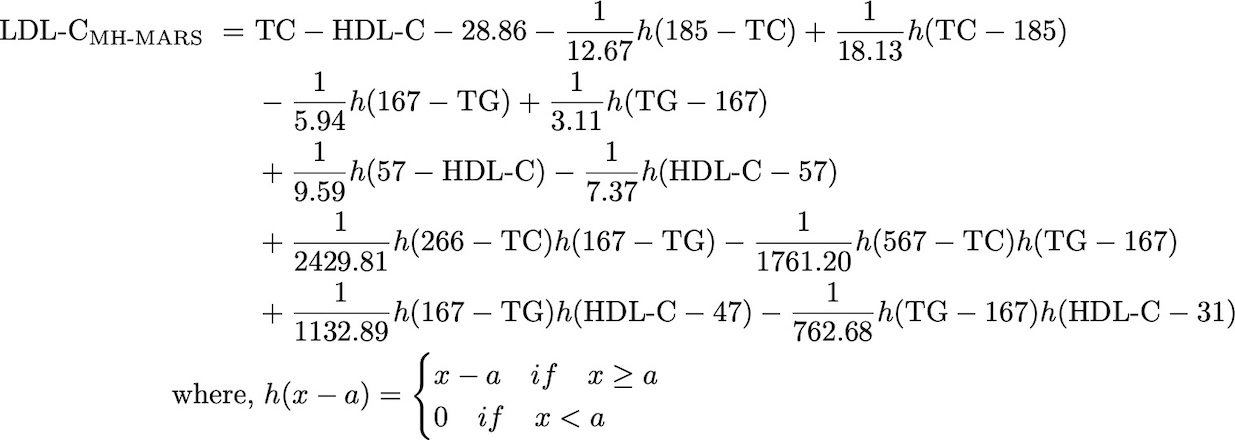Final ID: Mo2109
Development and Validation of a Simplified Martin/Hopkins Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Equation Using Machine Learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction/Background: The Martin-Hopkins equation is widely validated and used to estimate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C). However, some laboratories find implementation challenging and a machine learning-based approach may help overcome this by simplifying implementation to a single equation.
Research Question/Hypothesis: This study aims to develop a machine-learning based equation for estimating LDL-C using multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS) and compare its performance to the Friedewald (LDL-CF), Sampson-NIH (LDL-CS), and original Martin-Hopkins (LDL-CMH) equations.
Methods/Approach: We used data from the Very Large Database of Lipids (VLDbL), which includes lipid measurements collected using VAP ultracentrifugation between October 1, 2015, and June 30, 2019. The study included 4,939,528 patients with complete lipid panel data, who were randomly assigned to a training set (n=3,292,889) and a test set (n=1,646,639). A MARS model was developed to estimate LDL-C (Figure 1). The accuracy of LDL-C estimation was assessed using bias, root mean squared error (RMSE), and concordance with guideline-based categories between estimated and ultracentrifugation-measured LDL-C values.
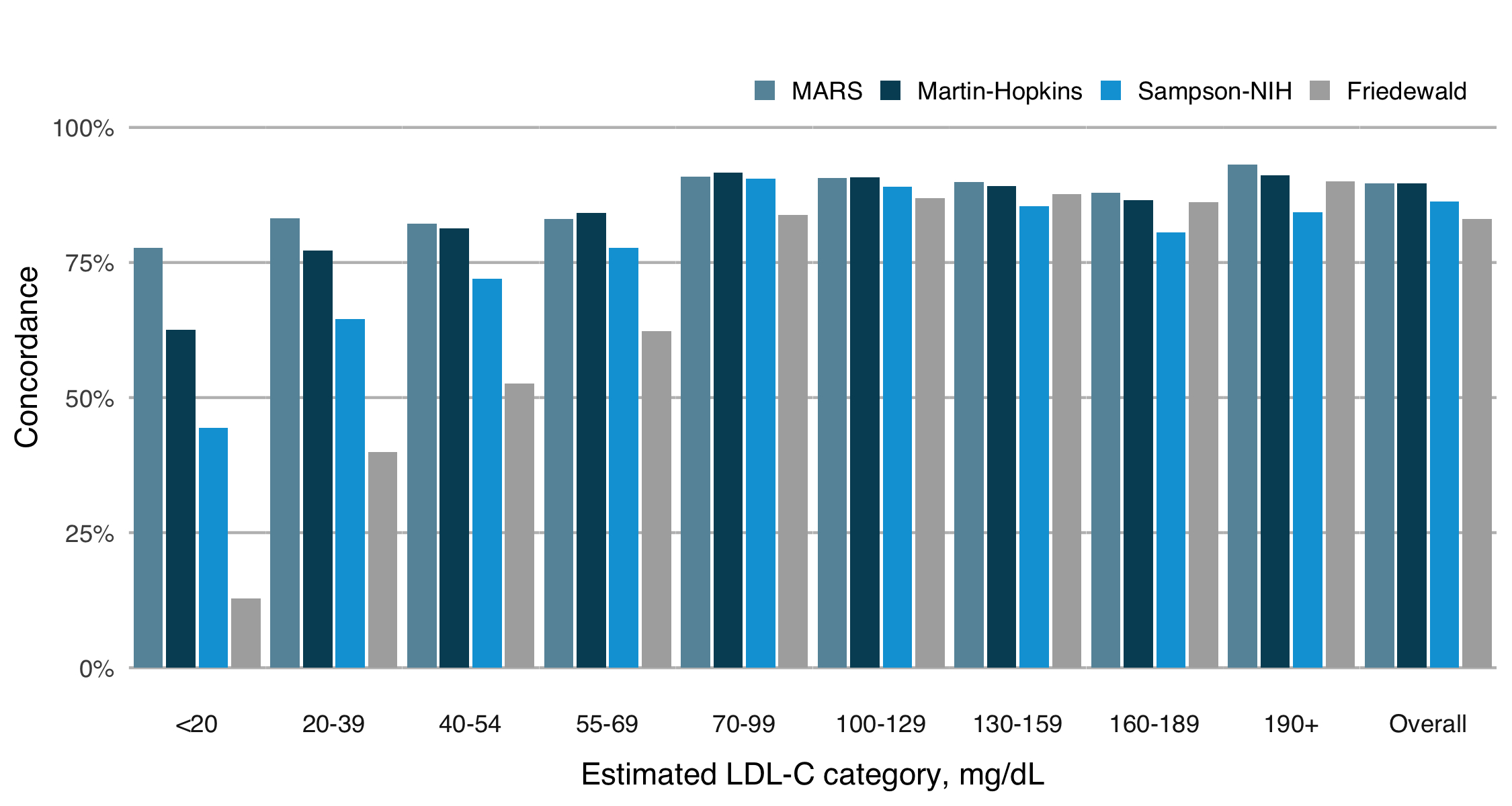
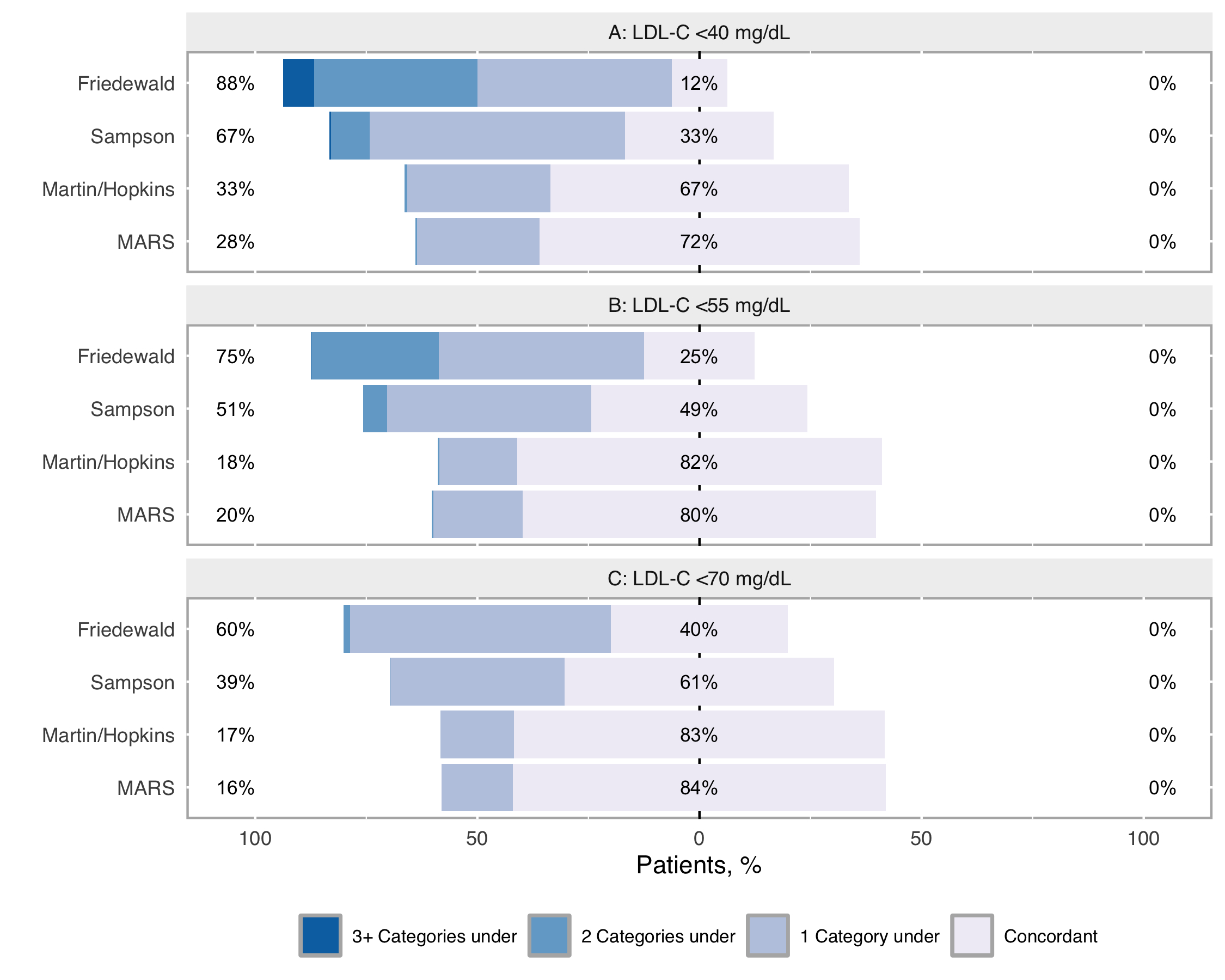
Results/Data: The new equation (LDL-CMH-MARS) showed a very low median bias (-0.14 mg/dL, IQR: -2.11–1.78), comparable to LDL-CMH (0.26 mg/dL, IQR: -1.62–2.37). The median bias was higher for LDL-CS (1.72 mg/dL, IQR: -1.29–4.14) and LDL-CF (-0.20 mg/dL, IQR: -4.40–2.60). The median difference between the MARS and original Martin-Hopkins equations was -0.51 mg/dL (IQR: -1.24–0.04), further suggesting comparability between the two methods. RMSE was lowest for LDL-CMH-MARS (4.68) and LDL-CMH (4.90), followed by LDL-CS (5.79) and LDL-CF (7.25). The proportion of patients correctly classified to clinical categories was nearly identical for LDL-CMH-MARS (89.69%) and LDL-CMH (89.60%), but lower for LDL-CS (86.28%) and LDL-CF (83.10%) (Figure 2). LDL-CS and LDL-CF underestimated LDL-C in 39% and 60% when classifying LDL-C <70 mg/dL in patients with triglyceride concentrations of 200–399 mg/dL, whereas this improved to <18% with both LDL-CMH-MARS and LDL-CMH (Figure 3).
Conclusions: The new machine learning-based LDL-C equation provides comparable results to the original Martin-Hopkins method while simplifying implementation to a single equation. The implementation of LDL-CMH-MARS would be straightforward with a single line of code in laboratory information systems.
Research Question/Hypothesis: This study aims to develop a machine-learning based equation for estimating LDL-C using multivariate adaptive regression spline (MARS) and compare its performance to the Friedewald (LDL-CF), Sampson-NIH (LDL-CS), and original Martin-Hopkins (LDL-CMH) equations.
Methods/Approach: We used data from the Very Large Database of Lipids (VLDbL), which includes lipid measurements collected using VAP ultracentrifugation between October 1, 2015, and June 30, 2019. The study included 4,939,528 patients with complete lipid panel data, who were randomly assigned to a training set (n=3,292,889) and a test set (n=1,646,639). A MARS model was developed to estimate LDL-C (Figure 1). The accuracy of LDL-C estimation was assessed using bias, root mean squared error (RMSE), and concordance with guideline-based categories between estimated and ultracentrifugation-measured LDL-C values.
Results/Data: The new equation (LDL-CMH-MARS) showed a very low median bias (-0.14 mg/dL, IQR: -2.11–1.78), comparable to LDL-CMH (0.26 mg/dL, IQR: -1.62–2.37). The median bias was higher for LDL-CS (1.72 mg/dL, IQR: -1.29–4.14) and LDL-CF (-0.20 mg/dL, IQR: -4.40–2.60). The median difference between the MARS and original Martin-Hopkins equations was -0.51 mg/dL (IQR: -1.24–0.04), further suggesting comparability between the two methods. RMSE was lowest for LDL-CMH-MARS (4.68) and LDL-CMH (4.90), followed by LDL-CS (5.79) and LDL-CF (7.25). The proportion of patients correctly classified to clinical categories was nearly identical for LDL-CMH-MARS (89.69%) and LDL-CMH (89.60%), but lower for LDL-CS (86.28%) and LDL-CF (83.10%) (Figure 2). LDL-CS and LDL-CF underestimated LDL-C in 39% and 60% when classifying LDL-C <70 mg/dL in patients with triglyceride concentrations of 200–399 mg/dL, whereas this improved to <18% with both LDL-CMH-MARS and LDL-CMH (Figure 3).
Conclusions: The new machine learning-based LDL-C equation provides comparable results to the original Martin-Hopkins method while simplifying implementation to a single equation. The implementation of LDL-CMH-MARS would be straightforward with a single line of code in laboratory information systems.
More abstracts on this topic:
A 50% or Greater Reduction in LDL-Cholesterol Is Associated with Improved Long-Term Outcomes and Lower Health Care Utilization After Myocardial Infarction - a SWEDEHEART study
Reitan Christian, Watanabe Alexandre, Bash Lori, Galvain Thibaut, Arnet Urs, Jernberg Tomas
A Machine Learning Algorithm to Detect Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Risk from Baseline ECGsArezoumand Amirhossein, Danala Gopichandh, Masnadi Khiabani Parisa, Ebert David, Behere Shashank