Final ID: Mo2008
Artificial Intelligence Based CCTA to Assess Sex-Based Differences in Coronary Atherosclerosis with Low Clinical Atheroma Volume
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
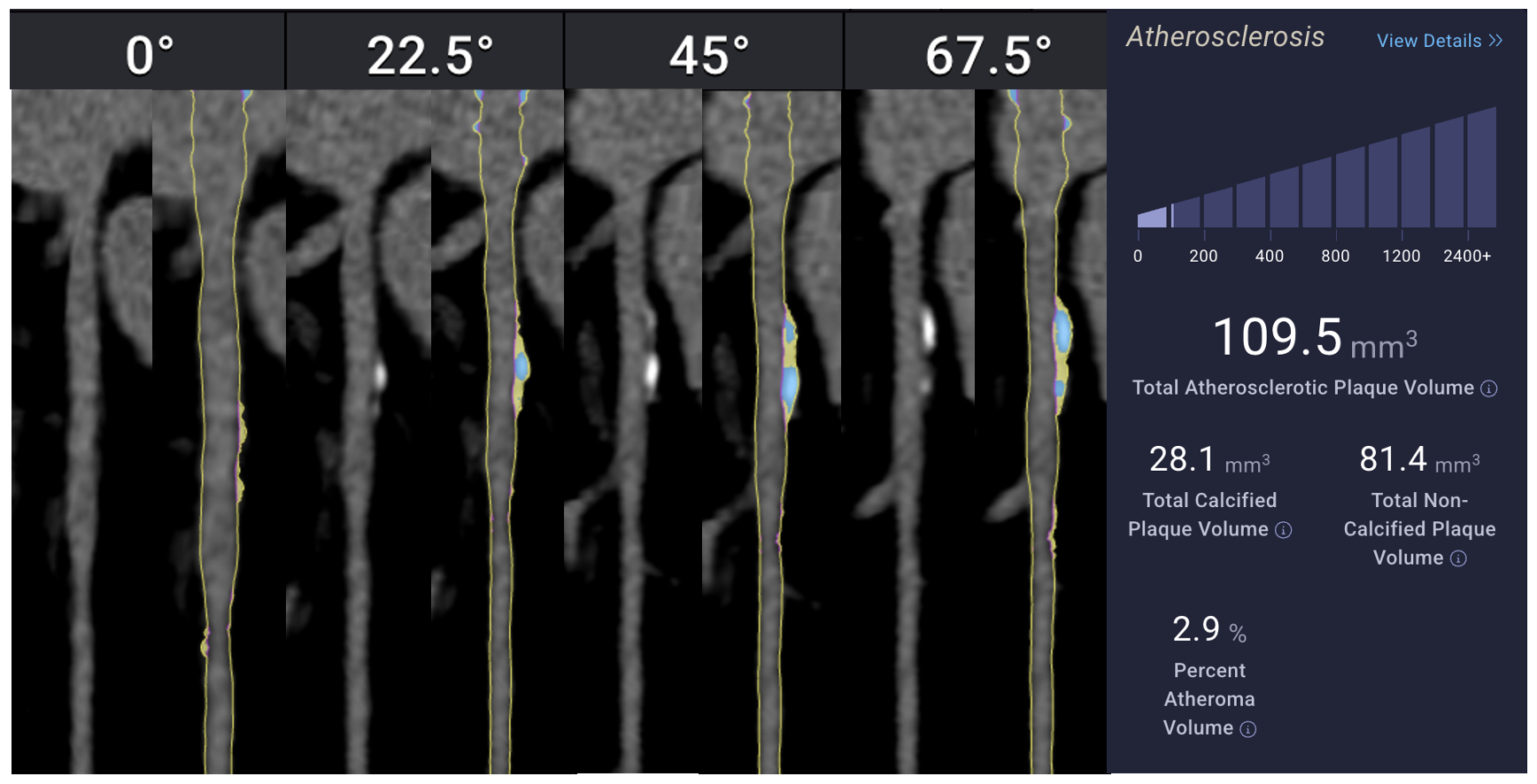
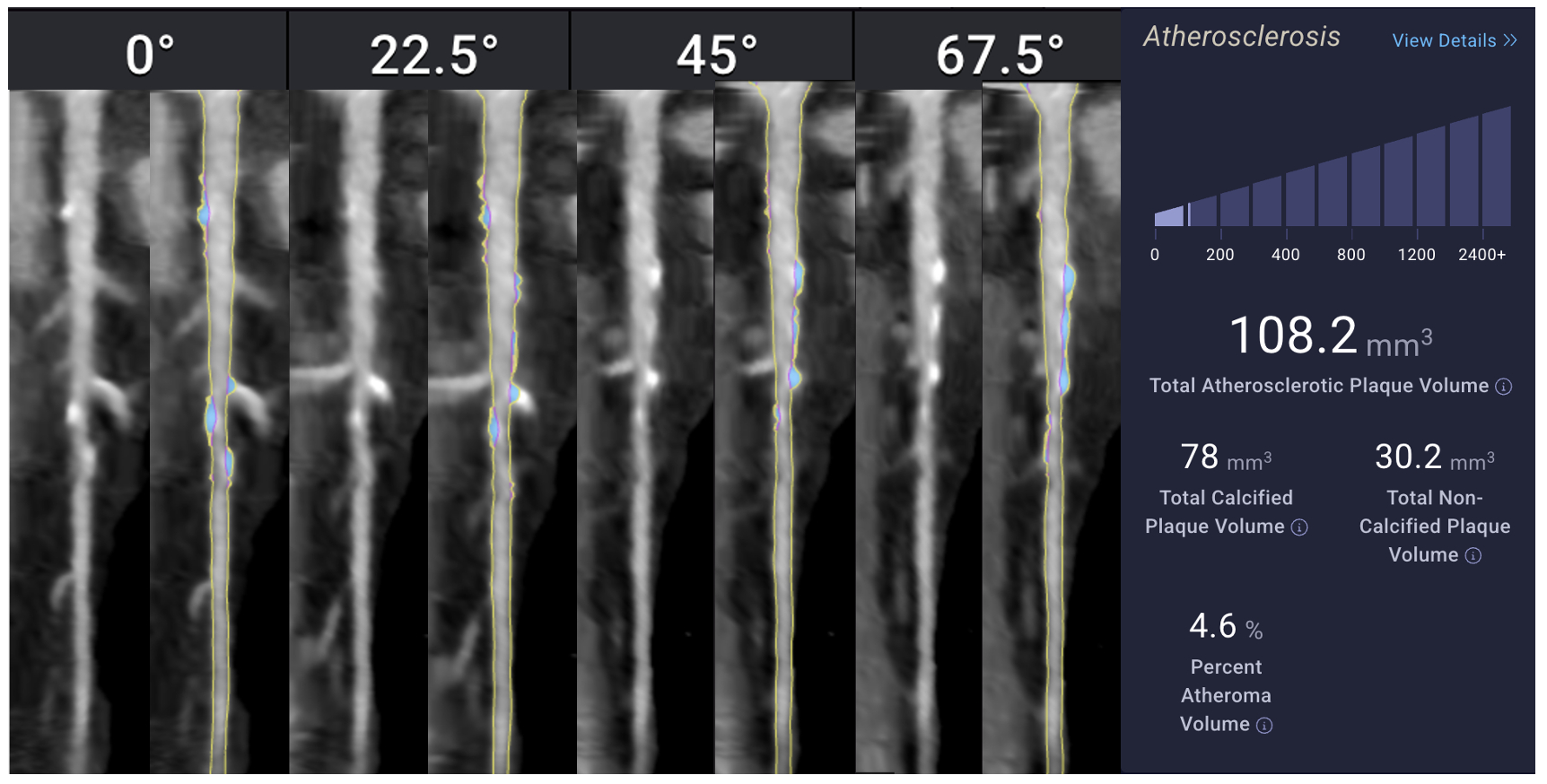
Traditional calcium-based risk assessment tools may underestimate coronary artery disease (CAD) burden, particularly in females, due to their inability to capture non-calcified, high-risk plaque. Artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) offers more precise plaque characterization. This study evaluates sex-based differences in coronary plaque composition among individuals with low total atheroma volume (TAV <250 mm^3).
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 100 patients undergoing AI-based CCTA. Volumetric plaque metrics—including total, calcified (CAV), non-calcified (NCAV), and low-density non-calcified (LD-NCAV) atheroma volumes—were quantified by artificial intelligence augmented CCTA (Cleerly). Gender differences were evaluated using Welch’s t-tests and multivariable linear regression adjusted for age.
Results:
In unadjusted comparisons, women had significantly lower total plaque volume (p = 0.018) and non-calcified plaque volume (p < 0.001) compared to men. There were no significant differences in calcified (p = 0.52) or low-density non-calcified plaque (p = 0.16). Regression analysis confirmed that male gender was independently associated with greater total plaque (β = 37.4 mm^3, p = 0.003) and non-calcified plaque (β = 39.3 mm^3, p < 0.001). Age was a significant predictor of total, calcified, and non-calcified plaque burden, but not of low-density plaque. Model explanatory power was modest (R^2 ≈ 0.20).
Conclusions:
Contrary to prior literature, men in this low-risk cohort had higher total and non-calcified plaque volumes than women, despite similar calcified burden. These findings highlight the limitations of calcification-based metrics in early risk stratification and underscore the utility of AI-based CCTA for detecting subclinical, non-calcified atherosclerosis. Future studies should explore reasons for these gender-based differences between studies and whether they influence long-term cardiovascular outcomes.
Traditional calcium-based risk assessment tools may underestimate coronary artery disease (CAD) burden, particularly in females, due to their inability to capture non-calcified, high-risk plaque. Artificial intelligence (AI)-enhanced coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) offers more precise plaque characterization. This study evaluates sex-based differences in coronary plaque composition among individuals with low total atheroma volume (TAV <250 mm^3).
Methods:
We conducted a retrospective cross-sectional analysis of 100 patients undergoing AI-based CCTA. Volumetric plaque metrics—including total, calcified (CAV), non-calcified (NCAV), and low-density non-calcified (LD-NCAV) atheroma volumes—were quantified by artificial intelligence augmented CCTA (Cleerly). Gender differences were evaluated using Welch’s t-tests and multivariable linear regression adjusted for age.
Results:
In unadjusted comparisons, women had significantly lower total plaque volume (p = 0.018) and non-calcified plaque volume (p < 0.001) compared to men. There were no significant differences in calcified (p = 0.52) or low-density non-calcified plaque (p = 0.16). Regression analysis confirmed that male gender was independently associated with greater total plaque (β = 37.4 mm^3, p = 0.003) and non-calcified plaque (β = 39.3 mm^3, p < 0.001). Age was a significant predictor of total, calcified, and non-calcified plaque burden, but not of low-density plaque. Model explanatory power was modest (R^2 ≈ 0.20).
Conclusions:
Contrary to prior literature, men in this low-risk cohort had higher total and non-calcified plaque volumes than women, despite similar calcified burden. These findings highlight the limitations of calcification-based metrics in early risk stratification and underscore the utility of AI-based CCTA for detecting subclinical, non-calcified atherosclerosis. Future studies should explore reasons for these gender-based differences between studies and whether they influence long-term cardiovascular outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
18F-NaF and 18F-FDG and calcification predict the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms and is attenuated by drug therapy
Nakahara Takehiro, Miyazawa Raita, Iwabuchi Yu, Tonda Kai, Narula Nupoor, Strauss Harry, Narula Jagat, Jinzaki Masahiro
A Competency-Based Screening Echocardiography Curriculum Designed for Rural American Indian Community Health RepresentativesThoroughman Rose, Riley Alan, De Loizaga Sarah, Adams David, Beaton Andrea, Buonfiglio Samantha, Danforth Kristen, Masyuko Sarah, Miller Mccall, Yadava Mrinal