Final ID: Mo2016
Comparative Evaluation of ChatGPT and DougallGPT on Interventional Cardiology Subspecialty Exam Content
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DougallGPT have shown growing potential in medical education. However, there are limited studies evaluating their performance in highly specialized domains such as interventional cardiology. In this study, we assessed and compared the capabilities of ChatGPT and DougallGPT using questions from the CathSAP (Catheterization Self-Assessment Program), a widely used resource among interventional cardiology fellows preparing for interventional cardiology board examinations.
Methods:
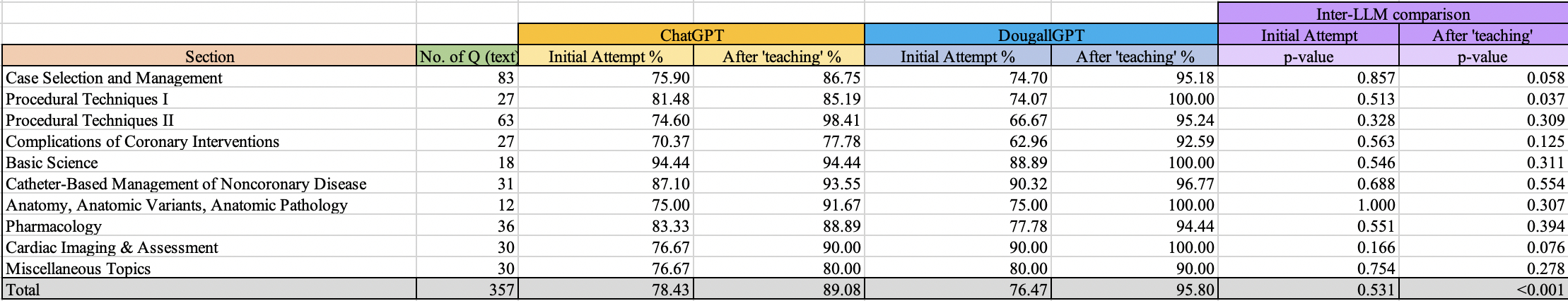
CathSAP contains 460 questions, including 357 text-based questions. Each LLM (ChatGPT [version 4.0] and DougallGPT) completed two sequential attempts on the text-based questions, allowing for assessment of initial performance and improvement after a ‘teaching’ intervention. The ‘teaching’ intervention involved providing the LLM with contextually relevant textual information from the 'Commentary' section of the corresponding CathSAP question. Subsequently, the statistical significance of differences in LLM response accuracy before and after exposure to relevant text was assessed using the chi-square test.
Results:
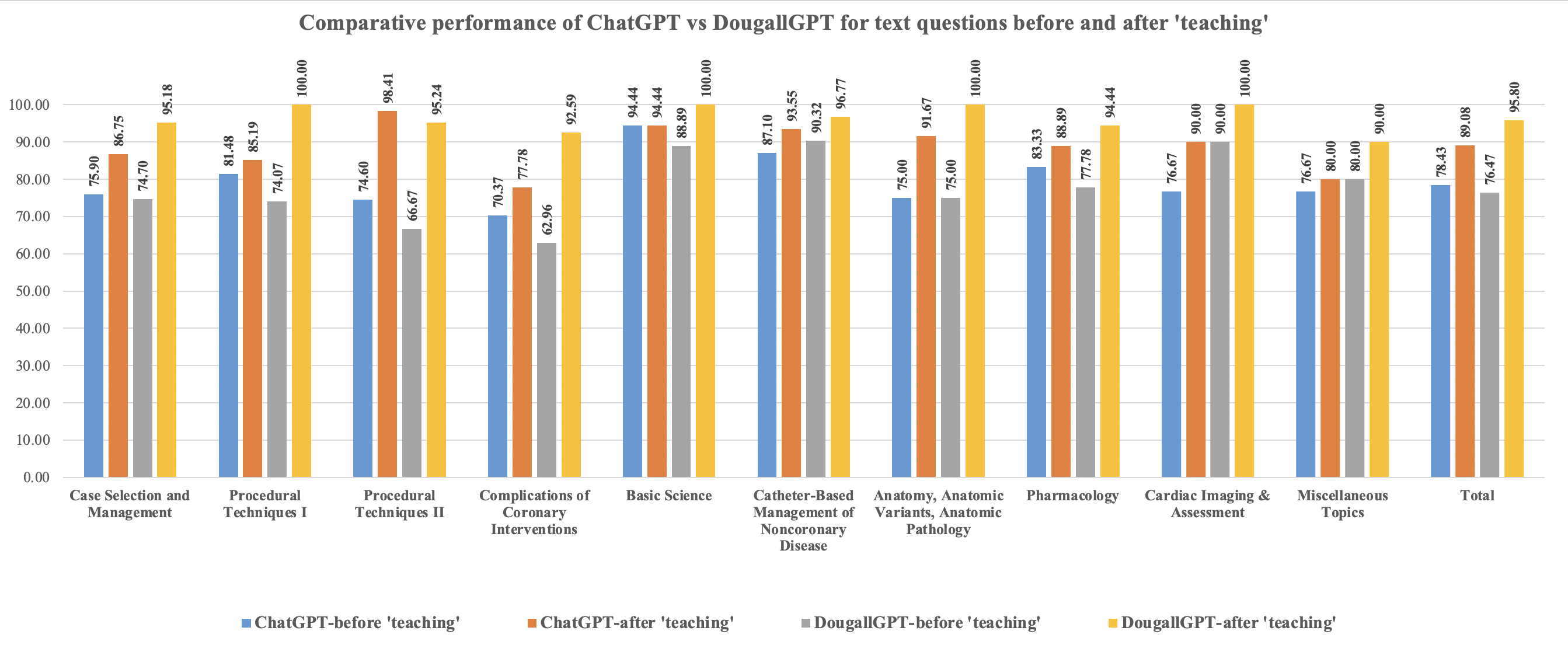
In the initial attempt, ChatGPT answered 78.4% of text questions correctly, compared to DougallGPT, which answered 76.47% of the questions correctly with no significant statistical difference overall (p=0.531) or within each section. DougallGPT showed a significantly greater improvement after ‘teaching’, achieving 95.8% correct compared to 89.1% for ChatGPT (p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Both ChatGPT and DougallGPT showed substantial performance gains after ‘teaching’ on interventional cardiology text-based questions. While ChatGPT demonstrated a strong baseline performance, DougallGPT showed significantly higher accuracy after ‘teaching’, suggesting that domain-specific optimization may enhance the educational utility of LLMs in interventional cardiology. DougallGPT’s marked improvement following the teaching intervention suggests it may be particularly well-suited to incorporate complex, context-rich educational material. These findings highlight the potential for tailored LLMs to serve as effective adjunctive tools in subspecialty training and self-assessment. Future research should explore their integration into curriculum design and their ability to adapt to evolving clinical guidelines.
Large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DougallGPT have shown growing potential in medical education. However, there are limited studies evaluating their performance in highly specialized domains such as interventional cardiology. In this study, we assessed and compared the capabilities of ChatGPT and DougallGPT using questions from the CathSAP (Catheterization Self-Assessment Program), a widely used resource among interventional cardiology fellows preparing for interventional cardiology board examinations.
Methods:
CathSAP contains 460 questions, including 357 text-based questions. Each LLM (ChatGPT [version 4.0] and DougallGPT) completed two sequential attempts on the text-based questions, allowing for assessment of initial performance and improvement after a ‘teaching’ intervention. The ‘teaching’ intervention involved providing the LLM with contextually relevant textual information from the 'Commentary' section of the corresponding CathSAP question. Subsequently, the statistical significance of differences in LLM response accuracy before and after exposure to relevant text was assessed using the chi-square test.
Results:
In the initial attempt, ChatGPT answered 78.4% of text questions correctly, compared to DougallGPT, which answered 76.47% of the questions correctly with no significant statistical difference overall (p=0.531) or within each section. DougallGPT showed a significantly greater improvement after ‘teaching’, achieving 95.8% correct compared to 89.1% for ChatGPT (p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Both ChatGPT and DougallGPT showed substantial performance gains after ‘teaching’ on interventional cardiology text-based questions. While ChatGPT demonstrated a strong baseline performance, DougallGPT showed significantly higher accuracy after ‘teaching’, suggesting that domain-specific optimization may enhance the educational utility of LLMs in interventional cardiology. DougallGPT’s marked improvement following the teaching intervention suggests it may be particularly well-suited to incorporate complex, context-rich educational material. These findings highlight the potential for tailored LLMs to serve as effective adjunctive tools in subspecialty training and self-assessment. Future research should explore their integration into curriculum design and their ability to adapt to evolving clinical guidelines.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGs
Arezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiographyJing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef