Final ID: MP2168
Validation of Ring-Type Cuffless Blood Pressure (BP) Monitoring Device for Detecting Awake-Asleep BP Variations Compared to Ambulatory BP Monitoring Device
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Based on recommendations for validating cuffless BP devices by the European Society of Hypertension (ESH), this is the first validation study assessing the accuracy of CART BP, a ring-type cuffless blood pressure (BP) monitoring device, in detecting awake-asleep BP variations compared to conventional 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM). Unlike traditional cuff-based methods, the ESH validation criteria for cuffless devices emphasize assessing the device's capability to accurately track variations in BP, crucial for their clinical applicability.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that the CART BP device would reliably detect awake-asleep BP variations compared to ABPM, demonstrating a high correlation (correlation coefficient ≥0.7) within an error margin of 5±8 mmHg (mean±standard deviation).
Methods
Participants were consecutively selected from initially recruited patients to ensure compliance with ESH recommendations: 30% with systolic BP (SBP) ≥130 mmHg and diastolic BP (DBP) ≥80 mmHg, and 30% with SBP <120 mmHg and DBP <70 mmHg, with the remaining 40% included sequentially based on recruitment order. Calibration of the CART BP device was performed at least 24 hours prior to monitoring. Participants simultaneously wore both the CART BP and ABPM devices on the non-dominant arm for 24 hours. Mean SBP/DBP values were calculated from ABPM and CART BP readings. The SBP/DBP changes between awake and asleep periods were compared.
Results
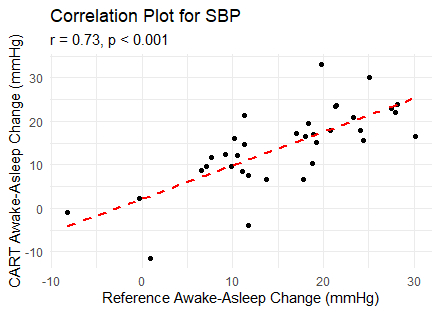
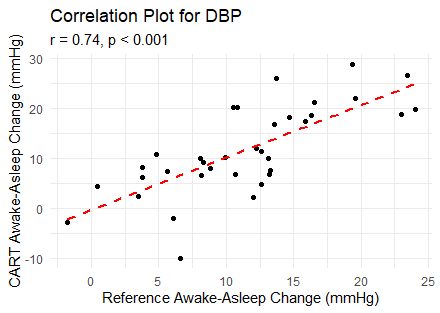
Of the 84 initially recruited participants, 35 were included in the final analysis: 30% (N=11) had SBP/DBP ≥130/80 mmHg, 30% (N=11) had SBP/DBP <120/70 mmHg, and the remaining 40% (N=13) were enrolled sequentially. The awake-asleep SBP/DBP changes were 15.61±8.74 / 11.35±6.22 mmHg with ABPM, and 14.15±9.18 / 11.61±8.85 mmHg with CART BP. Correlation coefficients were 0.73 for SBP and 0.74 for DBP (p<0.001 for both). Mean differences in awake-asleep BP changes between CART BP and ABPM were -1.46±6.57 mmHg for SBP and 0.26±5.98 mmHg for DBP, with no significant differences (p=0.197 and 0.798, respectively). The prevalence of dippers (74.3% VS 60%, p=0.131) was comparable between both devices.
Conclusion
CART BP demonstrated acceptable accuracy in detecting diurnal BP variations, aligning with ESH validation standards for cuffless BP monitoring devices.
Based on recommendations for validating cuffless BP devices by the European Society of Hypertension (ESH), this is the first validation study assessing the accuracy of CART BP, a ring-type cuffless blood pressure (BP) monitoring device, in detecting awake-asleep BP variations compared to conventional 24-hour ambulatory BP monitoring (ABPM). Unlike traditional cuff-based methods, the ESH validation criteria for cuffless devices emphasize assessing the device's capability to accurately track variations in BP, crucial for their clinical applicability.
Hypothesis
We hypothesized that the CART BP device would reliably detect awake-asleep BP variations compared to ABPM, demonstrating a high correlation (correlation coefficient ≥0.7) within an error margin of 5±8 mmHg (mean±standard deviation).
Methods
Participants were consecutively selected from initially recruited patients to ensure compliance with ESH recommendations: 30% with systolic BP (SBP) ≥130 mmHg and diastolic BP (DBP) ≥80 mmHg, and 30% with SBP <120 mmHg and DBP <70 mmHg, with the remaining 40% included sequentially based on recruitment order. Calibration of the CART BP device was performed at least 24 hours prior to monitoring. Participants simultaneously wore both the CART BP and ABPM devices on the non-dominant arm for 24 hours. Mean SBP/DBP values were calculated from ABPM and CART BP readings. The SBP/DBP changes between awake and asleep periods were compared.
Results
Of the 84 initially recruited participants, 35 were included in the final analysis: 30% (N=11) had SBP/DBP ≥130/80 mmHg, 30% (N=11) had SBP/DBP <120/70 mmHg, and the remaining 40% (N=13) were enrolled sequentially. The awake-asleep SBP/DBP changes were 15.61±8.74 / 11.35±6.22 mmHg with ABPM, and 14.15±9.18 / 11.61±8.85 mmHg with CART BP. Correlation coefficients were 0.73 for SBP and 0.74 for DBP (p<0.001 for both). Mean differences in awake-asleep BP changes between CART BP and ABPM were -1.46±6.57 mmHg for SBP and 0.26±5.98 mmHg for DBP, with no significant differences (p=0.197 and 0.798, respectively). The prevalence of dippers (74.3% VS 60%, p=0.131) was comparable between both devices.
Conclusion
CART BP demonstrated acceptable accuracy in detecting diurnal BP variations, aligning with ESH validation standards for cuffless BP monitoring devices.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Key Role of Proximal Tubule Renin-Angiotensin System in The Kidney in The Development of Kidney Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Li Xiao, Hassan Rumana, Katsurada Akemi, Sato Ryosuke, Zhuo Jia
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Afzal Hafsa, Khan Bilal, Muhammad Anza, Shafique Nouman, Bhatia Hitesh, Aafreen Asna, Adil Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib, Haider Muhammad Adnan