Final ID: Sa4035
Mapping the Gene Network Dysregulation in Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Reveals Candidate Therapeutic Targets
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Ascending aortic aneurysm is a complex multicellular disease with high mortality associated with both monogenic causes and sporadic disease. Known causative genes include FBN1 in Marfan syndrome or TGFB pathway variants in Loeys-Dietz Syndrome (LDS). However, sporadic ascending aortic aneurysms can also occur in patients without variants in known causative genes, especially with increasing age. Yet, it is not clear whether these sporadic cases share common mechanisms with monogenic subtypes.
Research Goal: Mapping the genetic regulatory network disrupted in monogenic and sporadic aortic aneurysm to identify shared and genotype-specific dysregulation and predict candidate therapeutic targets.
Methods: We leveraged single-cell RNA sequencing data from aortic tissue in sporadic and monogenic aortic aneurysm patients to map disease-dependent gene networks and predict candidate therapeutic targets. First, we inferred the gene network dysregulated in TGFBR1/2+/- smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and fibroblasts using CellOracle, mapping the rewiring in the most severe form of LDS aortic aneurysm. We next fine-tuned Geneformer – a foundational artificial intelligence (AI) model enabling context-specific predictions in network biology – to distinguish disease-dependent dysregulation in sporadic and monogenic cases stratified by genotype (heterozygous TGFBR1/2, SMAD3, FBN1, or ACTA2). Then, we performed in silico deletion to predict cell type-specific candidate therapeutic targets for monogenic and sporadic aortic aneurysms.
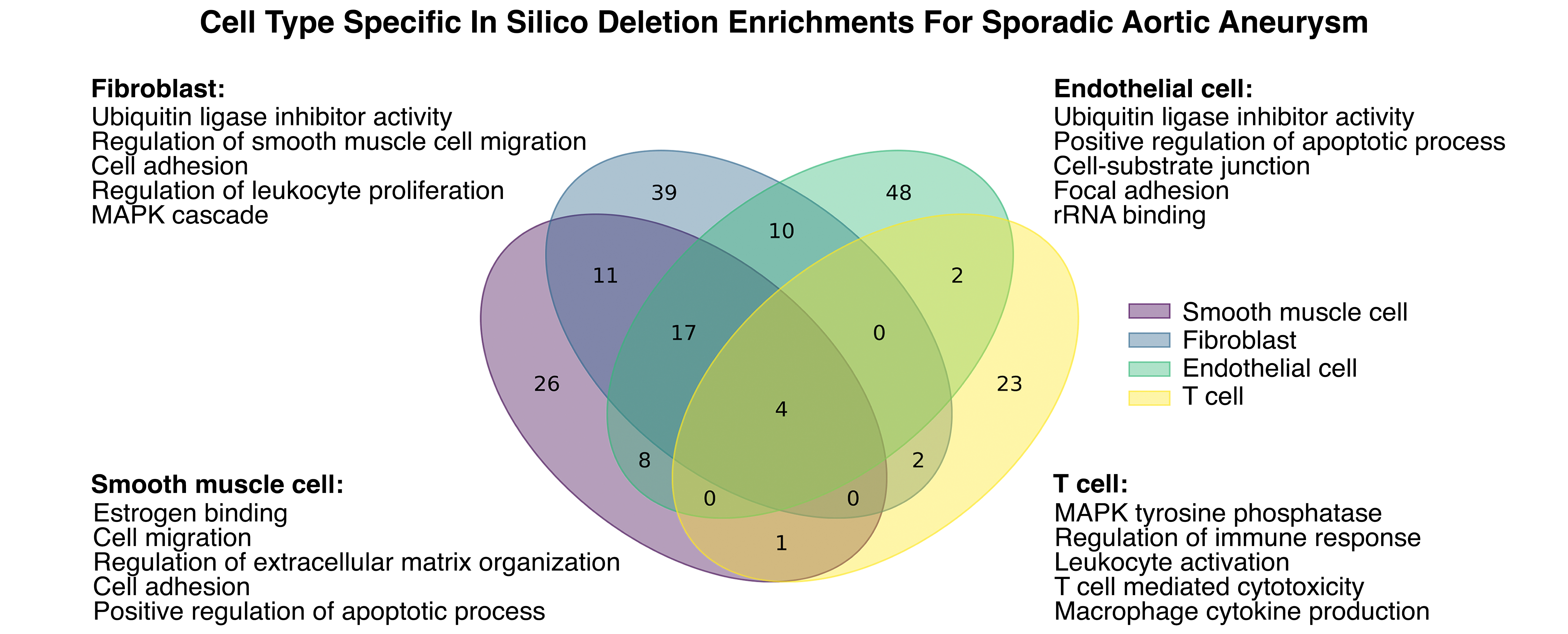
Results: We identified 10 network communities in the control vs TGFBR1/2+/- SMCs, each enriched for genes associated with distinct pathways such as contractility and immune activation. In TGFBR1/2+/- SMCs, KLF4 and KLF2 were central regulators of the network and key nodes within the contractility network community. Upon in silico deletion for monogenic and sporadic cases, targets whose repression was predicted to be beneficial in aneurysmal SMCs included NFATC2, which is reported to promote macrophage infiltration in vascular disease, IL-1, which promotes immune activation, and LMO7, a regulator of TGFB signaling.
Conclusions: We mapped the gene network disrupted in aortic aneurysm, revealing primary regulators in the disease-dependent network. Ongoing work is experimentally validating shared and genotype-specific AI-predicted therapeutic targets for their impact on in vitro SMC function and in vivo aortic aneurysm progression.
Research Goal: Mapping the genetic regulatory network disrupted in monogenic and sporadic aortic aneurysm to identify shared and genotype-specific dysregulation and predict candidate therapeutic targets.
Methods: We leveraged single-cell RNA sequencing data from aortic tissue in sporadic and monogenic aortic aneurysm patients to map disease-dependent gene networks and predict candidate therapeutic targets. First, we inferred the gene network dysregulated in TGFBR1/2+/- smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and fibroblasts using CellOracle, mapping the rewiring in the most severe form of LDS aortic aneurysm. We next fine-tuned Geneformer – a foundational artificial intelligence (AI) model enabling context-specific predictions in network biology – to distinguish disease-dependent dysregulation in sporadic and monogenic cases stratified by genotype (heterozygous TGFBR1/2, SMAD3, FBN1, or ACTA2). Then, we performed in silico deletion to predict cell type-specific candidate therapeutic targets for monogenic and sporadic aortic aneurysms.
Results: We identified 10 network communities in the control vs TGFBR1/2+/- SMCs, each enriched for genes associated with distinct pathways such as contractility and immune activation. In TGFBR1/2+/- SMCs, KLF4 and KLF2 were central regulators of the network and key nodes within the contractility network community. Upon in silico deletion for monogenic and sporadic cases, targets whose repression was predicted to be beneficial in aneurysmal SMCs included NFATC2, which is reported to promote macrophage infiltration in vascular disease, IL-1, which promotes immune activation, and LMO7, a regulator of TGFB signaling.
Conclusions: We mapped the gene network disrupted in aortic aneurysm, revealing primary regulators in the disease-dependent network. Ongoing work is experimentally validating shared and genotype-specific AI-predicted therapeutic targets for their impact on in vitro SMC function and in vivo aortic aneurysm progression.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Spatially Resolved Transcriptomic Signature of Atherosclerotic Plaque Stabilization and Regression
Persaud Luis, Lin Li-hsien, Weiss Robert, Kutschke William, Streeter Jennifer
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial GrowthHan Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E