Final ID: MP1597
Coronary Artery Proximity to Potential Ablation Sites in Children
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Coronary artery (CA) injury from catheter ablation is an uncommon complication, but the risk is under recognized. In pediatrics, CA imaging to assess for CA proximity is not commonly performed prior to ablation. The risk for CA injury significantly increases when a CA is within 3 mm of the site of ablation.
Research Question: How often is there a CA within 3 mm of a potential ablation site in pediatric patients?
Methods: A retrospective review of all coronary computed tomography angiograms (CTAs) in pediatric patients <18 years of age at Mayo Clinic from 2017 through 2023 was conducted. The proximity of CAs to potential ablation sites in the coronary sinus and the appendage bases were measured.
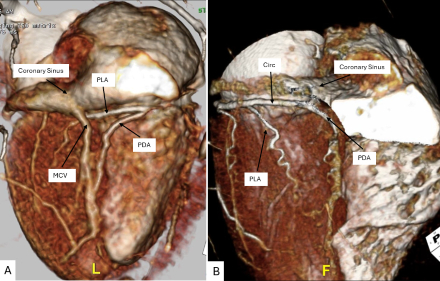
Results: Seventy-two CTAs in 67 patients >15 kg and <18 years old were included. Median age was 12 years and median weight was 41 kg. In right dominant CA circulation, 23/36 (64%) had a CA within 3 mm of the coronary sinus. For those within 3 mm, the mean distance from the coronary sinus was 1.4 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 10 mm +/- 2 mm (Figure 1A). In left and co-dominant CA circulation, 26/26 (100%) had a CA within 3 mm of the coronary sinus with a mean distance of 1.1 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 27 mm +/- 2 mm (Figure 1B).
The right CA was within 3 mm of the appendage base in 49/69 (71%). For those within 3 mm, the mean distance was 1.9 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 17 mm +/- 2 mm. The circumflex CA was within 3 mm of the appendage base in 50/68 (74%). Of the 50 within 3 mm, the mean distance was 2.1 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 9 mm +/- 2 mm.
Conclusion: Most pediatric patients have a CA ≤ 3 mm from potential ablation sites in the coronary sinus and base of the appendages. Before performing catheter ablation in these areas, precautions should be taken to avoid CA damage.
Research Question: How often is there a CA within 3 mm of a potential ablation site in pediatric patients?
Methods: A retrospective review of all coronary computed tomography angiograms (CTAs) in pediatric patients <18 years of age at Mayo Clinic from 2017 through 2023 was conducted. The proximity of CAs to potential ablation sites in the coronary sinus and the appendage bases were measured.
Results: Seventy-two CTAs in 67 patients >15 kg and <18 years old were included. Median age was 12 years and median weight was 41 kg. In right dominant CA circulation, 23/36 (64%) had a CA within 3 mm of the coronary sinus. For those within 3 mm, the mean distance from the coronary sinus was 1.4 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 10 mm +/- 2 mm (Figure 1A). In left and co-dominant CA circulation, 26/26 (100%) had a CA within 3 mm of the coronary sinus with a mean distance of 1.1 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 27 mm +/- 2 mm (Figure 1B).
The right CA was within 3 mm of the appendage base in 49/69 (71%). For those within 3 mm, the mean distance was 1.9 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 17 mm +/- 2 mm. The circumflex CA was within 3 mm of the appendage base in 50/68 (74%). Of the 50 within 3 mm, the mean distance was 2.1 mm +/- 0.2 mm for a length of 9 mm +/- 2 mm.
Conclusion: Most pediatric patients have a CA ≤ 3 mm from potential ablation sites in the coronary sinus and base of the appendages. Before performing catheter ablation in these areas, precautions should be taken to avoid CA damage.
More abstracts on this topic:
Characterizing Coronary Artery Outcomes with Real World Use of Etanercept for Kawasaki Disease with Coronary Involvement
Rogers Ryan, Olson Aaron, Sagiv Eyal, Portman Michael
Early-Life Sodium Restriction Programs Salt-Sensitivity of Autonomics and Blood Pressure in Adult C57BL/6J MiceLawton Samuel, Segar Jeffrey, Ziegler Alisha, Grobe Connie, Wagner Valerie, Brozoski Daniel, Fekete Eva, Sigmund Curt, Nakagawa Pablo, Grobe Justin