Final ID: MP2579
Growing Syphilis Epidemic Independently Affects Cardiovascular Outcomes Outcomes in New Orleans Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Treponema pallidum causes syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection that can lead to various cardiovascular (CV) complications. However, large scale studies demonstrating the CV effects of syphilis are limited. Our study aims to characterize the possible CV effects of the growing syphilis epidemic.
Hypothesis: Syphilis independently increases the risk of adverse CV outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study examines patients receiving care between 2016-2025 at a tertiary care healthcare system in New Orleans, Louisiana. Syphilis patients were identified based on ICD10 and matched 1:5 to unaffected controls based on age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, autoimmune disease, and cancer. Patients were excluded for having a history of CV comorbidity or HIV infection. Outcomes included acute myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, heart failure (HF), aortic regurgitation (AR), atrial fibrillation (AF), aortic aneurysm/dissection (AA/AD), non-atherosclerotic peripheral arteritis disease (PAD) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) were assessed. Kaplan-Meier and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios of syphilis for each cardiovascular outcome.
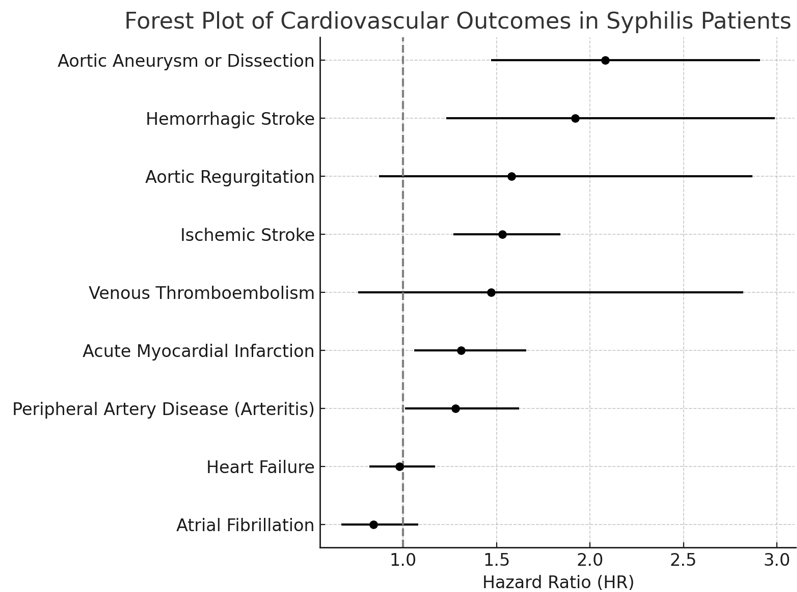
Results: The matched cohorts included 7,345 controls compared to 1,469 patients with syphilis. Gender distribution was similar between the groups (54.1% female vs. 53.9%, p = 0.84), and the mean ages were comparable (50.07 ± 17.03 vs. 49.96 ± 17.62 years; p = 0.77. During the study period, patients with syphilis demonstrated a significantly higher risk of AA/AD (HR: 1.84, p = 0.001), ischemic stroke (HR: 1.51, p < 0.001), hemorrhagic stroke (HR: 1.92, p = 0.004), PAD (HR: 1.28, p = 0.039) and MI (HR: 1.36, p = 0.012) compared to matched controls. HF, AF, VTE and AR did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusion: Syphilis is associated with independent increased risk of cardiovascular outcomes, particularly aortic aneurysm/dissection, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, non-atherosclerotic peripheral artery disease and myocardial infarction.
Hypothesis: Syphilis independently increases the risk of adverse CV outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective cohort study examines patients receiving care between 2016-2025 at a tertiary care healthcare system in New Orleans, Louisiana. Syphilis patients were identified based on ICD10 and matched 1:5 to unaffected controls based on age, sex, diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, liver disease, autoimmune disease, and cancer. Patients were excluded for having a history of CV comorbidity or HIV infection. Outcomes included acute myocardial infarction (MI), ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, heart failure (HF), aortic regurgitation (AR), atrial fibrillation (AF), aortic aneurysm/dissection (AA/AD), non-atherosclerotic peripheral arteritis disease (PAD) and venous thromboembolism (VTE) were assessed. Kaplan-Meier and multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios of syphilis for each cardiovascular outcome.
Results: The matched cohorts included 7,345 controls compared to 1,469 patients with syphilis. Gender distribution was similar between the groups (54.1% female vs. 53.9%, p = 0.84), and the mean ages were comparable (50.07 ± 17.03 vs. 49.96 ± 17.62 years; p = 0.77. During the study period, patients with syphilis demonstrated a significantly higher risk of AA/AD (HR: 1.84, p = 0.001), ischemic stroke (HR: 1.51, p < 0.001), hemorrhagic stroke (HR: 1.92, p = 0.004), PAD (HR: 1.28, p = 0.039) and MI (HR: 1.36, p = 0.012) compared to matched controls. HF, AF, VTE and AR did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusion: Syphilis is associated with independent increased risk of cardiovascular outcomes, particularly aortic aneurysm/dissection, ischemic stroke, hemorrhagic stroke, non-atherosclerotic peripheral artery disease and myocardial infarction.
More abstracts on this topic:
10-Year Trend Analysis of Medicare Payment in Stroke Inpatient Hospital Admission
Wong Ka-ho, Krothapalli Neeharika, Littig Lauren, Champagne Alison, Majersik Jennifer, Reddy Vivek, De Havenon Adam
Beyond Antibiotics: Transcatheter AngioVac Debulking of Right-Sided Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis in a Hemodialysis PatientAghasili Chukwuemeka, Nawaz Haleema, Frimpong Smith, Hassan Rafla, Al-abboud Omar, Ahmad Tariq Ali