Final ID: MP2230
Comparative Effectiveness of SGLT2 Inhibitors with and without GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Heart Failure and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
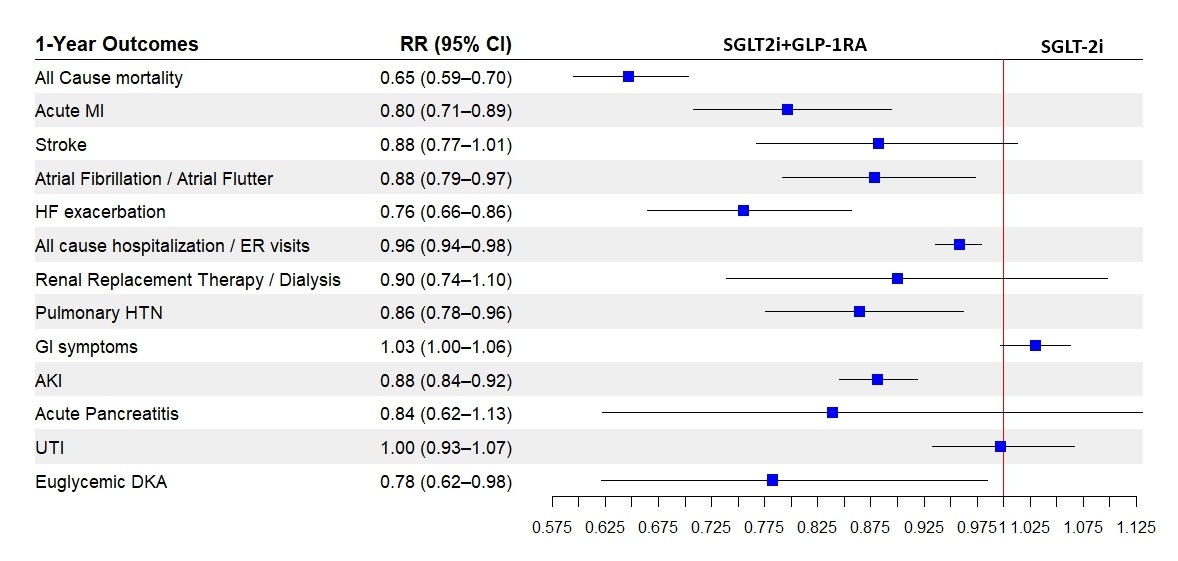
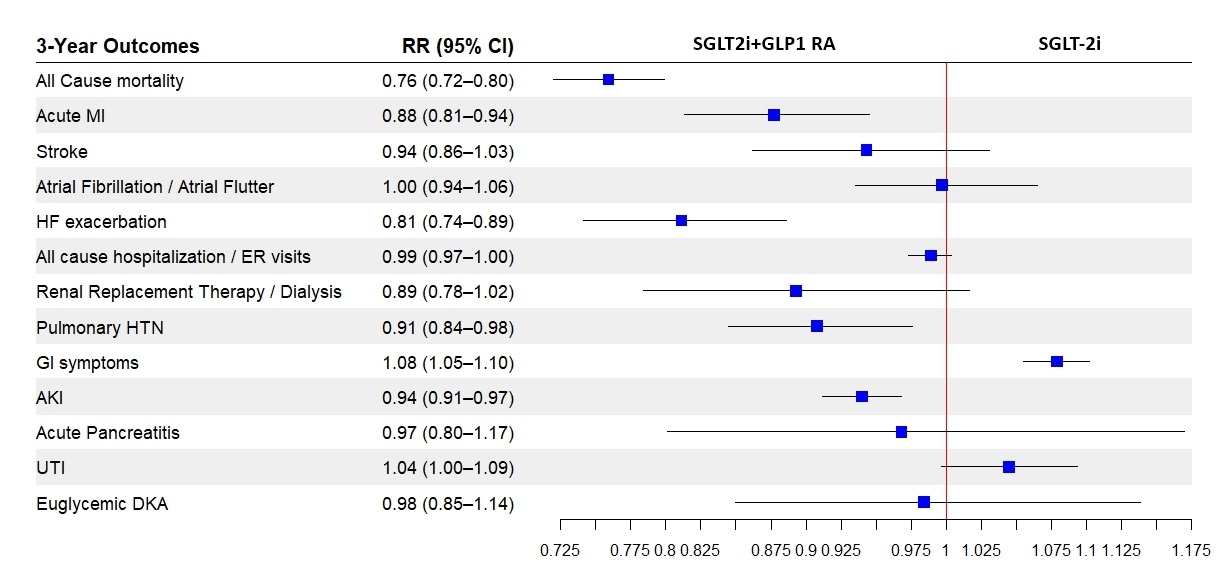
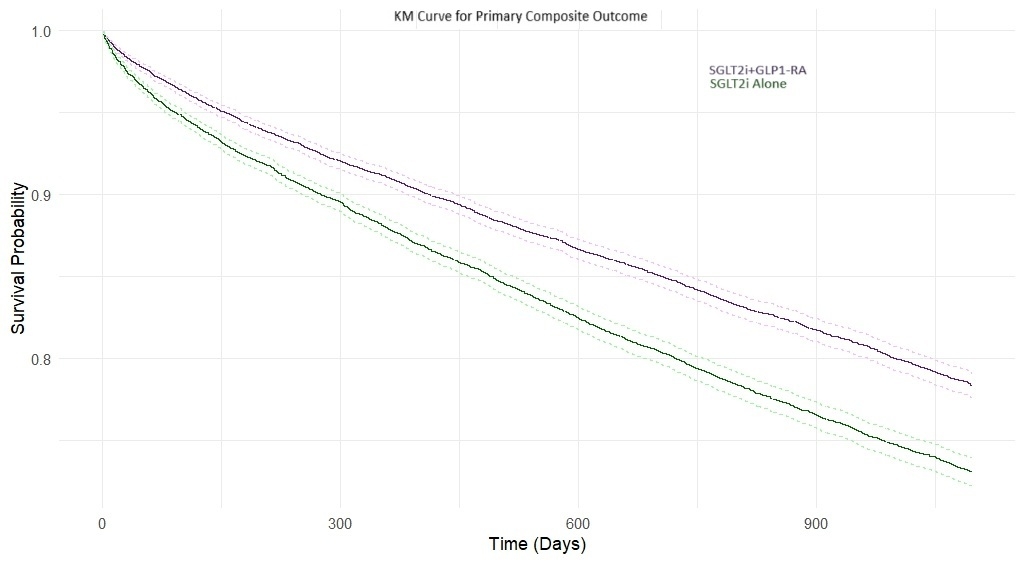
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:SGLT2i and GLP-1RA Independently Improve CV outcomes in pts with T2DM.Their combined effect in real-world pts with coexisting HF and T2DM remains underexplored.Methods:We conducted a propensity-matched cohort study using the TriNetX global federated health research network.We identified adults (≥18 years) with HF and T2DM who initiated either SGLT2i with GLP1-RA (Cohort A) or SGLT2i alone (Cohort B) across 102 healthcare organizations.Among 58,525 adults, 22,322 pts received SGLT2i with GLP-1RA, and 36,203 pts were on SGLT2i alone between Jan 2015 and May 2022.After propensity score matching 18,141 pts were included in each cohort.The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause mortality,acute myocardial infarction(AMI),or stroke at 1 year and 3 years.Secondary outcomes included individual event rates,hospitalizations,HFexacerbations,and safety events.Results:At 1 year,combination therapy with SGLT2i and GLP-1RA was associated with a significantly lower risk of the primary composite outcome than SGLT2i alone.Specifically, the combination group showed reduced all-cause mortality(RR: 0.647; 95% CI: 0.595–0.703; p<0.001),AMI (RR: 0.796; 95% CI: 0.708–0.894; p<0.001).Among secondary outcomes,HF exacerbations(RR: 0.755; 95% CI: 0.665–0.857; p<0.001)and AKI(RR: 0.881; 95% CI: 0.845–0.919; p<0.001)were also significantly lower in the combination group.These clinical benefits remained consistent over a 3-year follow-up,with ongoing reductions in all-cause mortality and AMI observed in the combination group.No significant increase in stroke risk was observed.The 1-year RR was 0.882(95% CI: 0.767–1.013; p=0.075),and the 3-year RR was 0.943(95% CI: 0.862–1.031; p=0.198).Similarly, adverse events—including atrial fibrillation/atrial flutter, need for renal replacement therapy or dialysis, pulmonary HTN, acute pancreatitis, UTI, and euglycemic DKA—did not show significant differences.All-cause hospitalization or emergency room visits were significantly reduced at 1 year in the combination therapy(RR: 0.958; 95% CI: 0.936–0.979; p<0.001),though this difference was no longer significant at 3 years(RR: 0.989; 95% CI: 0.973–1.004; p=0.157).Conclusion:In a large real-world cohort of patients with HF and T2DM, combined SGLT2i and GLP1-RA therapy was associated with significantly improved CV outcomes and survival over 1 and 3 years,with no increase in major adverse safety events.These findings support the consideration of dual therapy in this high-risk population.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Bridge from Sweet to Sour: A Case of Recurrent Myocardial Stunning in Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Satish Vikyath, Pargaonkar Sumant, Slipczuk Leandro, Schenone Aldo, Maliha Maisha, Chi Kuan Yu, Sunil Kumar Sriram, Borkowski Pawel, Vyas Rhea, Rodriguez Szaszdi David Jose Javier, Kharawala Amrin, Seo Jiyoung
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular DiseasePerera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan