Final ID: Sa2052
Prevalence of cardiometabolic conditions across body mass index categories—the distinct burden of severe (class III) obesity
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiometabolic (CM) conditions are a recognized complication of obesity, although their comparative burden among patients with severe (class III) obesity is less well known.
Objective: To characterize the prevalence of CM conditions among US adults as a function of body mass index (BMI, kg/m2).
Methods: Nationally representative, cross-sectional data from the 2017–2020 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), the most recent survey with comprehensive condition coverage, were evaluated to determine the prevalence of CM conditions as a function of BMI. Seven CM conditions were evaluated: type 2 diabetes (T2DM), cardiovascular disease (atherosclerotic disease or heart failure) (CVD), hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia (DLP), metabolic syndrome (MetS), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (LD, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis), and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Patients were categorized by BMI as normal weight (18.5–24.9), overweight (25.0–29.9), obesity class I (30.0–34.9), obesity class II (35.0–39.9), and obesity class III (40.0 and higher). Population-representative prevalence estimates were derived using NHANES sampling weights and distributions were evaluated with χ2 tests.
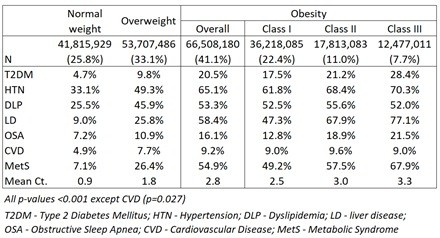
Results: In the NHANES weighted sample (n=162,031,595) mean age was 47.7 years, with 50.3% male and 35.1% non-white or Hispanic. The burden of CM conditions was greatest among patients with class III obesity (Table). The prevalence of CM conditions increased in a near-linear fashion across BMI groups, ranging from 0.9 mean total conditions among normal weight adults to 3.3 among those with class III obesity.
Conclusion: The burden of CM conditions increases with severity of obesity and is greatest among patients with class III obesity, with patients experiencing an average of 3.3 conditions. Lowering BMI via obesity reduction efforts including anti-obesity medications may attenuate the CM burden associated with obesity.
Objective: To characterize the prevalence of CM conditions among US adults as a function of body mass index (BMI, kg/m2).
Methods: Nationally representative, cross-sectional data from the 2017–2020 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), the most recent survey with comprehensive condition coverage, were evaluated to determine the prevalence of CM conditions as a function of BMI. Seven CM conditions were evaluated: type 2 diabetes (T2DM), cardiovascular disease (atherosclerotic disease or heart failure) (CVD), hypertension (HTN), dyslipidemia (DLP), metabolic syndrome (MetS), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (LD, including metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis), and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Patients were categorized by BMI as normal weight (18.5–24.9), overweight (25.0–29.9), obesity class I (30.0–34.9), obesity class II (35.0–39.9), and obesity class III (40.0 and higher). Population-representative prevalence estimates were derived using NHANES sampling weights and distributions were evaluated with χ2 tests.
Results: In the NHANES weighted sample (n=162,031,595) mean age was 47.7 years, with 50.3% male and 35.1% non-white or Hispanic. The burden of CM conditions was greatest among patients with class III obesity (Table). The prevalence of CM conditions increased in a near-linear fashion across BMI groups, ranging from 0.9 mean total conditions among normal weight adults to 3.3 among those with class III obesity.
Conclusion: The burden of CM conditions increases with severity of obesity and is greatest among patients with class III obesity, with patients experiencing an average of 3.3 conditions. Lowering BMI via obesity reduction efforts including anti-obesity medications may attenuate the CM burden associated with obesity.
More abstracts on this topic:
A blood test based on RNA-seq and machine learning for the detection of steatotic liver disease: A Pilot Study on Cardiometabolic Health
Poggio Rosana, Berdiñas Ignacio, La Greca Alejandro, Luzzani Carlos, Miriuka Santiago, Rodriguez-granillo Gaston, De Lillo Florencia, Rubilar Bibiana, Hijazi Razan, Solari Claudia, Rodríguez Varela María Soledad, Mobbs Alan, Manchini Estefania
Adverse Maternal and Offspring Outcomes in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Pregnancies: Impact of a Maternal Hypertensive High-Fat DietGomes Viviane, Watts Stephanie, Fink Gregory, Kim Lauren, Lopez Krystal, Gilbert Bryce, Bailey Victoria, Marques Bruno, Garver Hannah, Mckenzie Mckenzie, Lauver Adam