Final ID: Su2032
AI-Augmented Interpretation of Coronary CT Angiography Reports: A Large Language Model-Based Framework
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is a valuable clinical tool for evaluation of coronary artery disease. However, the standardized framework, Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS), is not consistently applied to classify CCTA reports due to variability in terminology and narrative format. We address the gap by developing an artificial intelligence-based system leveraging large language models (LLM) to automate the interpretation of CCTA reports and support guideline-directed clinical decision-making.
Methods:
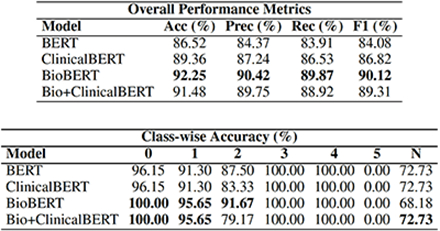
CCTA reports from native coronary artery evaluation protocols were selected. The training dataset (940 reports) was established from CCTA reports selected from a clinical database at our institution between January 2020 and July 2024. The dataset exhibits a natural class imbalance based on clinical indications of CCTA. Four LLMs previously validated for medical applications were evaluated. BioBERT demonstrated the highest performance and was therefore selected for model deployment. External validation was further conducted using an independent test set (500 reports) comprising CCTA reports between August 2024 and April 2025 at our institution. Concordance between radiologist-interpreted and AI-generated CAD-RADS classfication was assessed. All data handling adhered to HIPAA regulations.
Results:
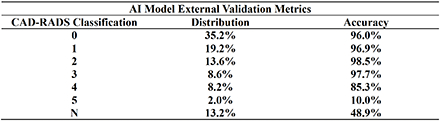
The distribution of CAD-RADS classifications in the training dataset was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (35.9%), CAD-RADS 1 (14.9%), CAD-RADS 2 (14.2%), CAD-RADS 3 (7.9%), CAD-RADS 4 (7.7%), CAD-RADS 5(0.7%), and CAD-RADS N (18.7%). The overall accuracy of AI-interpreted CAD-RADS classification was 87.6% (438/ 500). The distribution of CAD-RADS classifications in the testing dataset was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (35.2%), CAD-RADS 1 (19.2%), CAD-RADS 2 (13.6%), CAD-RADS 3 (8.6%), CAD-RADS 4 (8.2%), CAD-RADS 5 (2.0%), and CAD-RADS N (13.2%). The class-wise accuracy of the AI model on the testing dataset for CAD-RADS classification was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (96.0%), CAD-RADS 1 (96.9%), CAD-RADS 2 (98.5%), CAD-RADS 3 (97.7%), CAD-RADS 4 (85.3%), CAD-RADS 5(10.0%), and CAD-RADS N (48.9%).
Conclusion:
We propose an artificial intelligence tool powered by the BioBERT LLM to enhance the interpretation of CCTA reports. This approach aims to address the existing discrepancies and heterogeneity in CCTA reporting systems. Further effort is needed to optimize the tool in supporting clinical decision-making among internal medicine and cardiology providers.
Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is a valuable clinical tool for evaluation of coronary artery disease. However, the standardized framework, Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS), is not consistently applied to classify CCTA reports due to variability in terminology and narrative format. We address the gap by developing an artificial intelligence-based system leveraging large language models (LLM) to automate the interpretation of CCTA reports and support guideline-directed clinical decision-making.
Methods:
CCTA reports from native coronary artery evaluation protocols were selected. The training dataset (940 reports) was established from CCTA reports selected from a clinical database at our institution between January 2020 and July 2024. The dataset exhibits a natural class imbalance based on clinical indications of CCTA. Four LLMs previously validated for medical applications were evaluated. BioBERT demonstrated the highest performance and was therefore selected for model deployment. External validation was further conducted using an independent test set (500 reports) comprising CCTA reports between August 2024 and April 2025 at our institution. Concordance between radiologist-interpreted and AI-generated CAD-RADS classfication was assessed. All data handling adhered to HIPAA regulations.
Results:
The distribution of CAD-RADS classifications in the training dataset was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (35.9%), CAD-RADS 1 (14.9%), CAD-RADS 2 (14.2%), CAD-RADS 3 (7.9%), CAD-RADS 4 (7.7%), CAD-RADS 5(0.7%), and CAD-RADS N (18.7%). The overall accuracy of AI-interpreted CAD-RADS classification was 87.6% (438/ 500). The distribution of CAD-RADS classifications in the testing dataset was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (35.2%), CAD-RADS 1 (19.2%), CAD-RADS 2 (13.6%), CAD-RADS 3 (8.6%), CAD-RADS 4 (8.2%), CAD-RADS 5 (2.0%), and CAD-RADS N (13.2%). The class-wise accuracy of the AI model on the testing dataset for CAD-RADS classification was as follows: CAD-RADS 0 (96.0%), CAD-RADS 1 (96.9%), CAD-RADS 2 (98.5%), CAD-RADS 3 (97.7%), CAD-RADS 4 (85.3%), CAD-RADS 5(10.0%), and CAD-RADS N (48.9%).
Conclusion:
We propose an artificial intelligence tool powered by the BioBERT LLM to enhance the interpretation of CCTA reports. This approach aims to address the existing discrepancies and heterogeneity in CCTA reporting systems. Further effort is needed to optimize the tool in supporting clinical decision-making among internal medicine and cardiology providers.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Caseous Mitral Annular Calcification and the Utility of Multimodality Cardiac Imaging
Nguyen Amanda, English Carter, Ghasemiesfe Ahmadreza, Venugopal Sandhya
A multi-task deep learning algorithm for detecting obstructive coronary artery disease using fundus photographsZeng Yong, Ding Yaodong