Final ID: Sa1023
Right Atrial Longitudinal Strain Phenotypes in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Right ventricular diastolic dysfunction (RVDD) is a critical yet underrecognized driver of morbidity and mortality in systemic sclerosis (SSc), with gold-standard assessment relying on invasive pressure-volume loop analysis. Right atrial (RA) remodeling, reflecting early RA–RV uncoupling, may serve as a sensitive, noninvasive marker of emerging RVDD. In this study, we applied cluster analysis to raw speckle-tracking echocardiography (STE)-derived measures of RA mechanics to identify clinically meaningful phenotypes and evaluate their association with mortality in SSc.
Methods: We analyzed a well-characterized cohort of patients with SSc from Johns Hopkins Medicine with quantifiable STE-derived RA strain metrics performed within six-months of invasive hemodynamics. Demographic, clinical, and echocardiographic data were assessed, and RA strain curves were stratified using machine learning derived time series k-means clustering with dynamic time warping to identify phenotypes of RA function. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models, adjusted for SSc disease duration, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and body surface area (BSA) were utilized to classify inter-cluster risk for a composite clinical endpoint of all-cause mortality, stroke, myocardial infarction, and heart failure hospitalization.
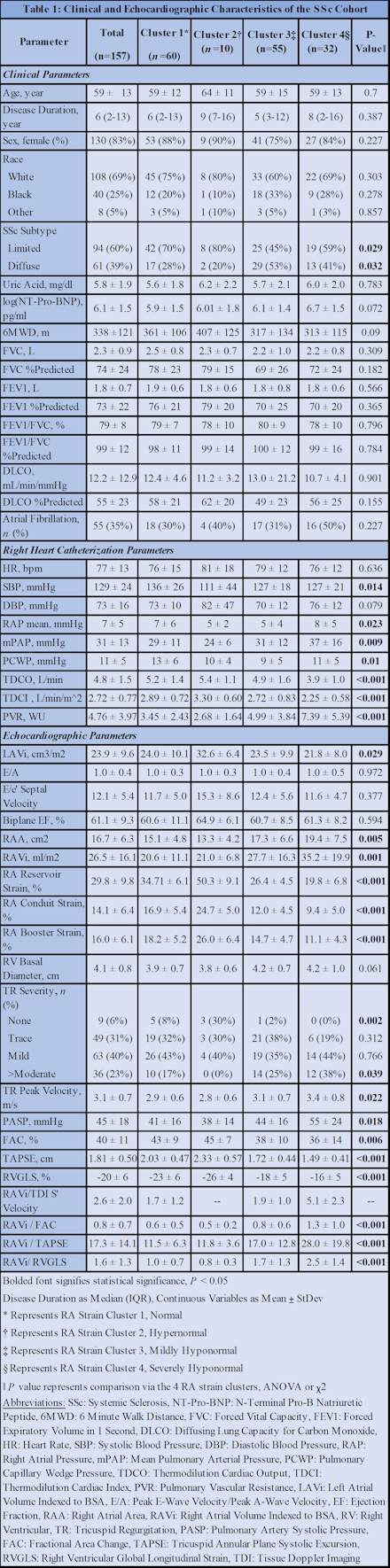
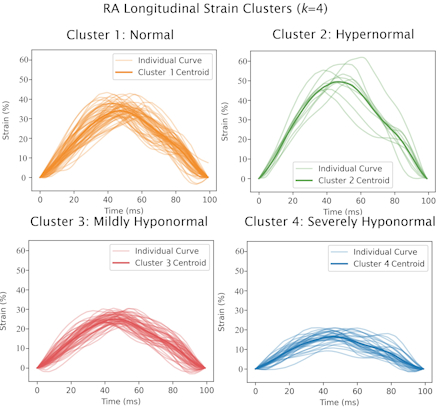
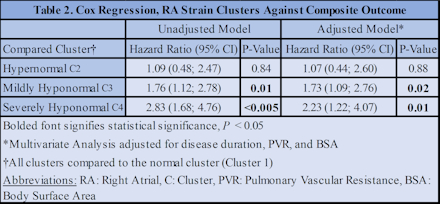
Results: Our cohort consisted of 157 SSc patients with a mean age 59 ± 13 years, 83% female, 69% White, and 60% with limited SSc subtype, Table 1. Time series k-means clustering revealed 4 distinct RA longitudinal strain phenotypes: normal (n=60), hypernomal (n=10), mildly hyponormal (n=55), and severely hyponormal (n=32), Figure 1. After multivariable adjustment, Cox regression revealed 73% and 123% increased risk of the composite clinical endpoint in the mildly and severely hyponormal subgroups, respectively, compared to the normal cluster, Table 2.
Conclusion: Distinct clusters of abnormal RA strain mechanics represent clinically meaningful phenotypes that are strongly associated with increased risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with SSc. These findings underscore the prognostic significance of RA functional phenotyping and support the use of comprehensive assessment of RA phasic function as a noninvasive, clinically viable tool for early detection of RVDD and improved risk stratification in this high-risk population.
Methods: We analyzed a well-characterized cohort of patients with SSc from Johns Hopkins Medicine with quantifiable STE-derived RA strain metrics performed within six-months of invasive hemodynamics. Demographic, clinical, and echocardiographic data were assessed, and RA strain curves were stratified using machine learning derived time series k-means clustering with dynamic time warping to identify phenotypes of RA function. Univariate and multivariate Cox regression models, adjusted for SSc disease duration, pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), and body surface area (BSA) were utilized to classify inter-cluster risk for a composite clinical endpoint of all-cause mortality, stroke, myocardial infarction, and heart failure hospitalization.
Results: Our cohort consisted of 157 SSc patients with a mean age 59 ± 13 years, 83% female, 69% White, and 60% with limited SSc subtype, Table 1. Time series k-means clustering revealed 4 distinct RA longitudinal strain phenotypes: normal (n=60), hypernomal (n=10), mildly hyponormal (n=55), and severely hyponormal (n=32), Figure 1. After multivariable adjustment, Cox regression revealed 73% and 123% increased risk of the composite clinical endpoint in the mildly and severely hyponormal subgroups, respectively, compared to the normal cluster, Table 2.
Conclusion: Distinct clusters of abnormal RA strain mechanics represent clinically meaningful phenotypes that are strongly associated with increased risk of adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with SSc. These findings underscore the prognostic significance of RA functional phenotyping and support the use of comprehensive assessment of RA phasic function as a noninvasive, clinically viable tool for early detection of RVDD and improved risk stratification in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Meta-analysis of the Right Ventricle Changes in Cancer Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity - The Forgotten Ventricle in Cardio-Oncology
De Oliveira Fischer Bacca Caroline, Huntermann Ramon, Gomes Rodrigo, Alexandrino Francisco, Yoshie Sato Mariane, De Sant Anna Melo Edielle
A Hemodynamic Warning Sign: Continuous Mitral Regurgitation and Normal Sinus RhythmMahi Ishani, Chowdhury Mahdi, Madan Hritik, Garg Vaani