Final ID: MP1980
Polygenic Risk Score and the Risk of Repeat Coronary Revascularization After Index Procedure: Findings from the UK Biobank
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Patients undergoing coronary revascularization (CR), including percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), are at increased risk of repeat CR. This risk often overlaps with factors predisposing patients to coronary artery disease based on their polygenic risk score (PRS).
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis using UK Biobank data (03/13/2006–06/12/2023). Adults (≥18 years) who underwent index CR after recruitment were included. The primary outcome was repeat CR risk. Outcomes were assessed across three PRS categories for coronary artery disease: high (>80th percentile), intermediate (20th–80th percentile), and low (<20th percentile). Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated, with statistical significance set at p<0.05.
Results
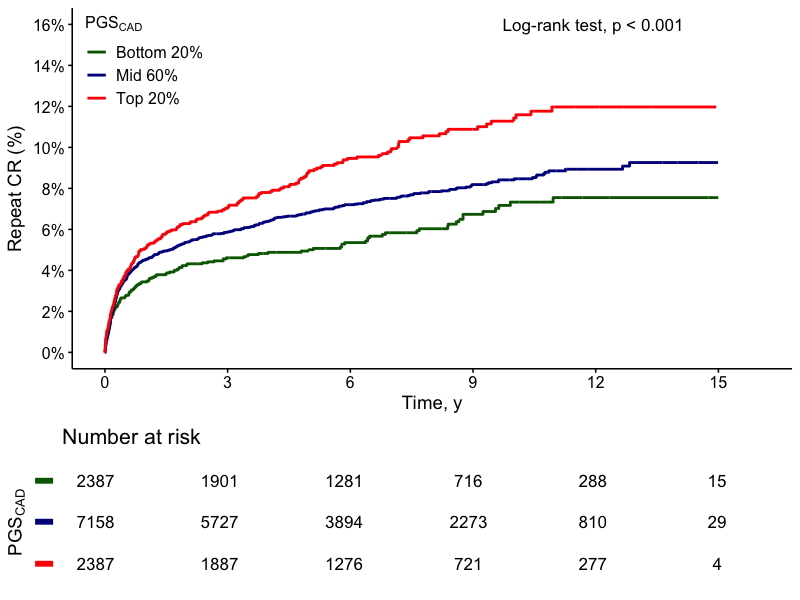
The study included 12,288 patients with a history of CR. The average age at diagnosis of CR was 66.89 years [95% CI: 66.76–67.02], with high-risk PRS patients presenting at a younger age than those at low risk [65.51 vs. 68.15 years; p<0.001]. A higher proportion of females was observed in the high-risk PRS group compared to the low-risk group [30.88% vs. 20.36%; p<0.001]. The risk of repeat CR after index procedure was significantly higher in high-risk PRS patients [HR: 1.73; 95% CI: 1.39–2.14; p<0.001] and intermediate-risk patients [HR: 1.30; 95% CI: 1.08–1.57; p=0.01] compared to low-risk PRS patients (Figure 1). High PRS risk was also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular-related mortality [HR: 1.32; 95% CI: 1.08–1.62; p=0.01]. The risk of major adverse cardiovascular events [HR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.88–1.04; p=0.31], all-cause mortality [HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 0.93–1.28; p=0.28], and non-fatal ischemic stroke [HR: 1.35; 95% CI: 0.96–1.91; p=0.08] were comparable between high- and low-risk PRS groups.
Subgroup analysis showed that patients who underwent index PCI had a higher risk of repeat CR in the high-risk vs. low-risk PRS group [HR: 1.90; 95% CI: 1.53–2.37; p<0.001]. In contrast, repeat CR risk was similar across PRS groups for those undergoing CABG [HR: 1.25; 95% CI: 0.95–1.65; p=0.10].
Conclusion
Patients with a high PRS for coronary artery disease had an increased likelihood of repeat CR and cardiovascular-related mortality after the index procedure. The strategic use of PRS models may aid in identifying those who would benefit from routine monitoring and/or intensive management following the index procedure.
Background
Patients undergoing coronary revascularization (CR), including percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), are at increased risk of repeat CR. This risk often overlaps with factors predisposing patients to coronary artery disease based on their polygenic risk score (PRS).
Methods
We conducted a retrospective analysis using UK Biobank data (03/13/2006–06/12/2023). Adults (≥18 years) who underwent index CR after recruitment were included. The primary outcome was repeat CR risk. Outcomes were assessed across three PRS categories for coronary artery disease: high (>80th percentile), intermediate (20th–80th percentile), and low (<20th percentile). Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated, with statistical significance set at p<0.05.
Results
The study included 12,288 patients with a history of CR. The average age at diagnosis of CR was 66.89 years [95% CI: 66.76–67.02], with high-risk PRS patients presenting at a younger age than those at low risk [65.51 vs. 68.15 years; p<0.001]. A higher proportion of females was observed in the high-risk PRS group compared to the low-risk group [30.88% vs. 20.36%; p<0.001]. The risk of repeat CR after index procedure was significantly higher in high-risk PRS patients [HR: 1.73; 95% CI: 1.39–2.14; p<0.001] and intermediate-risk patients [HR: 1.30; 95% CI: 1.08–1.57; p=0.01] compared to low-risk PRS patients (Figure 1). High PRS risk was also associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular-related mortality [HR: 1.32; 95% CI: 1.08–1.62; p=0.01]. The risk of major adverse cardiovascular events [HR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.88–1.04; p=0.31], all-cause mortality [HR: 1.09; 95% CI: 0.93–1.28; p=0.28], and non-fatal ischemic stroke [HR: 1.35; 95% CI: 0.96–1.91; p=0.08] were comparable between high- and low-risk PRS groups.
Subgroup analysis showed that patients who underwent index PCI had a higher risk of repeat CR in the high-risk vs. low-risk PRS group [HR: 1.90; 95% CI: 1.53–2.37; p<0.001]. In contrast, repeat CR risk was similar across PRS groups for those undergoing CABG [HR: 1.25; 95% CI: 0.95–1.65; p=0.10].
Conclusion
Patients with a high PRS for coronary artery disease had an increased likelihood of repeat CR and cardiovascular-related mortality after the index procedure. The strategic use of PRS models may aid in identifying those who would benefit from routine monitoring and/or intensive management following the index procedure.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Health Coach-Based Multi-Level Personalized Strategy Lowers LDL-Cholesterol and Enhances Lipid Control in Veterans with Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease – The VA Lipid Optimization Reimagined Quality Improvement Project at VA New York Harbor Healthcare System
Chen Tina, Ingerman Diana, Haley Leah, Salovaara Priscilla, Nicholson Andrew, Illenberger Nicholas, Natarajan Sundar
Beyond Closure: A Case Report on Coronary Steal Syndrome by Previously Embolized Internal Mammary Artery Side BranchFuentes Jose, Garcia Almonte Karla, Suero Claudia, Urena Neme Ana Paula, Tarafa Jorge A., Urena V Pedro