Final ID: Sa3028
Antithrombotic Strategies and Outcomes in Neonates and Infants with Cardiac Shunts: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiac shunt thrombosis in neonates and infants remains a concern for shunt failure and mortality. Thromboprophylaxis for the prevention of shunt thrombosis is not an accepted standard due to a lack of high-level evidence. Despite the use of various antiplatelet and anticoagulant agents, thrombosis remains a common complication. In addition, limited evidence on the ideal antithrombotic approach for cardiac shunts, and there is variation in the agent selection and dosing utilized. Ultimately, the optimal strategy for thromboprophylaxis remains unknown.
Objective: This systematic review aims to characterize antithrombotic strategies and outcomes in neonates and infants with a cardiac shunt.
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane’s CENTRAL were searched from inception through July 2024 for studies reporting shunt thrombosis prevalence among infants who received a cardiac shunt. We estimated the pooled prevalence of shunt thrombosis using random-effects meta-analysis. In the subgroup analysis, we evaluated the effects of shunt type and antithrombotic strategies on shunt thrombosis prevalence.
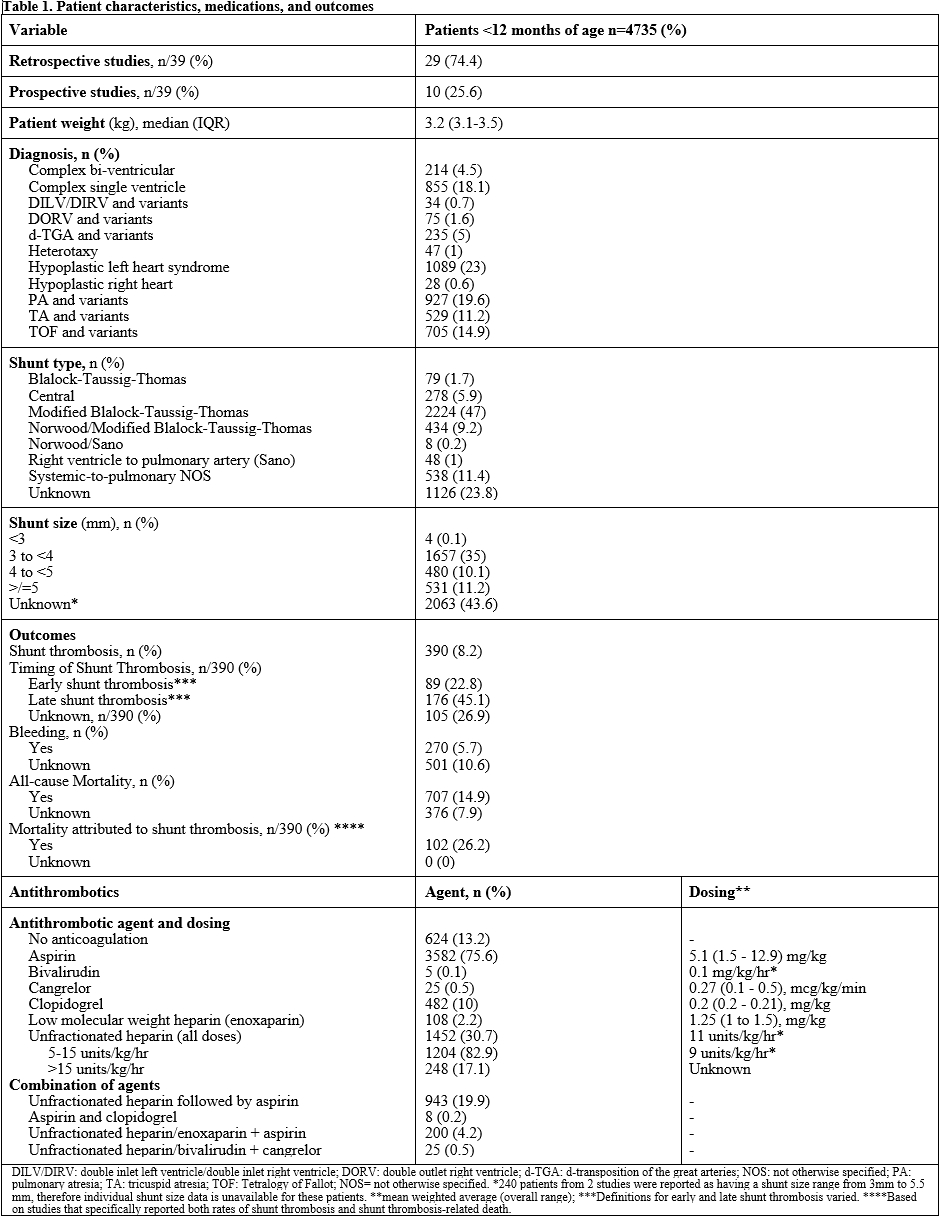
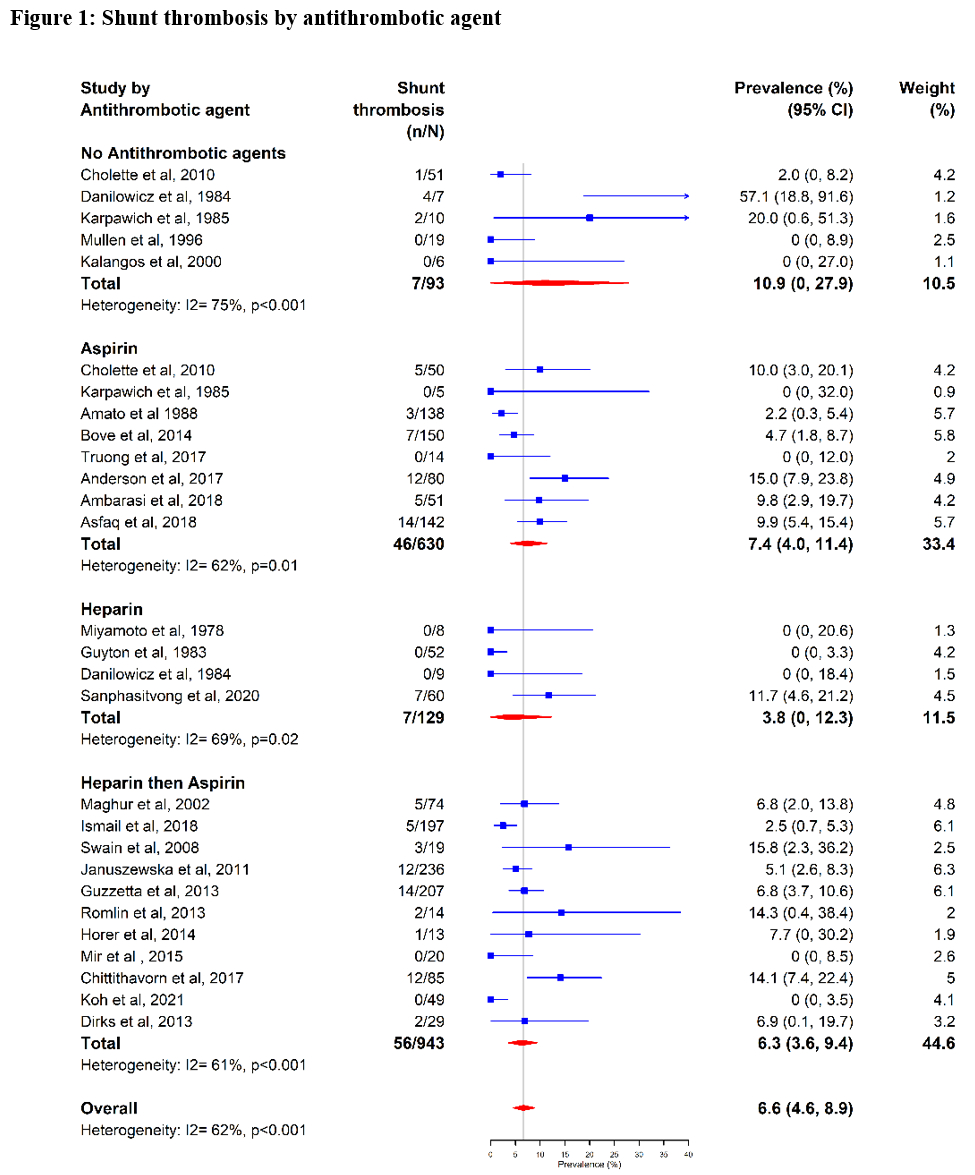
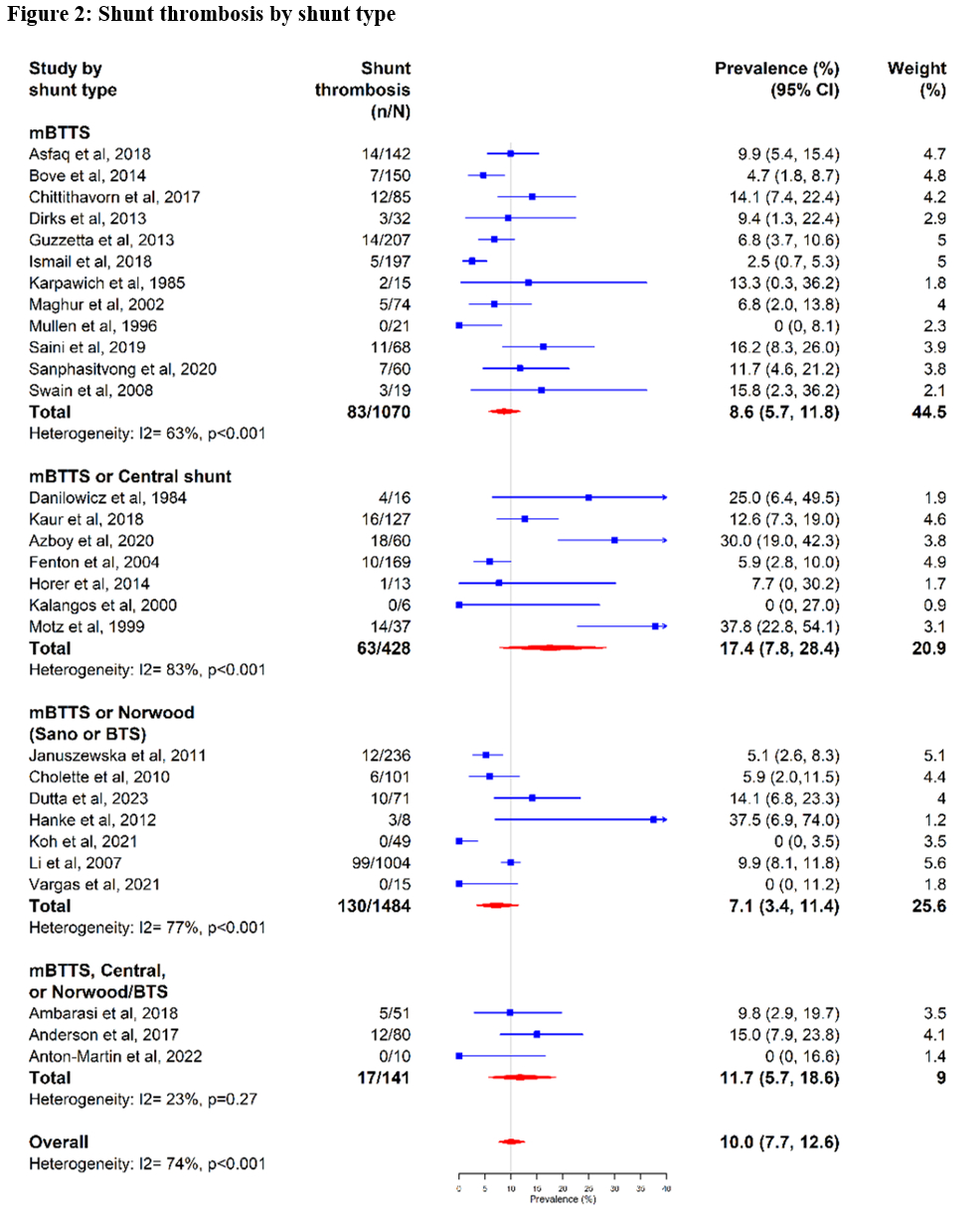
Results: A total of 39 studies (29 retrospective, 10 prospective) were included, totaling 4735 patients. The most common shunt type was the modified Blalock-Taussig (mBTTS) (n=2224, 47%). Mortality related to shunt thrombosis occurred in 102 (26.2%) of patients with shunt thrombosis. The most common antithrombotic agents in the acute post-op setting were unfractionated heparin (UFH, n=1452, 30.7%) or aspirin (n=1413, 29.3%). The pooled prevalence of shunt thrombosis was 8.4% (95% Confidence Interval [CI], 6.5%-10.4%) and varied among antithrombotic agents: aspirin: 7.4% (95% CI, 4.0%-11.4%), UFH: 3.8% (95% CI, 0%-12.3%), or UFH followed by aspirin: 6.3% (95% CI, 3.6%-9.4%).
Conclusions: This systematic review of nearly 5,000 neonates and infants reveals a high rate of mortality associated with shunt thrombosis. Collaborative prospective studies are warranted to evaluate antithrombotic regimen-outcome relationships and prognostic factors for shunt thrombosis and bleeding outcomes in these children.
Objective: This systematic review aims to characterize antithrombotic strategies and outcomes in neonates and infants with a cardiac shunt.
Methods: MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane’s CENTRAL were searched from inception through July 2024 for studies reporting shunt thrombosis prevalence among infants who received a cardiac shunt. We estimated the pooled prevalence of shunt thrombosis using random-effects meta-analysis. In the subgroup analysis, we evaluated the effects of shunt type and antithrombotic strategies on shunt thrombosis prevalence.
Results: A total of 39 studies (29 retrospective, 10 prospective) were included, totaling 4735 patients. The most common shunt type was the modified Blalock-Taussig (mBTTS) (n=2224, 47%). Mortality related to shunt thrombosis occurred in 102 (26.2%) of patients with shunt thrombosis. The most common antithrombotic agents in the acute post-op setting were unfractionated heparin (UFH, n=1452, 30.7%) or aspirin (n=1413, 29.3%). The pooled prevalence of shunt thrombosis was 8.4% (95% Confidence Interval [CI], 6.5%-10.4%) and varied among antithrombotic agents: aspirin: 7.4% (95% CI, 4.0%-11.4%), UFH: 3.8% (95% CI, 0%-12.3%), or UFH followed by aspirin: 6.3% (95% CI, 3.6%-9.4%).
Conclusions: This systematic review of nearly 5,000 neonates and infants reveals a high rate of mortality associated with shunt thrombosis. Collaborative prospective studies are warranted to evaluate antithrombotic regimen-outcome relationships and prognostic factors for shunt thrombosis and bleeding outcomes in these children.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Polypill Strategy for Lipid Lowering and Anti-Platelet Therapy After Acute Coronary Syndrome: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial
Keshvani Neil, Wang Thomas, Pandey Ambarish, Coellar Juan David, Rizvi Syed Kazim, Jain Anand, Bustillo-rubio M. Karina, Segar Matthew, Lokesh Nidhish, Miller James, Yates Sean
A Non-Contacting Blood Flow Sensor for Assessing Pediatric Vascular Graft PatencyChen Ruitong, Hudson Trevor, Wang Xuechun, Liang Jingjing, Nowlen Alanna, Nigam Vishal, Meng Ellis