Final ID: Sa4057
Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Aging: The Female Heart at Risk
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Heart failure is a leading cause of death in postmenopausal women, yet the molecular mechanisms of cardiac decline in females remain unclear. While studies in male models have linked aging to heart failure and myocardial injury through mitochondrial (MITO) dysfunction driven by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, data on aging female hearts are limited. We examined age-induced ER stress and MITO dysfunction in the female heart, focusing on the electron transport chain (ETC) and potential MITO-driven injury through mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening. Identifying these mechanisms may reveal sex-specific therapeutic targets for cardiac aging.
Hypothesis
Aging in the female heart induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, leading to MITO dysfunction followed by impaired cardiac function.
Methods
Female mice aged 6 (adult), 24 (elderly), and 27 months (very elderly; n=10 per group) from NIA were studied. Cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography. MITO were isolated for assessment of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) via respirometry and MPTP susceptibility by calcium retention capacity (CRC). ER stress was assessed by C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) immunoblotting. ETC complex IV enzyme activity was measured in frozen-thawed, detergent-solubilized MITO.
Results
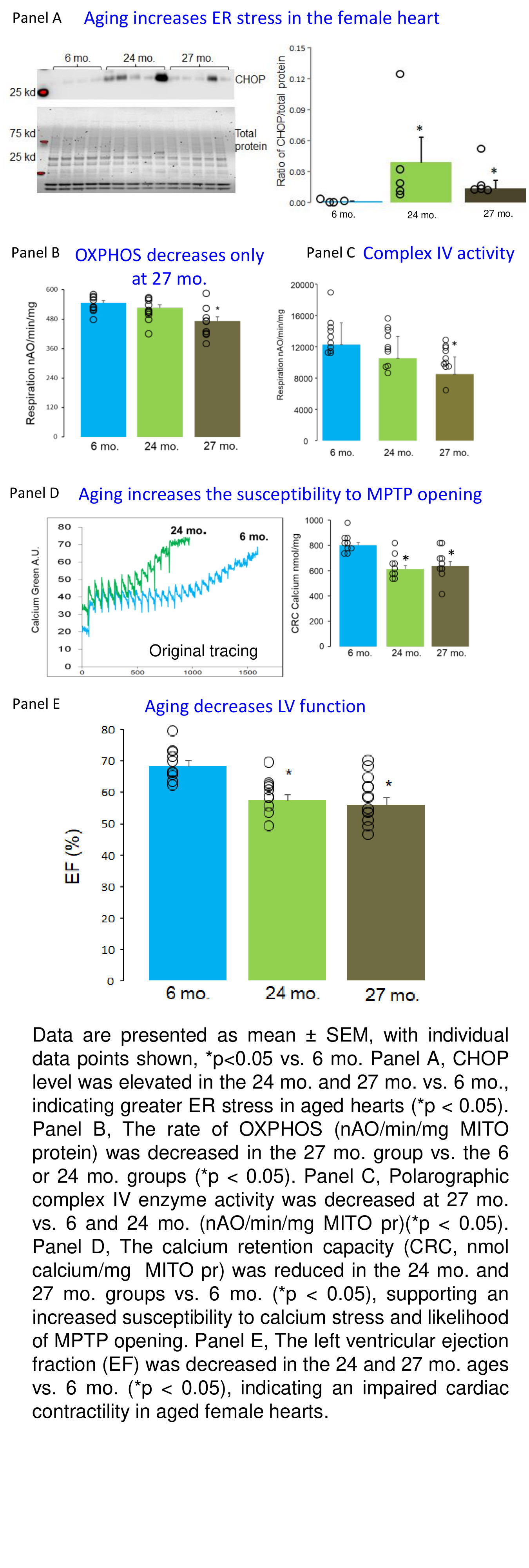
CHOP content was increased in 24 and 27 mo. elderly female vs. 6 mo. adults (p < 0.05), indicating increased ER stress with aging (Panel A). The rate of OXPHOS in intact MITO was unchanged between 6 and 24 mo. but decreased at 27 mo. (p < 0.05) (Panel B). Congruent with decreased respiration at 27 mo., ETC complex IV activity declined (p < 0.05) (Panel C). CRC was reduced at both 24 and 27 mo. (p < 0.05), supporting increased susceptibility to MPTP opening with aging (Panel D). Cardiac function was impaired in both 24 and 27 mo. hearts vs. 6 mo. (p < 0.05) (Panel E).
Conclusion
Aging increased ER stress in the elderly female heart and increased sensitivity to MPTP opening. Age-induced cardiac dysfunction tracked with the increased sensitivity to MPTP opening rather than the decrease in OXPHOS and ETC activity. Future studies will evaluate the role of increased ER stress to cause calcium stress in MITO favoring MPTP opening leading to cardiac dysfunction during aging in the female heart. Cardiac MITO, especially MPTP opening, emerge as a novel therapeutic target to treat the age-enhanced susceptibility to cardiac disease in the female heart.
Heart failure is a leading cause of death in postmenopausal women, yet the molecular mechanisms of cardiac decline in females remain unclear. While studies in male models have linked aging to heart failure and myocardial injury through mitochondrial (MITO) dysfunction driven by endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, data on aging female hearts are limited. We examined age-induced ER stress and MITO dysfunction in the female heart, focusing on the electron transport chain (ETC) and potential MITO-driven injury through mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening. Identifying these mechanisms may reveal sex-specific therapeutic targets for cardiac aging.
Hypothesis
Aging in the female heart induces endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, leading to MITO dysfunction followed by impaired cardiac function.
Methods
Female mice aged 6 (adult), 24 (elderly), and 27 months (very elderly; n=10 per group) from NIA were studied. Cardiac function was assessed by echocardiography. MITO were isolated for assessment of oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) via respirometry and MPTP susceptibility by calcium retention capacity (CRC). ER stress was assessed by C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP) immunoblotting. ETC complex IV enzyme activity was measured in frozen-thawed, detergent-solubilized MITO.
Results
CHOP content was increased in 24 and 27 mo. elderly female vs. 6 mo. adults (p < 0.05), indicating increased ER stress with aging (Panel A). The rate of OXPHOS in intact MITO was unchanged between 6 and 24 mo. but decreased at 27 mo. (p < 0.05) (Panel B). Congruent with decreased respiration at 27 mo., ETC complex IV activity declined (p < 0.05) (Panel C). CRC was reduced at both 24 and 27 mo. (p < 0.05), supporting increased susceptibility to MPTP opening with aging (Panel D). Cardiac function was impaired in both 24 and 27 mo. hearts vs. 6 mo. (p < 0.05) (Panel E).
Conclusion
Aging increased ER stress in the elderly female heart and increased sensitivity to MPTP opening. Age-induced cardiac dysfunction tracked with the increased sensitivity to MPTP opening rather than the decrease in OXPHOS and ETC activity. Future studies will evaluate the role of increased ER stress to cause calcium stress in MITO favoring MPTP opening leading to cardiac dysfunction during aging in the female heart. Cardiac MITO, especially MPTP opening, emerge as a novel therapeutic target to treat the age-enhanced susceptibility to cardiac disease in the female heart.
More abstracts on this topic:
A "non-muscle" alpha-actinin is an intrinsic component of the cardiac Z-disc and regulates sarcomere turnover, contractility, and heart remodeling
Hayes James, Smart Kyra, Choudhary Dharmendra, Reinhart-king Cynthia, Liu Qi, Tyska Matthew, Tabdanov Erdem, Wells Quinn, Knapik Ela, Burnette Dylan, Ritter Dylan, Neininger-castro Abigail, Willet Alaina, Caplan Leah, Wang Yu, Liu Xiao, Taneja Nilay, Sanchez Zachary
Effect Of Grandmaternal Diabetes and High Fat Diet on Cardiometabolic Dysfunction in the Second Generation (F2) NewbornsAyyappan Prathapan, Larsen Tricia, Klein Abigail, Gandy Ty, Baack Michelle