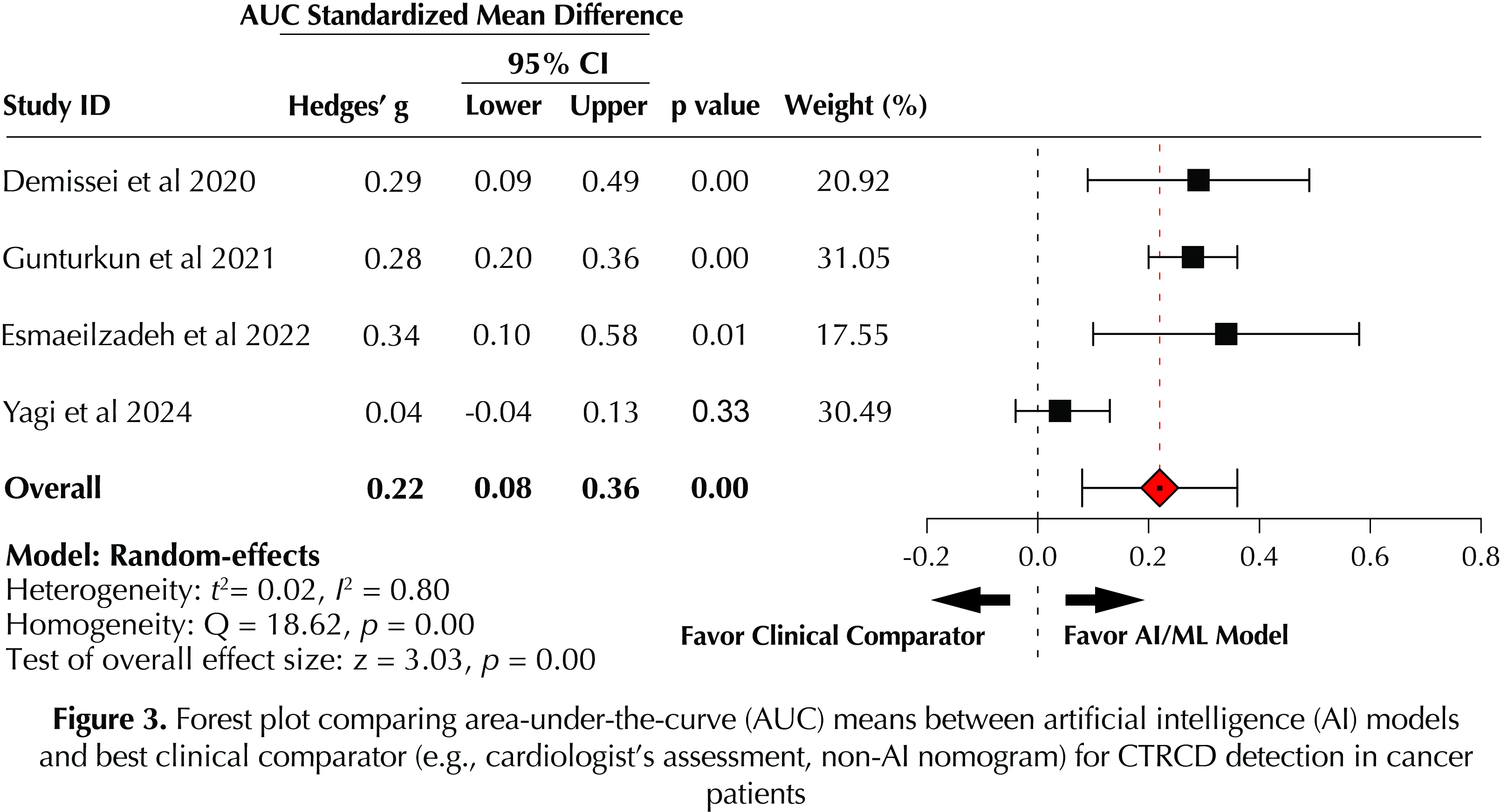
A total of 11 studies involving 5,801 adult and 289 pediatric patients were included for analysis. On bivariate modeling, AI models yielded pooled sensitivity of 0.771 (95% CI 0.618 – 0.875); specificity of 0.869 (95% CI 0.746 – 0.938); diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 19.055 (95% CI 11.383 – 31.895); and AUC of 0.87 (95% CI 0.84 – 0.89), for CTRCD detection in cancer patients or survivors (Fig. 1A-C, 2). By pooling and comparing mean AUCs for AI models and corresponding clinical comparators, AI models outperformed the best reported clinical comparator (Fig. 3) with an hedges’ g standardized mean difference (SMD) of 0.22 (95% CI 0.08 – 0.36, p = 0.00).
Conclusion
AI models surpassed even the best clinical standard for CTRCD detection. More research is needed to delineate their utility across various cancer diagnoses, treatment modalities, and for detecting other cardiotoxicity forms.
Significant advances in cancer diagnosis and treatment, have yielded improved survival among cancer patients. This predisposes patients to cardiovascular compromise, which have become a major cause of mortality in cancer survivors. Thus, effective, non-invasive screening procedures for early detection of cardiovascular dysfunction in high-risk patients are needed. Several AI models incorporating clinical and radiologic parameters have been developed to detect cancer therapy-related cardiac dysfunction (CTRCD) in cancer patients or survivors.
Aim & Hypothesis
We sought to investigate the pooled diagnostic performance of these models for CTRCD detection in oncology patients. We hypothesized that AI models would be effective for and would outperform clinical comparators including non-AI nomograms and cardiologist’s assessment in CTRCD detection among cancer patients and survivors.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed/Medline, Scopus, and Cochrane from inception till May 2025 was performed to identify studies investigating the use of an AI model for CTRCD detection (defined as post-treatment LVEF<50% or >10% LVEF drop from baseline). For meta-analysis inclusion, studies either (a) provided complete AI model confusion matrix data; or (b) provided area-under-the-curve (AUC) mean and 95% confidence interval (CI) for both AI model and a clinical comparator. Inverse variance random effects model meta-analysis was performed. Pooled performance estimates with corresponding 95% CIs are presented in forest plots and a summary receiver operating characteristics (sROC) curve.
Results
A total of 11 studies involving 5,801 adult and 289 pediatric patients were included for analysis. On bivariate modeling, AI models yielded pooled sensitivity of 0.771 (95% CI 0.618 – 0.875); specificity of 0.869 (95% CI 0.746 – 0.938); diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) of 19.055 (95% CI 11.383 – 31.895); and AUC of 0.87 (95% CI 0.84 – 0.89), for CTRCD detection in cancer patients or survivors (Fig. 1A-C, 2). By pooling and comparing mean AUCs for AI models and corresponding clinical comparators, AI models outperformed the best reported clinical comparator (Fig. 3) with an hedges’ g standardized mean difference (SMD) of 0.22 (95% CI 0.08 – 0.36, p = 0.00).
Conclusion
AI models surpassed even the best clinical standard for CTRCD detection. More research is needed to delineate their utility across various cancer diagnoses, treatment modalities, and for detecting other cardiotoxicity forms.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Comparison Between Global Longitudinal Strain (GLS) Derived with CMR Feature-Tracking (CMR-FT) and 2D Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography (2D-STE) to Monitor Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction (CTRCD)
Kar Julia, Cohen Michael, Revere Cherie, Mcquiston Samuel, Malozzi Christopher
A novel mechanism of pediatric DCM that recapitulates aspects of the human disease via Notch signaling: a pathway to new therapeutics?Nyarko Obed, Sucharov Carmen