Final ID: MP1490
Upfront Combination of High-Intensity Statin and Ezetimibe Reduces Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Acute Myocardial Infarction: A Target-Trial Emulation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
High-intensity statin treatment has well-established benefits in patients following acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, the efficacy of combination therapy with ezetimibe in AMI is uncertain. Until recently, ezetimibe was reserved as add-on therapy for secondary lipid lowering post-AMI.
Research Question
Does the upfront combination of high-intensity statin treatment with ezetimibe improve cardiovascular outcomes compared with high-intensity statin treatment alone in patients with AMI?
Method
We conducted a target-trial emulation using retrospective data from the TriNetX global platform. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with AMI undergoing revascularization between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2023, were included. Patients with prior use of high-intensity statins (defined as atorvastatin ≥ 40 mg or rosuvastatin ≥ 20 mg daily), ezetimibe, or previous AMI with revascularization were excluded. Eligible patients were assigned to either combination therapy (high-intensity statin plus ezetimibe) or monotherapy (high-intensity statin alone) within one week of the index AMI. Propensity-score matching (1:1) was used to balance covariates. The primary efficacy outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), a composite of all-cause mortality, recurrent AMI, and stroke or transient ischemic attack. Secondary endpoints included individual components of MACE, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, and the rate of achieving LDL-C ≤ 70 mg/dL. Primary safety endpoints were rhabdomyolysis and acute liver failure. Pneumonia was set as a falsification endpoint. Follow-up continued until one year, death, loss to follow-up, or the occurrence of measures. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence interval.
Results
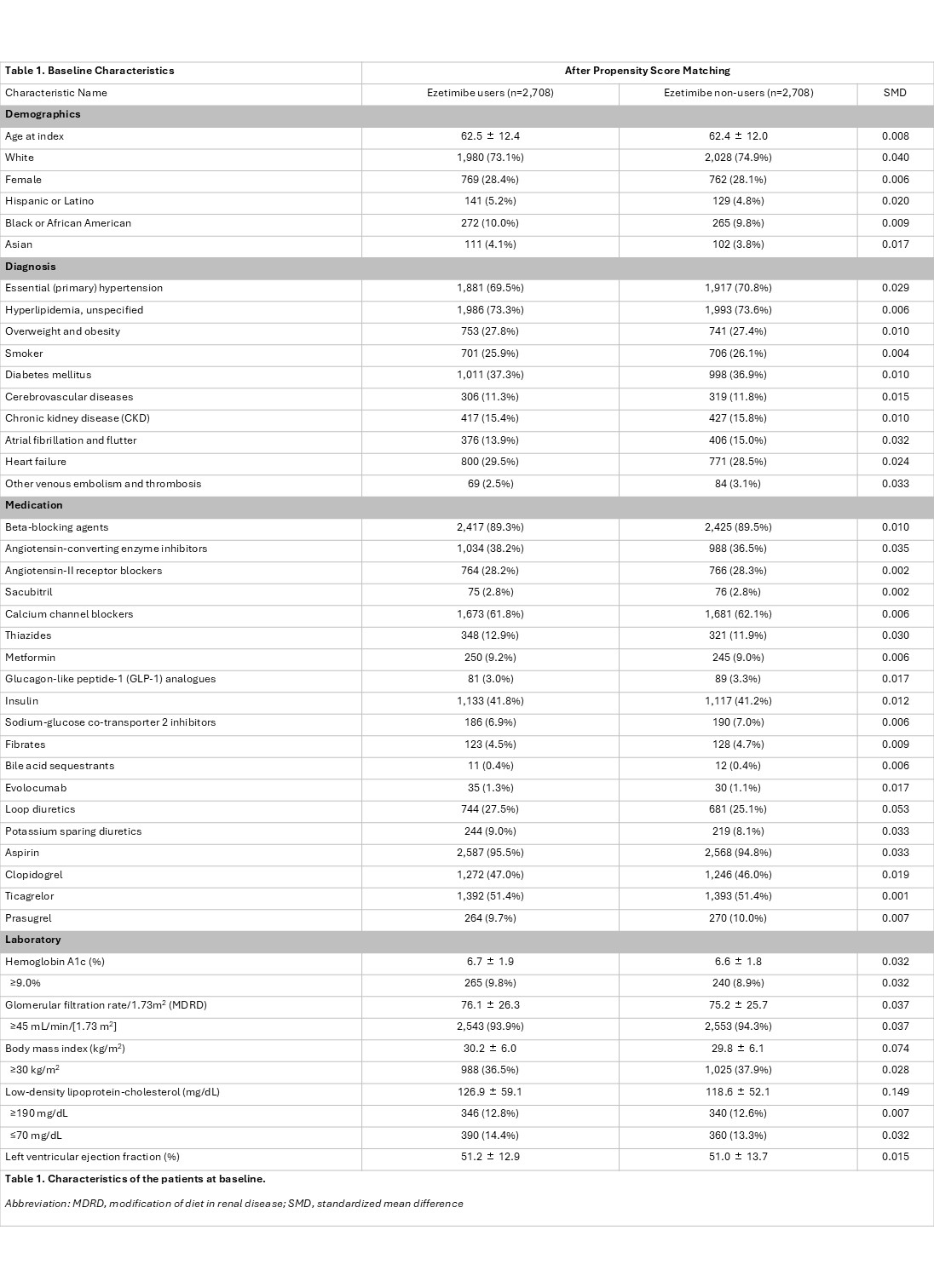
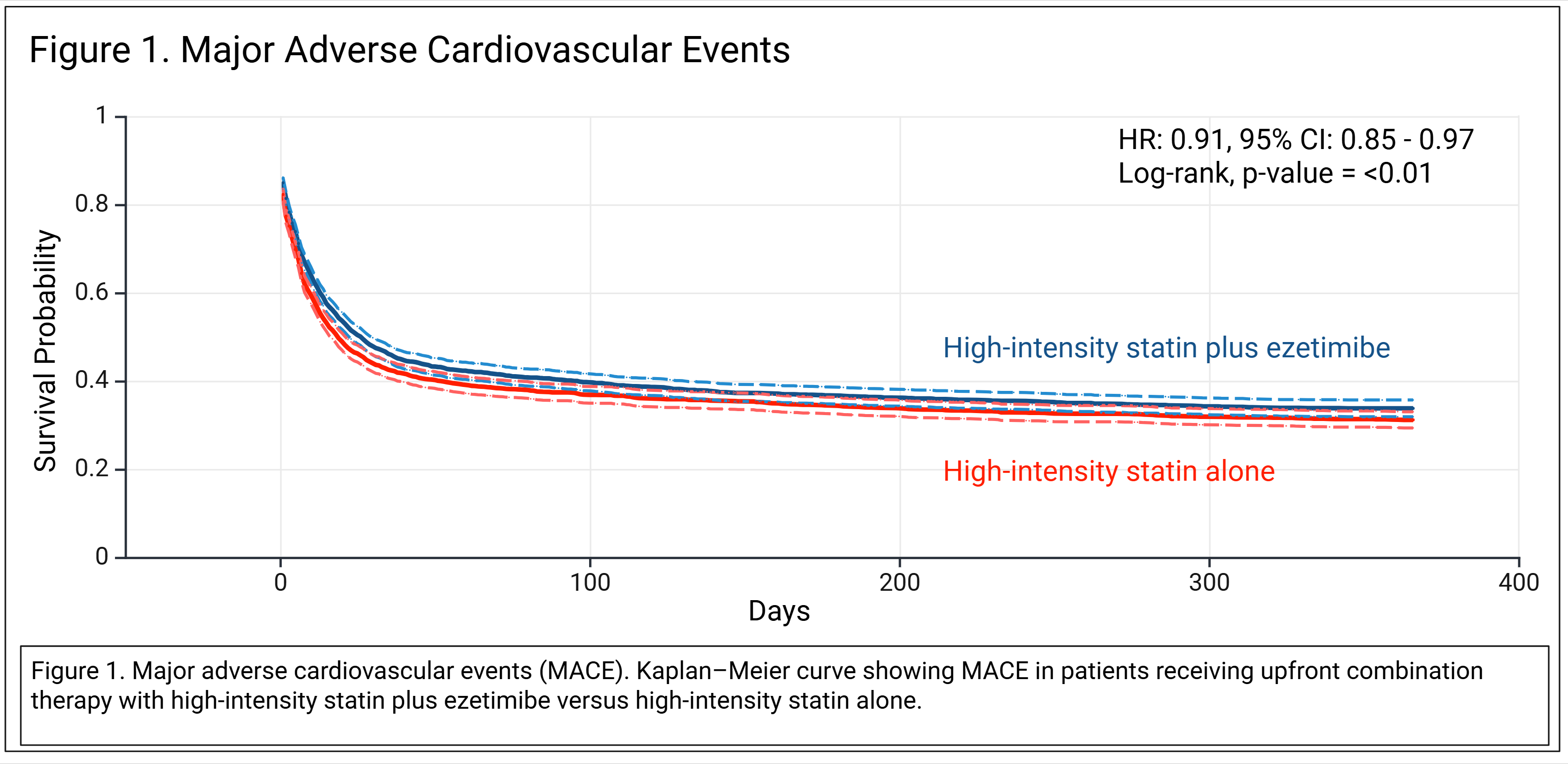
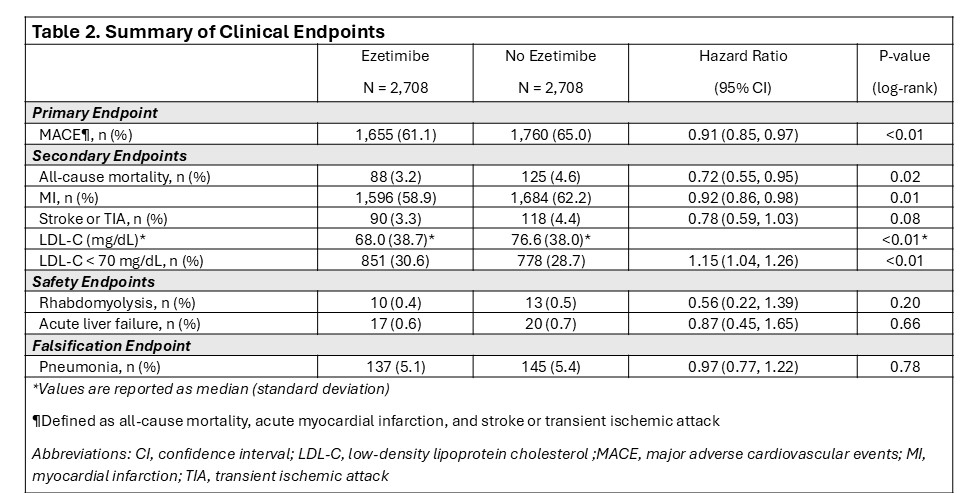
A total of 5,416 patients (2,708 per group) were included after propensity-score matching. All covariates were balanced (Table 1). Combination of high-intensity statin and ezetimibe was associated with a significant reduction in MACE compared with statin alone (Figure 1), as well as reductions in mortality, AMI, and LDL-C (Table 2). The rate of achieving LDL-C ≤ 70 mg/dL was superior in the combination group. Safety and falsification endpoints were similar between groups (Table 2).
Conclusion
In patients with AMI undergoing revascularization, upfront combination of a high-intensity statin and ezetimibe was associated with improved cardiovascular outcomes and more effective LDL-C lowering.
High-intensity statin treatment has well-established benefits in patients following acute myocardial infarction (AMI). However, the efficacy of combination therapy with ezetimibe in AMI is uncertain. Until recently, ezetimibe was reserved as add-on therapy for secondary lipid lowering post-AMI.
Research Question
Does the upfront combination of high-intensity statin treatment with ezetimibe improve cardiovascular outcomes compared with high-intensity statin treatment alone in patients with AMI?
Method
We conducted a target-trial emulation using retrospective data from the TriNetX global platform. Adult patients (≥ 18 years) with AMI undergoing revascularization between January 1, 2013, and December 31, 2023, were included. Patients with prior use of high-intensity statins (defined as atorvastatin ≥ 40 mg or rosuvastatin ≥ 20 mg daily), ezetimibe, or previous AMI with revascularization were excluded. Eligible patients were assigned to either combination therapy (high-intensity statin plus ezetimibe) or monotherapy (high-intensity statin alone) within one week of the index AMI. Propensity-score matching (1:1) was used to balance covariates. The primary efficacy outcome was major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), a composite of all-cause mortality, recurrent AMI, and stroke or transient ischemic attack. Secondary endpoints included individual components of MACE, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level, and the rate of achieving LDL-C ≤ 70 mg/dL. Primary safety endpoints were rhabdomyolysis and acute liver failure. Pneumonia was set as a falsification endpoint. Follow-up continued until one year, death, loss to follow-up, or the occurrence of measures. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate hazard ratios and 95% confidence interval.
Results
A total of 5,416 patients (2,708 per group) were included after propensity-score matching. All covariates were balanced (Table 1). Combination of high-intensity statin and ezetimibe was associated with a significant reduction in MACE compared with statin alone (Figure 1), as well as reductions in mortality, AMI, and LDL-C (Table 2). The rate of achieving LDL-C ≤ 70 mg/dL was superior in the combination group. Safety and falsification endpoints were similar between groups (Table 2).
Conclusion
In patients with AMI undergoing revascularization, upfront combination of a high-intensity statin and ezetimibe was associated with improved cardiovascular outcomes and more effective LDL-C lowering.
More abstracts on this topic:
Bempedoic acid monotherapy, LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular events: a secondary analysis of the CLEAR Outcomes trial
Zingano Carolina, Brennan Danielle, Li Na, Herout Peter, Powell Heather, Bloedon Leanne, Nissen Steven, Laffin Luke
Cardiology Follow-Up as a Determinant of LDL-C Management Success in Secondary Cardiovascular PreventionSedrakyan Surik, Laband William, Nadeem Bilawal, Lam Uyen