Final ID: MP148
Distance between the Anterior Papillary Muscle and Interventricular Septum Evaluated by Echocardiography to Diagnose Mid-ventricular Obstruction in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Left ventricular mid-ventricular obstruction (MVO) is thought to be dynamic with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). Therefore, the distance between the anterior papillary muscle and interventricular septum was employed as a parameter named APM-IVS distance for assessing MVO by rest echocardiography.
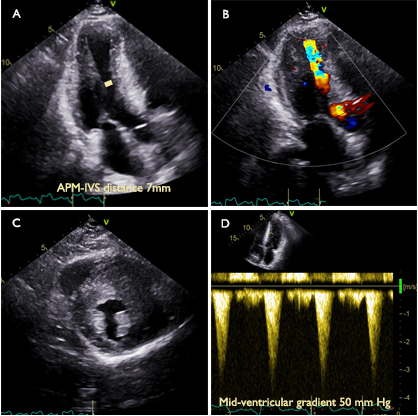
Methods: MVO was defined as a mid-ventricular gradient of ≥ 30 mmHg at rest or after being provoked. Patients with both left ventricular outflow tract obstruction and MVO were included in the MVO group. APM-IVS distance was analyzed on apical three chamber view at end-diastole (Image 1).
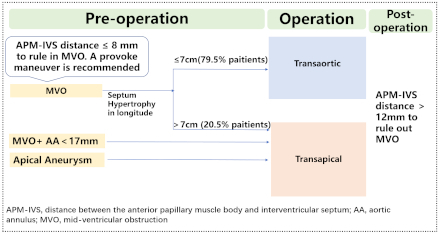
Results: A total of 2125 patients with HCM were recruited from both the outpatient and inpatient settings of the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at Fuwai Hospital. Among these, data from 1453 patients with measurable APM-IVS distances were analyzed. Of the 1453 patients, 596 had MVO, while 857 did not exhibit MVO. Multivariate logistic regression analyses showed that APM-IVS distance was an independent indicator of MVO (adjusted odds ratio [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 0.487 [0.448–0.529]). The APM-IVS distance demonstrated the highest diagnostic accuracy in identifying MVO, exhibiting an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.949 (95% CI: 0.937–0.960). An APM-IVS distance greater than 12 mm was associated with the absence of MVO, demonstrating a negative predictive value of 95.7%. Conversely, an APM-IVS distance of 8 mm or less was indicative of the presence of MVO, with a positive predictive value of 92.8% (Image 2). The presence of a smaller APM-IVS distance was correlated with increased incidence of left ventricular apical aneurysm and MVO, elevated levels of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, as well as higher New York Heart Association functional class. Among those with MVO, 198 patients underwent surgical myectomy and were followed up after a median time of 12 months. APM-IVS distance increased from 7.6±2.2 mm to 18.9±4.9 mm, and the peak mid-ventricular gradient decreased from 50 mm Hg (36–57 mmHg) to 3 mmHg (3–7 mmHg) at follow-up.
Conclusions: A small APM-IVS distance was associated with MVO, which was alleviated after myectomy following an increase in APM-IVS distance.
Methods: MVO was defined as a mid-ventricular gradient of ≥ 30 mmHg at rest or after being provoked. Patients with both left ventricular outflow tract obstruction and MVO were included in the MVO group. APM-IVS distance was analyzed on apical three chamber view at end-diastole (Image 1).
Results: A total of 2125 patients with HCM were recruited from both the outpatient and inpatient settings of the Department of Cardiovascular Surgery at Fuwai Hospital. Among these, data from 1453 patients with measurable APM-IVS distances were analyzed. Of the 1453 patients, 596 had MVO, while 857 did not exhibit MVO. Multivariate logistic regression analyses showed that APM-IVS distance was an independent indicator of MVO (adjusted odds ratio [95% confidence interval (CI)]: 0.487 [0.448–0.529]). The APM-IVS distance demonstrated the highest diagnostic accuracy in identifying MVO, exhibiting an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.949 (95% CI: 0.937–0.960). An APM-IVS distance greater than 12 mm was associated with the absence of MVO, demonstrating a negative predictive value of 95.7%. Conversely, an APM-IVS distance of 8 mm or less was indicative of the presence of MVO, with a positive predictive value of 92.8% (Image 2). The presence of a smaller APM-IVS distance was correlated with increased incidence of left ventricular apical aneurysm and MVO, elevated levels of N-terminal pro brain natriuretic peptide, as well as higher New York Heart Association functional class. Among those with MVO, 198 patients underwent surgical myectomy and were followed up after a median time of 12 months. APM-IVS distance increased from 7.6±2.2 mm to 18.9±4.9 mm, and the peak mid-ventricular gradient decreased from 50 mm Hg (36–57 mmHg) to 3 mmHg (3–7 mmHg) at follow-up.
Conclusions: A small APM-IVS distance was associated with MVO, which was alleviated after myectomy following an increase in APM-IVS distance.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Hemodynamic Warning Sign: Continuous Mitral Regurgitation and Normal Sinus Rhythm
Mahi Ishani, Chowdhury Mahdi, Madan Hritik, Garg Vaani
A Multicenter Observational Study of Bleeding Events in Critically Ill Surgical and Trauma AdolescentsRahman Fahmid, Faustino E. Vincent, Popham Jonathan