Final ID: MP218
Influence of Religiosity on Symptoms and the Quality of end-of-life Cardiovascular Disease Patients
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction Religiosity is a core component of palliative care and whose roles in patients with cancer were described. However, there is a paucity of studies in cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Hypothesis Religiosity can alleviate the symptoms of CVD patients in end-of-life (EOL).
Aims To clarify the influence of religiosity on physical symptoms, quality of care (QOC) and quality of death (QOD) in EOL care for CVD patients.
Methods We conducted a nationwide cross-sectional mortality follow-back survey using a questionnaire for bereaved caregivers of patients who had died of CVD in Japan. Measurements included Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale (MSAS), Care Evaluation Scale (CES) and Good Death Inventory (GDI). We assessed each outcome by the presence of religiosity.
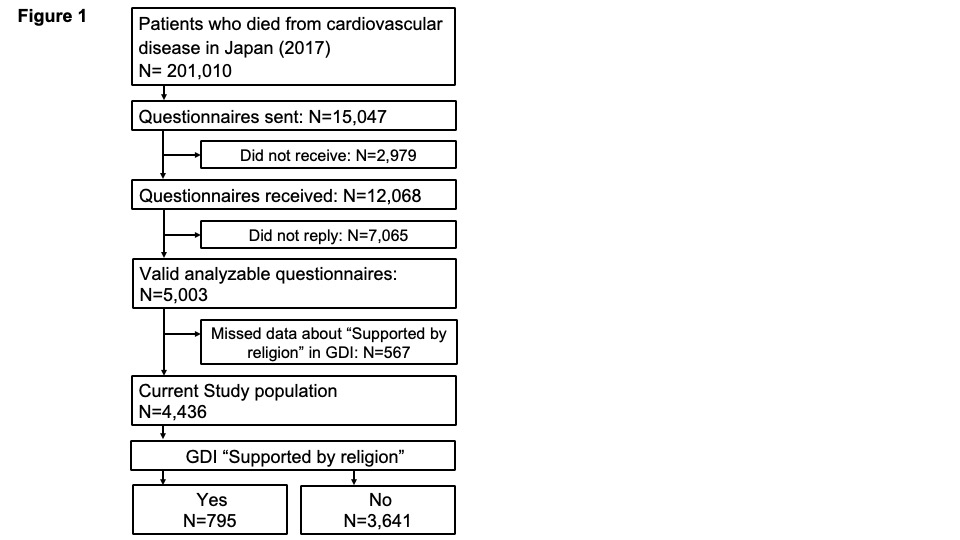
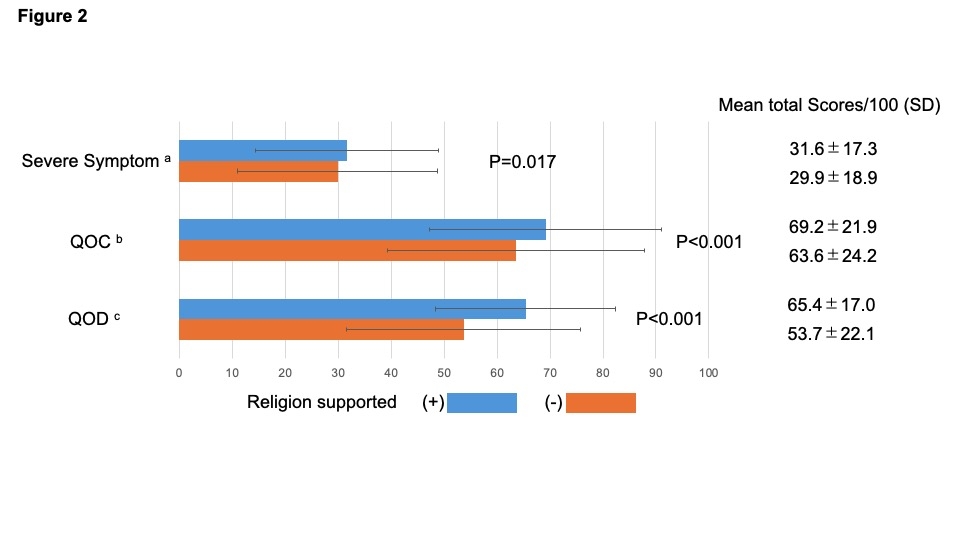
Results Of the questionnaire distributed to 15,047 descendants, we finally analyzed 4,436 responses about religiosity. 795 (17.9%) descendants answered that patients had been supported by religion 1 month before death. The religion-supported group was older (Religion: 88.9±8.7 vs. No Religion: 86.7±9.4, P<0.001), more frequent in females (70.9% vs. 60.3%, P<0.001), less frequently stayed at hospital 1 months before death (15.8% vs. 24.0%, P<0.001), and significantly more likely to report having fewer symptoms in MSAS sub-score and being more satisfied in CES and GDI sub-score. The results were the same except for “Lack of energy” and “Nausea” in MSAS after adjusting the confounders. The total mean score of CES and GDI was also significantly higher in the religion-supported group (69.2±21.9 vs. 63.6±24.2, P<0.001, 65.4±17.0 vs. 53.7±22.1, P<0.001, respectively).
Conclusion Religiosity could benefit CVD patients in EOL care by reducing physical symptoms and improving QOC and QOD.
Hypothesis Religiosity can alleviate the symptoms of CVD patients in end-of-life (EOL).
Aims To clarify the influence of religiosity on physical symptoms, quality of care (QOC) and quality of death (QOD) in EOL care for CVD patients.
Methods We conducted a nationwide cross-sectional mortality follow-back survey using a questionnaire for bereaved caregivers of patients who had died of CVD in Japan. Measurements included Memorial Symptom Assessment Scale (MSAS), Care Evaluation Scale (CES) and Good Death Inventory (GDI). We assessed each outcome by the presence of religiosity.
Results Of the questionnaire distributed to 15,047 descendants, we finally analyzed 4,436 responses about religiosity. 795 (17.9%) descendants answered that patients had been supported by religion 1 month before death. The religion-supported group was older (Religion: 88.9±8.7 vs. No Religion: 86.7±9.4, P<0.001), more frequent in females (70.9% vs. 60.3%, P<0.001), less frequently stayed at hospital 1 months before death (15.8% vs. 24.0%, P<0.001), and significantly more likely to report having fewer symptoms in MSAS sub-score and being more satisfied in CES and GDI sub-score. The results were the same except for “Lack of energy” and “Nausea” in MSAS after adjusting the confounders. The total mean score of CES and GDI was also significantly higher in the religion-supported group (69.2±21.9 vs. 63.6±24.2, P<0.001, 65.4±17.0 vs. 53.7±22.1, P<0.001, respectively).
Conclusion Religiosity could benefit CVD patients in EOL care by reducing physical symptoms and improving QOC and QOD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Social Support and Blood Pressure Control Among Older US Adults (1999-2008)
David Michelle, Choi Eunhee, Fernandez Sedano Brandon, Shurovi Sumayya, Dansoko Fatma, Abdalla Marwah
Reclaiming Life Amid Constraint: The Ventricular Assist Device ExperienceBechthold Avery, Wells Rachel, Abshire Saylor Martha, Mcilvennan Colleen, Matlock Dan, Moser Debra, Dionne-odom James