Final ID: MP2004
Motion-Corrected Coronary CT Angiography in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Segment-Based Image Quality Assessment
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction:
The image quality of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) has improved considerably; however, it remains suboptimal in certain cases, particularly in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) due to motion artifacts. Recently, deep learning-based reconstruction techniques have emerged to address this limitation.
Purpose:
To evaluate the image quality of motion-corrected CCTA using CLEAR Motion (Canon Medical Systems Corporation), a deep learning-based motion correction algorithm, compared with conventional reconstruction in AF patients.
Methods:
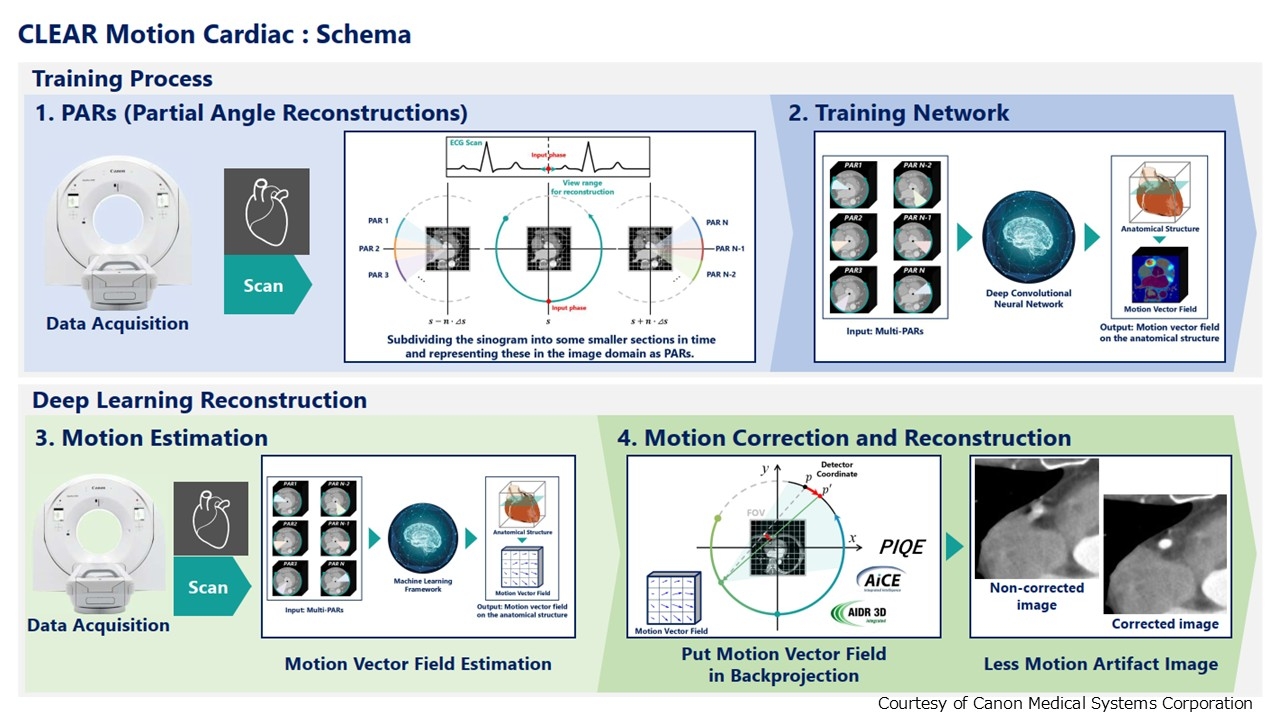
CLEAR Motion was installed on our CT system for clinical use. This algorithm applies Partial Angle Reconstructions (PARs) to estimate motion vector fields for the three major epicardial vessels, enabling motion correction and improved image quality. The motion vector fields are incorporated into backprojection, reducing motion artifacts through deep learning. We retrospectively analyzed consecutive AF patients who underwent CCTA between July 2023 and May 2024, excluding those with prior percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting. Image quality was assessed segmentally using a five-point scale (1–5) based on the American Heart Association and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines by a blinded cardiologist.
Results:
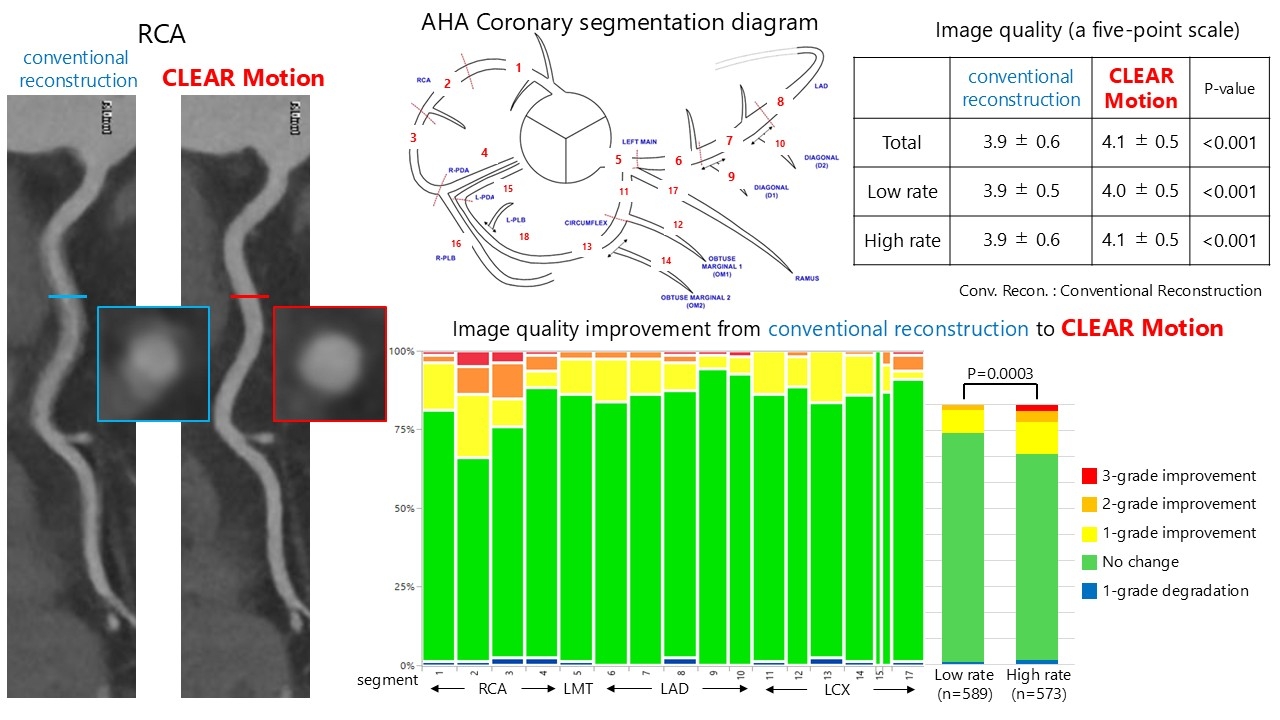
We evaluated 1,162 coronary segments from 80 patients (mean age 67.9 ± 9.5 years; 78% male; median heart rate 70 bpm). CLEAR Motion significantly improved image quality compared with conventional reconstruction (4.1 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.6; P < 0.001). Image quality improved across all segments, with the most pronounced enhancement observed in the mid-right coronary artery (RCA), where motion artifacts are typically most severe. In contrast, side branches showed the least improvement, likely due to the algorithm's focus on the three major epicardial coronary arteries. Patients were stratified by R–R interval into low-rate (>854 msec) and high-rate (<854 msec) groups. Image quality improved significantly in both groups (low-rate: 4.0 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.5, P < 0.001; high-rate: 4.1 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.6, P < 0.001), with a significantly greater improvement in image quality scores in the high-rate group (P < 0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
Conclusions:
CLEAR Motion significantly enhances image quality in AF patients, particularly in the mid-RCA and in those with higher heart rates.
The image quality of coronary CT angiography (CCTA) has improved considerably; however, it remains suboptimal in certain cases, particularly in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) due to motion artifacts. Recently, deep learning-based reconstruction techniques have emerged to address this limitation.
Purpose:
To evaluate the image quality of motion-corrected CCTA using CLEAR Motion (Canon Medical Systems Corporation), a deep learning-based motion correction algorithm, compared with conventional reconstruction in AF patients.
Methods:
CLEAR Motion was installed on our CT system for clinical use. This algorithm applies Partial Angle Reconstructions (PARs) to estimate motion vector fields for the three major epicardial vessels, enabling motion correction and improved image quality. The motion vector fields are incorporated into backprojection, reducing motion artifacts through deep learning. We retrospectively analyzed consecutive AF patients who underwent CCTA between July 2023 and May 2024, excluding those with prior percutaneous coronary intervention or coronary artery bypass grafting. Image quality was assessed segmentally using a five-point scale (1–5) based on the American Heart Association and Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography guidelines by a blinded cardiologist.
Results:
We evaluated 1,162 coronary segments from 80 patients (mean age 67.9 ± 9.5 years; 78% male; median heart rate 70 bpm). CLEAR Motion significantly improved image quality compared with conventional reconstruction (4.1 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.6; P < 0.001). Image quality improved across all segments, with the most pronounced enhancement observed in the mid-right coronary artery (RCA), where motion artifacts are typically most severe. In contrast, side branches showed the least improvement, likely due to the algorithm's focus on the three major epicardial coronary arteries. Patients were stratified by R–R interval into low-rate (>854 msec) and high-rate (<854 msec) groups. Image quality improved significantly in both groups (low-rate: 4.0 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.5, P < 0.001; high-rate: 4.1 ± 0.5 vs. 3.9 ± 0.6, P < 0.001), with a significantly greater improvement in image quality scores in the high-rate group (P < 0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
Conclusions:
CLEAR Motion significantly enhances image quality in AF patients, particularly in the mid-RCA and in those with higher heart rates.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Approach to Predict Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with Critical Illness and Signs of Myocardial Injury
Mueller Joshua, Stepanova Daria, Chidambaram Vignesh, Nakarmi Ukash, Al'aref Subhi
A comparison of the efficacy of initial high energy versus initial low energy biphasic shocks for cardioversion of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter – a real-life experienceAlampoondi Venkataramanan Sai Vikram, Vunnam Ramarao, Voruganti Dinesh, Tsai Shane