Final ID: Mo3080
Pregnancy Outcomes in Heart Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Maternal and Neonatal Morbidities.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Advances in heart transplant (HTx) have increased the number of reproductive-aged women with grafts considering pregnancy. However, this remains a high-risk scenario due to maternal morbidity, graft rejection, hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia, and adverse neonatal outcomes. Current literature on comprehensive pregnancy outcomes and long-term graft implications remains limited.
Objective: Evaluate maternal, and neonatal morbidity outcomes among HTx recipients.
Methods:
A meta-analysis was conducted using data from 1982 to 2022, derived from multiple database searches that included 7 retrospective cohort studies. Outcomes assessed included maternal and neonatal mortality, preeclampsia, neonatal preterm, low birth weight, graft rejection in pregnancy, miscarriage, chronic and gestational hypertension (HTN), congenital malformation, cesarians, unplanned pregnancy, and maternal infection within a 15 years follow-up time. Prevalences were pooled using events per 100 observations, along with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and I2 for heterogeneity, employing a random-effects model.
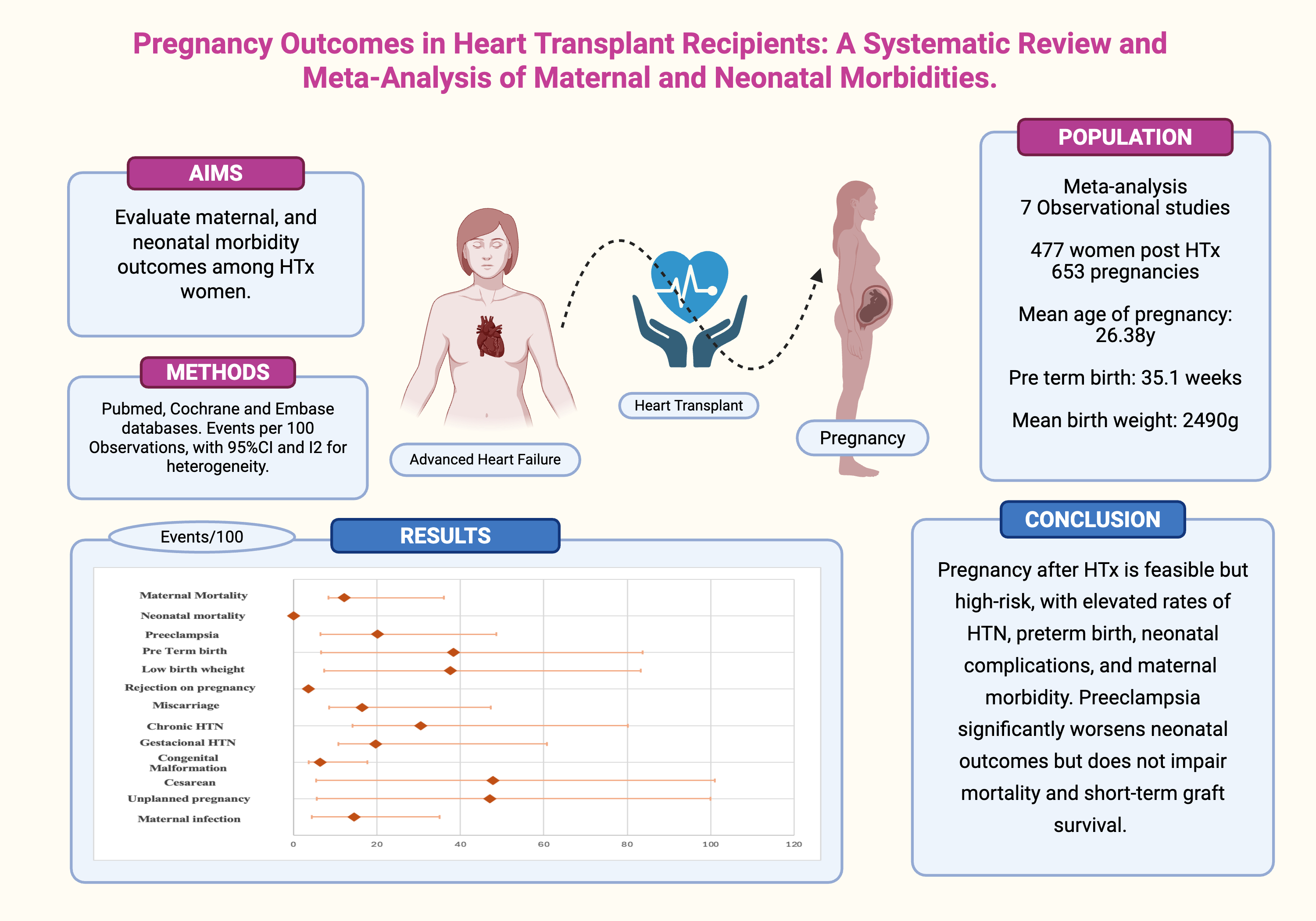
Results:
Among 653 pregnancies and 477 pregnant women studied in 7 observational studies, preeclampsia occurred in 20.10% and was associated with increased maternal mortality (12.15%). Preterm birth (38.34%; median 35.1 weeks), and lower birth weights (37.58%; median 2490 g), were expressive. Congenital malformations were identified in 6.44%, while neonatal mortality proportion was 0.00%. However, low rates of graft loss during pregnancy 3.57% were observed. HTN was presented as a chronic manifestation in 30.56%, whether gestational 19.74%. Cesarians were performed in 47.76% patients and the data of unplanned pregnancy reached 47.12%.
Conclusion:
Pregnancy after HTx is feasible but high-risk, with elevated rates of HTN, preterm birth, neonatal complications, and maternal morbidity. Preeclampsia significantly worsens neonatal outcomes but does not impair short-term graft survival. Multidisciplinary care, individualized immunosuppressive management, and rigorous preconception counseling are crucial for optimizing outcomes. These findings inform clinical decision-making and reproductive planning for HTx women.
Advances in heart transplant (HTx) have increased the number of reproductive-aged women with grafts considering pregnancy. However, this remains a high-risk scenario due to maternal morbidity, graft rejection, hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia, and adverse neonatal outcomes. Current literature on comprehensive pregnancy outcomes and long-term graft implications remains limited.
Objective: Evaluate maternal, and neonatal morbidity outcomes among HTx recipients.
Methods:
A meta-analysis was conducted using data from 1982 to 2022, derived from multiple database searches that included 7 retrospective cohort studies. Outcomes assessed included maternal and neonatal mortality, preeclampsia, neonatal preterm, low birth weight, graft rejection in pregnancy, miscarriage, chronic and gestational hypertension (HTN), congenital malformation, cesarians, unplanned pregnancy, and maternal infection within a 15 years follow-up time. Prevalences were pooled using events per 100 observations, along with 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and I2 for heterogeneity, employing a random-effects model.
Results:
Among 653 pregnancies and 477 pregnant women studied in 7 observational studies, preeclampsia occurred in 20.10% and was associated with increased maternal mortality (12.15%). Preterm birth (38.34%; median 35.1 weeks), and lower birth weights (37.58%; median 2490 g), were expressive. Congenital malformations were identified in 6.44%, while neonatal mortality proportion was 0.00%. However, low rates of graft loss during pregnancy 3.57% were observed. HTN was presented as a chronic manifestation in 30.56%, whether gestational 19.74%. Cesarians were performed in 47.76% patients and the data of unplanned pregnancy reached 47.12%.
Conclusion:
Pregnancy after HTx is feasible but high-risk, with elevated rates of HTN, preterm birth, neonatal complications, and maternal morbidity. Preeclampsia significantly worsens neonatal outcomes but does not impair short-term graft survival. Multidisciplinary care, individualized immunosuppressive management, and rigorous preconception counseling are crucial for optimizing outcomes. These findings inform clinical decision-making and reproductive planning for HTx women.
More abstracts on this topic:
Aberrant MicroRNA Expression May Underlie Cardiac Dysfunction in a rat model of Preeclampsia
Vaka Ramana, Campbell Nathan, Edwards Kristin, Hoang Ngoc, Zheng Baoying, Lamarca Babbette
Bridging to Delivery and Respecting Maternal Choice : Wearable Cardioverter Defibrillator Management of Sustained Ventricular Tachycardia in PregnancyFrimpong Smith, Aghasili Chukwuemeka, Nawaz Haleema, Patel Ketul, Appiah John