Final ID: MP2788
Therapeutic effects of extracellular vesicles from hPSC-derived epicardial cells in myocardial infarct healing
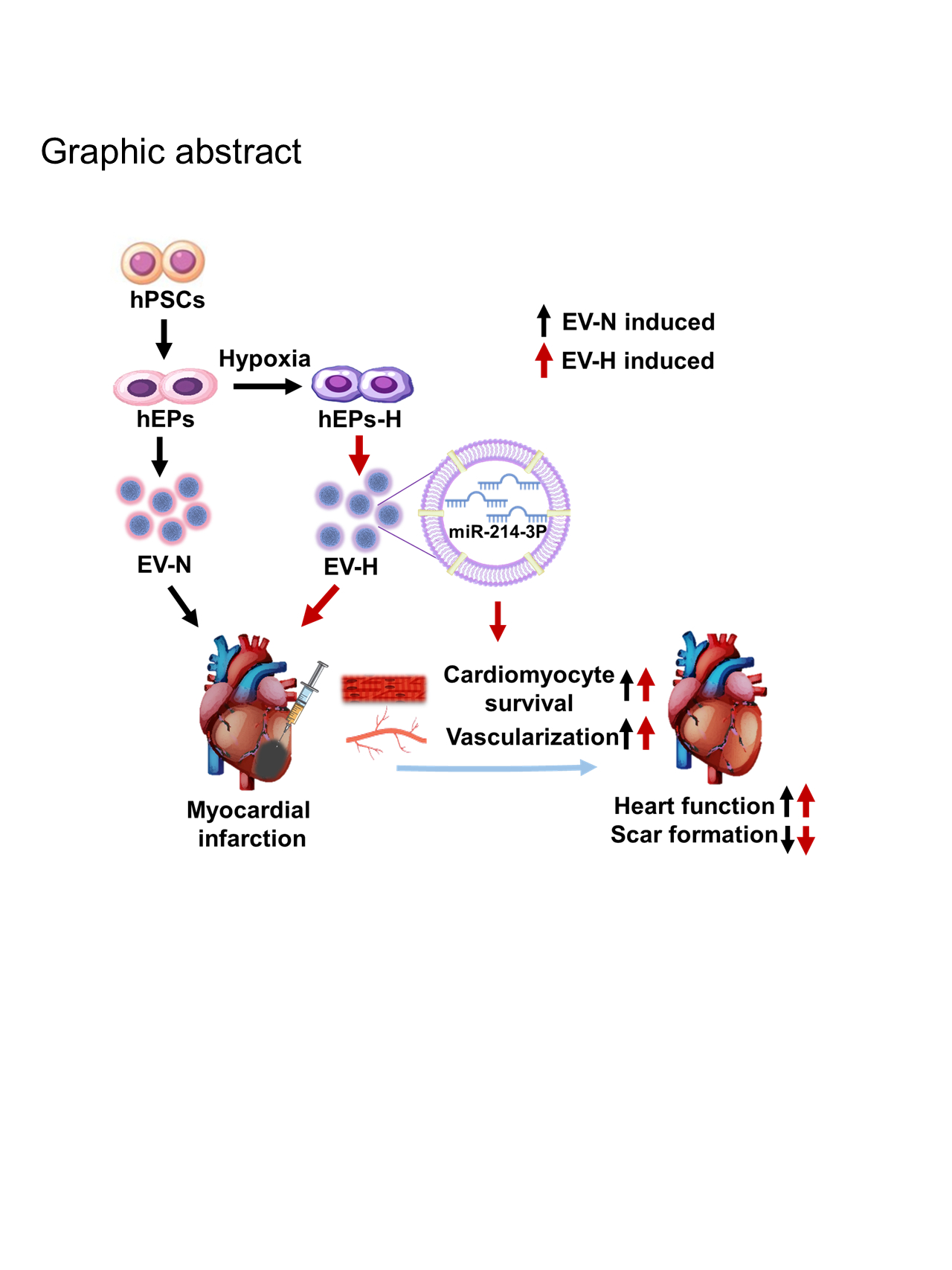
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: hPSC-derived epicardial cells (hEPs) have been demonstrated to promote infarct healing. However, the therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicles (EVs) secreted by hEPs (hEP-EVs) for infarcted hearts remains to be elucidated. The epicardium undergoes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process following myocardial infarction (MI) to regulate tissue repair, and the differentiation of epicardial cells is induced after hypoxia in vitro. However, the potential of hypoxia to initiate EMT of hEPs and the subsequent reanimation of the dynamic roles of hEP-EVs in cardiac repair remains unclear. Aims: to determine and compare the cardioprotective effects of the hEP-EVs under normoxic (EV-N) and hypoxic (EV-H) conditions in the infarcted heart, and identify the miRNA-related mechanisms involved. Results: Following a 48-hour culture under hypoxic conditions, a significant decrease in the expression of epicardial marker and an increase in levels of EMT-related genes were observed in the hEPs. Furthermore, immunostaining analysis demonstrated an increased number of hEPs expressing vimentin and α-smooth muscle actin. Subsequently, the hEP-EVs were collected and confirmed. Intramyocardial injection of hEP-EVs enhanced cardiac function, while only EV-H alleviated the progression of left ventricular dilation. Consistently, the scar formation was reduced by EV-N and further inhibited by EV-H at day 28 post-MI, concomitantly with enhanced pro-survival and pro-vascularization effects (vs. EV-N). Meanwhile, the EV-H was more efficacious than EV-N in promoting the tube formation and migration of HUVECs and diminishing the apoptotic cardiomyocytes and lactate activity following oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) injury. Further miRNA seq analysis revealed altered miRNA composition, with 115 upregulated miRNAs in EV-H than EV-N, in which the miR-214-3p was particularly prominent. Intramyocardial injection of miR-214-3p mimic ameliorated functional worsening and scar formation at day 28 post-MI. Further, miR-214-3p mimic enhanced the cardiomyocyte survival and vascularization both in vivo and in vitro. Conversely, the antagomir-mediated inhibition of miR-214-3p in the EV-H resulted in the suppression of these effects in vitro. Conclusions: This study demonstrates the reparative effects of hEP-EVs in infarcted heart and reveal the enhanced efficacy of hEP-EVs after cell hypoxia-conditioning, which may be partially attributed to the presence of miR-214-3p.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Bridge from Sweet to Sour: A Case of Recurrent Myocardial Stunning in Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Satish Vikyath, Pargaonkar Sumant, Slipczuk Leandro, Schenone Aldo, Maliha Maisha, Chi Kuan Yu, Sunil Kumar Sriram, Borkowski Pawel, Vyas Rhea, Rodriguez Szaszdi David Jose Javier, Kharawala Amrin, Seo Jiyoung
6-Nitrodopamine potentiates the positive chronotopic and inotropic effect induced by noradrenaline in the rat isolated heartLima Antonio, Sobanski Joao Fernando, Antunes Edson, De Nucci Gilberto