Final ID: MP2424
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Lower Readmission Rates Without Impacting Mortality After CABG in Adults with Congenital Heart Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are increasingly prescribed for type-2 diabetes and obesity, with emerging evidence of cardiovascular benefits. However, their impact on postoperative outcomes in adult congenital heart disease (CHD) patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remains underexplored.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using de-identified patient data from the TriNetX Research Network from 2005-2025. Adult CHD patients (ICD-10: Q20-Q28) who underwent CABG (CPT: 1006208, 1006217, 1006200) were divided into two cohorts: those with documented GLP-1 agonist use (ATC: A10BJ) prior to or within 6 months after surgery and those without (control). Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance cohorts based on race, ethnicity, sex, age at surgery, comorbidities including diabetes, obesity, and heart failure, and CHD diagnoses.
Primary outcomes included 6-month all-cause mortality and hospital readmission rate. Secondary outcomes included GLP-1-related complications (acute pancreatitis, gastroparesis, weight loss) and postoperative events (acute kidney injury [AKI], myocardial infarction [MI], transient ischemic attack [TIA], cerebral infarction, and hypoglycemic event).
Results:
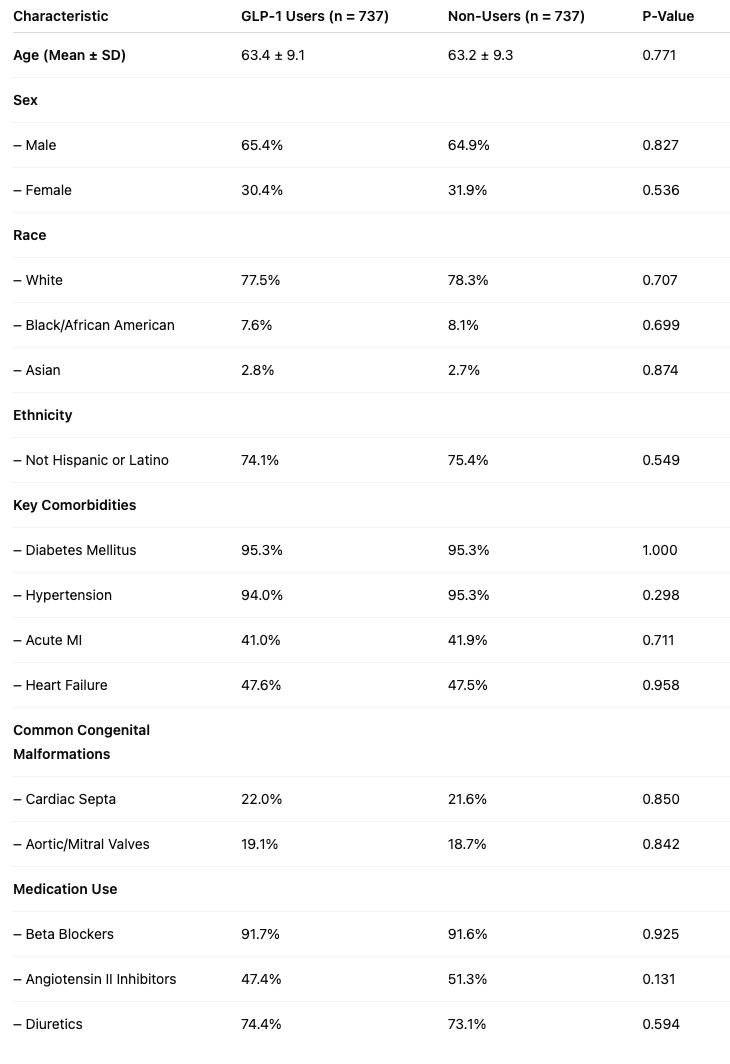
The total number of patients included in the study was 1468, of which 734 patients were in GLP-1 group and control group, respectively. After matching, no differences were observed between the cohorts in the prevalence of key comorbidities prior to CABG: chronic ischemic heart disease, nonrheumatic aortic valve disorders, cerebrovascular diseases, acute MI, and angina pectoris (Table 1)
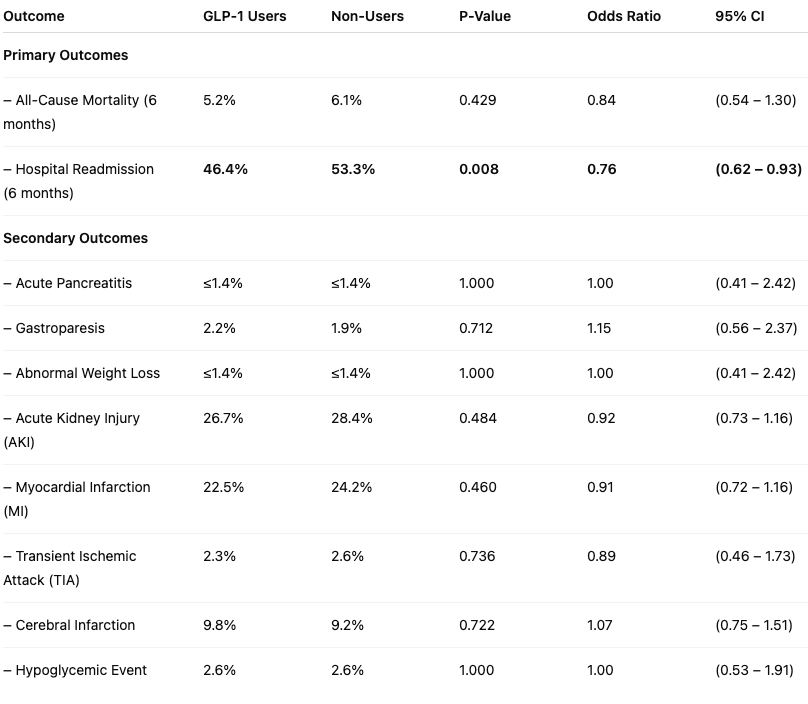
GLP-1 agonist use was associated with a significant reduction in 6-month hospital readmission rate (Odds Ratio [OR]=0.76, p=0.008) but no difference in 6-month mortality (OR=0.84, p=0.43) compared to controls. No differences were noted among known complications of GLP-1 agonists: acute pancreatitis (OR=1, p=1), gastroparesis (OR=1.146, p=0.71) and abnormal weight loss (OR=1, p=1). Other post-operative outcomes such as AKI, MI, TIA, cerebral infarction and hypoglycemic event, were not significant either (Table 2).
Conclusion:
In adult CHD patients undergoing CABG, preoperative use of GLP-1 receptor agonists was associated with a significant reduction in 6-month hospital readmission rate. However, their use was not associated with differences in other postoperative outcomes or known complications.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are increasingly prescribed for type-2 diabetes and obesity, with emerging evidence of cardiovascular benefits. However, their impact on postoperative outcomes in adult congenital heart disease (CHD) patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remains underexplored.
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using de-identified patient data from the TriNetX Research Network from 2005-2025. Adult CHD patients (ICD-10: Q20-Q28) who underwent CABG (CPT: 1006208, 1006217, 1006200) were divided into two cohorts: those with documented GLP-1 agonist use (ATC: A10BJ) prior to or within 6 months after surgery and those without (control). Propensity score matching (1:1) was used to balance cohorts based on race, ethnicity, sex, age at surgery, comorbidities including diabetes, obesity, and heart failure, and CHD diagnoses.
Primary outcomes included 6-month all-cause mortality and hospital readmission rate. Secondary outcomes included GLP-1-related complications (acute pancreatitis, gastroparesis, weight loss) and postoperative events (acute kidney injury [AKI], myocardial infarction [MI], transient ischemic attack [TIA], cerebral infarction, and hypoglycemic event).
Results:
The total number of patients included in the study was 1468, of which 734 patients were in GLP-1 group and control group, respectively. After matching, no differences were observed between the cohorts in the prevalence of key comorbidities prior to CABG: chronic ischemic heart disease, nonrheumatic aortic valve disorders, cerebrovascular diseases, acute MI, and angina pectoris (Table 1)
GLP-1 agonist use was associated with a significant reduction in 6-month hospital readmission rate (Odds Ratio [OR]=0.76, p=0.008) but no difference in 6-month mortality (OR=0.84, p=0.43) compared to controls. No differences were noted among known complications of GLP-1 agonists: acute pancreatitis (OR=1, p=1), gastroparesis (OR=1.146, p=0.71) and abnormal weight loss (OR=1, p=1). Other post-operative outcomes such as AKI, MI, TIA, cerebral infarction and hypoglycemic event, were not significant either (Table 2).
Conclusion:
In adult CHD patients undergoing CABG, preoperative use of GLP-1 receptor agonists was associated with a significant reduction in 6-month hospital readmission rate. However, their use was not associated with differences in other postoperative outcomes or known complications.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multicentre Study for Hands Only CPR (HOCPR) training assessment towards building a ‘Nation of Life Savers” in India
Ravikumar Thanjavur, Sarma Kvs, Ravikumar Thanjavur, Sarkar Manuj, Debnath Dhrubajyoti, Behera Priyamadhaba, Ghate Jayshri, Trikha Divay, Samantaray A, Madhavi K
A peptoid derivative of alpha-calcitonin gene related peptide improves cardiac function in pressure-overload heart failure miceKumar Ambrish, Deloach Sarah, Dipette Donald, Potts Jay