Final ID: Su4036
Multi-Omics Biomarkers in Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Towards Precision Prognostication and Therapy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Heart failure (HF) is a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality, yet current clinical biomarkers offer limited prognostic precision and therapeutic guidance. Emerging multi-omics approaches encompassing transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, and genomics promise deeper insights into HF pathophysiology and personalized care.
Objective: To systematically synthesize and quantitatively analyze the prognostic and therapeutic value of multi-omics biomarkers in HF, bridging molecular discoveries with clinical outcomes.
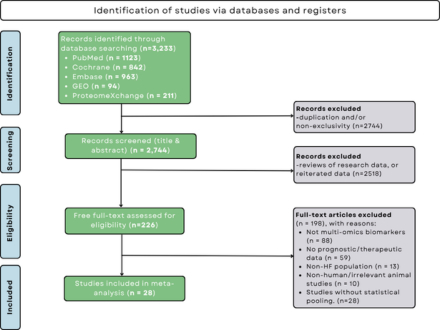
Methods: We conducted a PRISMA-guided systematic review and meta-analysis, querying PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, GEO and ProteomeXchange up to March 2025. Inclusion criteria focused on adult HF populations with reported associations between multi-omics biomarkers and clinical endpoints. Primary outcomes included hazard ratios (HR) for adverse events and biomarker predictive metrics.
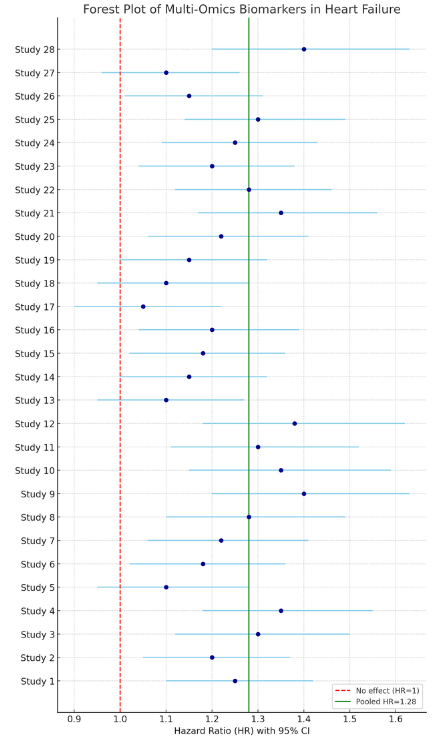
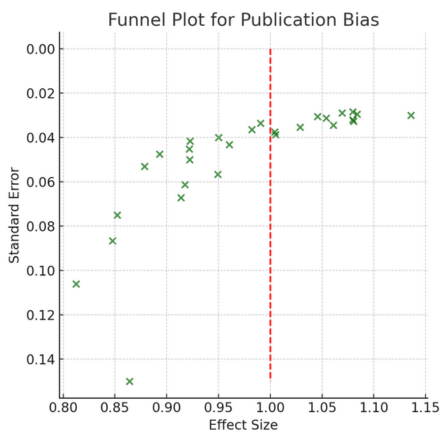
Results: Twenty-eight studies (including large-scale RCTs and prospective cohorts) encompassing diverse HF phenotypes (HFrEF, HFpEF) were analyzed. The pooled standardized mean difference was 0.273 (95% CI: 0.226–0.320), with a combined HR of 1.28 (95% CI: 1.10–1.48), underscoring a robust link between multi-omics signatures and adverse HF outcomes. Transcriptomic analyses revealed key gene expression patterns implicating inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling; proteomic data highlighted biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction and HF subtypes; metabolomic profiles identified metabolic shifts correlated with therapy responsiveness. Moderate heterogeneity (49.8%) and low publication bias affirm the consistency of findings.
Conclusion: Our comprehensive multi-omics meta-analysis substantiates the clinical potential of integrative molecular biomarkers to refine HF risk stratification and therapeutic targeting. Future efforts must prioritize methodological standardization, cross-validation, and translational pipelines to unlock precision medicine in heart failure.
Impact Statement: This work pioneers a unified multi-omics framework that could revolutionize HF management by enabling precise, personalized prognostication and therapy ushering in the next era of cardiovascular precision medicine.
Objective: To systematically synthesize and quantitatively analyze the prognostic and therapeutic value of multi-omics biomarkers in HF, bridging molecular discoveries with clinical outcomes.
Methods: We conducted a PRISMA-guided systematic review and meta-analysis, querying PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, GEO and ProteomeXchange up to March 2025. Inclusion criteria focused on adult HF populations with reported associations between multi-omics biomarkers and clinical endpoints. Primary outcomes included hazard ratios (HR) for adverse events and biomarker predictive metrics.
Results: Twenty-eight studies (including large-scale RCTs and prospective cohorts) encompassing diverse HF phenotypes (HFrEF, HFpEF) were analyzed. The pooled standardized mean difference was 0.273 (95% CI: 0.226–0.320), with a combined HR of 1.28 (95% CI: 1.10–1.48), underscoring a robust link between multi-omics signatures and adverse HF outcomes. Transcriptomic analyses revealed key gene expression patterns implicating inflammation and extracellular matrix remodeling; proteomic data highlighted biomarkers of mitochondrial dysfunction and HF subtypes; metabolomic profiles identified metabolic shifts correlated with therapy responsiveness. Moderate heterogeneity (49.8%) and low publication bias affirm the consistency of findings.
Conclusion: Our comprehensive multi-omics meta-analysis substantiates the clinical potential of integrative molecular biomarkers to refine HF risk stratification and therapeutic targeting. Future efforts must prioritize methodological standardization, cross-validation, and translational pipelines to unlock precision medicine in heart failure.
Impact Statement: This work pioneers a unified multi-omics framework that could revolutionize HF management by enabling precise, personalized prognostication and therapy ushering in the next era of cardiovascular precision medicine.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Cardiac Targeting Peptide Linked to miRNA106a Targets and Suppresses Genes Known to Cause Heart Failure: Reversing Heart Failure at the Source
Lu Ming, Deng Claire, Taskintuna Kaan, Ahern Gerard, Yurko Ray, Islam Kazi, Zahid Maliha, Gallicano Ian
3D Statistical Shape Analysis Predicts Type A Aortic Dissection Better Than Aortic DiametersMarway Prabhvir, Campello Jorge Carlos Alberto, Wagner Catherine, Baker Timothy, Burris Nicholas