Final ID: MP909
Mortality and Disease Burden of Smoking-Related Lower Extremity Peripheral Artery Disease: A Comparative Analysis of the U.S. and High Socio-Demographic Index Countries
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Background
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) significantly contributes to cardiovascular morbidity. Smoking, a key modifiable risk factor, accelerates PAD progression and increases risks of cardiovascular events, limb loss, and reduced quality of life. Yet, the global burden of smoking-related PAD remains understudied.
Methods
Smoking-related lower extremity PAD data were sourced from the GBD 2021 study. Age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) from 1990–2021 were analyzed for the U.S. and compared to high socio-demographic index (SDI) countries with comparable economic development and education levels. Annual percentage change (APC), average APC difference (AAPCD), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) assessed relative burden changes. Significance was set at p<0.05.
Results
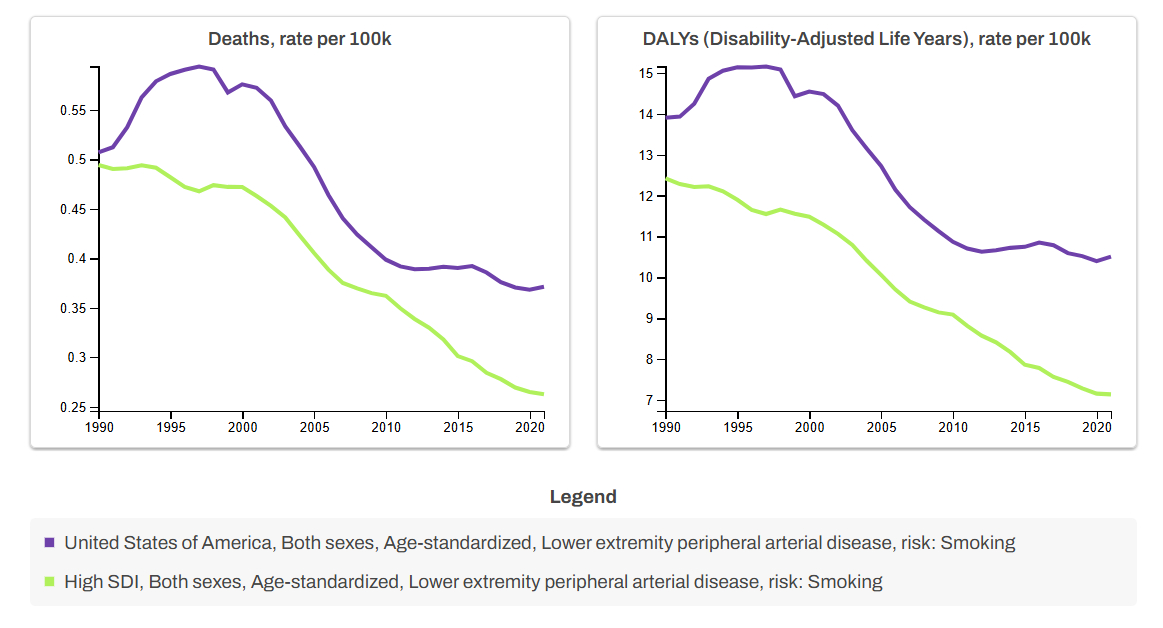
In the U.S., smoking-related PAD ASDR dropped from 0.51 (95% CI: 0.38–0.65) in 1990 to 0.37 (95% CI: 0.27–0.48) in 2021. It rose from 1990–1995 (APC: 3.51; 95% CI: 2.71–4.39; p<0.01), then declined in 1995–2002 (APC: -0.80; 95% CI: -1.36 to -0.28; p<0.01), 2002–2009 (APC: -4.66; 95% CI: -5.47 to -4.17; p<0.01), and slowed in 2009–2021 (APC: -0.73; 95% CI: -0.96 to -0.44; p<0.01). In high SDI countries, ASDR declined from 0.49 (95% CI: 0.38–0.63) to 0.26 (95% CI: 0.19–0.34), with consistent reductions and no 2010–2019 deceleration as seen in the U.S. (Figure 1: Left Panel). Overall ASDR decline was greater in high SDI countries (AAPCD: -1.25; 95% CI: -1.54 to -0.96; p<0.01).
U.S. DALY rate fell from 13.90 (95% CI: 10.23–18.33) in 1990 to 10.51 (95% CI: 7.62–13.94) in 2021. It rose from 1990–1995 (APC: 2.16; 95% CI: 1.47–3.00; p<0.01), declined in 1995–2002 (APC: -1.08; 95% CI: -1.59 to -0.60; p<0.01) and 2002–2009 (APC: -3.70; 95% CI: -4.62 to -3.26; p<0.01), then slowed in 2009–2021 (APC: -0.32; 95% CI: -0.55 to -0.06; p=0.02). High SDI countries saw DALY rates drop from 12.42 (95% CI: 9.27–16.34) to 7.14 (95% CI: 5.22–9.63) with consistent declines (Figure 1: Right Panel). Their overall reduction exceeded that of the U.S. (AAPCD: -1.08; 95% CI: -1.31 to -0.85; p<0.01).
Conclusions
Mortality and disease burden from smoking-related PAD declined in both the U.S. and high SDI countries from 1990 to 2021. However, in the past decade, the rate of decline in the U.S. has slowed compared to high SDI countries. Our study highlights the need for stricter smoking control programs, the development of effective PAD screening guidelines, and prompt public health action.
Background
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) significantly contributes to cardiovascular morbidity. Smoking, a key modifiable risk factor, accelerates PAD progression and increases risks of cardiovascular events, limb loss, and reduced quality of life. Yet, the global burden of smoking-related PAD remains understudied.
Methods
Smoking-related lower extremity PAD data were sourced from the GBD 2021 study. Age-standardized death rates (ASDR) and disability-adjusted life years (DALY) from 1990–2021 were analyzed for the U.S. and compared to high socio-demographic index (SDI) countries with comparable economic development and education levels. Annual percentage change (APC), average APC difference (AAPCD), and 95% confidence intervals (CI) assessed relative burden changes. Significance was set at p<0.05.
Results
In the U.S., smoking-related PAD ASDR dropped from 0.51 (95% CI: 0.38–0.65) in 1990 to 0.37 (95% CI: 0.27–0.48) in 2021. It rose from 1990–1995 (APC: 3.51; 95% CI: 2.71–4.39; p<0.01), then declined in 1995–2002 (APC: -0.80; 95% CI: -1.36 to -0.28; p<0.01), 2002–2009 (APC: -4.66; 95% CI: -5.47 to -4.17; p<0.01), and slowed in 2009–2021 (APC: -0.73; 95% CI: -0.96 to -0.44; p<0.01). In high SDI countries, ASDR declined from 0.49 (95% CI: 0.38–0.63) to 0.26 (95% CI: 0.19–0.34), with consistent reductions and no 2010–2019 deceleration as seen in the U.S. (Figure 1: Left Panel). Overall ASDR decline was greater in high SDI countries (AAPCD: -1.25; 95% CI: -1.54 to -0.96; p<0.01).
U.S. DALY rate fell from 13.90 (95% CI: 10.23–18.33) in 1990 to 10.51 (95% CI: 7.62–13.94) in 2021. It rose from 1990–1995 (APC: 2.16; 95% CI: 1.47–3.00; p<0.01), declined in 1995–2002 (APC: -1.08; 95% CI: -1.59 to -0.60; p<0.01) and 2002–2009 (APC: -3.70; 95% CI: -4.62 to -3.26; p<0.01), then slowed in 2009–2021 (APC: -0.32; 95% CI: -0.55 to -0.06; p=0.02). High SDI countries saw DALY rates drop from 12.42 (95% CI: 9.27–16.34) to 7.14 (95% CI: 5.22–9.63) with consistent declines (Figure 1: Right Panel). Their overall reduction exceeded that of the U.S. (AAPCD: -1.08; 95% CI: -1.31 to -0.85; p<0.01).
Conclusions
Mortality and disease burden from smoking-related PAD declined in both the U.S. and high SDI countries from 1990 to 2021. However, in the past decade, the rate of decline in the U.S. has slowed compared to high SDI countries. Our study highlights the need for stricter smoking control programs, the development of effective PAD screening guidelines, and prompt public health action.
More abstracts on this topic:
Changes in Management of Acute Aortic Syndrome with Vascular Medicine Involvement in a Multidisciplinary Aortic Team
Pettinato Anthony, Milioglou Ioannis, Diggins Caroline, Krawisz Anna, Schmaier Alec, Secemsky Eric, Khabbaz Kamal, Schermerhorn Marc, Carroll Brett
Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes Are Associated with Incident Peripheral Artery Disease, Results from the Women’s Health Initiative.Jackson Elizabeth, Leblanc Erin, Haring Bernhard, Harrington Laura, Allison Matthew, Eaton Charles, Lamonte Michael, Hovey Kathleen, Andrews Chris, Wells Gretchen, Manson Joann, Levitan Emily, Spracklen Cassandra, Wild Robert