Final ID: Su2035
Real time assessment of Primary Care Hypertension Management in an Urban Health System using MDClone
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Primary Care Providers (PCPs) diagnose patients with hypertension (HTN) and initiate antihypertensive therapies that prevent end organ damage. Outpatient HTN management remains challenging and improved metrics of successful blood pressure (BP) control are needed. Timely reports of HTN management could empower better BP outcomes.
Objective: Use a novel data exploration platform to rapidly identify opportunities for improved BP management among PCPs at an academic health system.
MethodsIn this observational quality improvement analysis, we reviewed electronic health record (EHR) data using a cloud-based, machine-learning platform, MDClone ADAMS (2024) to assess outpatient HTN management at the University of Chicago (112 PCPs, 23 clinics). Between January 2022-March 2025, we identified hypertensive patients who had been clinically evaluated by PCPs. Patient-level variables were extracted from the EHR including current age; sex; race; systolic and diastolic BP during the study period; antihypertensive drug class and dose; serum creatinine; and referrals to specialists (cardiology, nephrology). Between-group differences were compared with t-tests or X2 using a 2-sided significance level of 0.05. The project was IRB exempt.
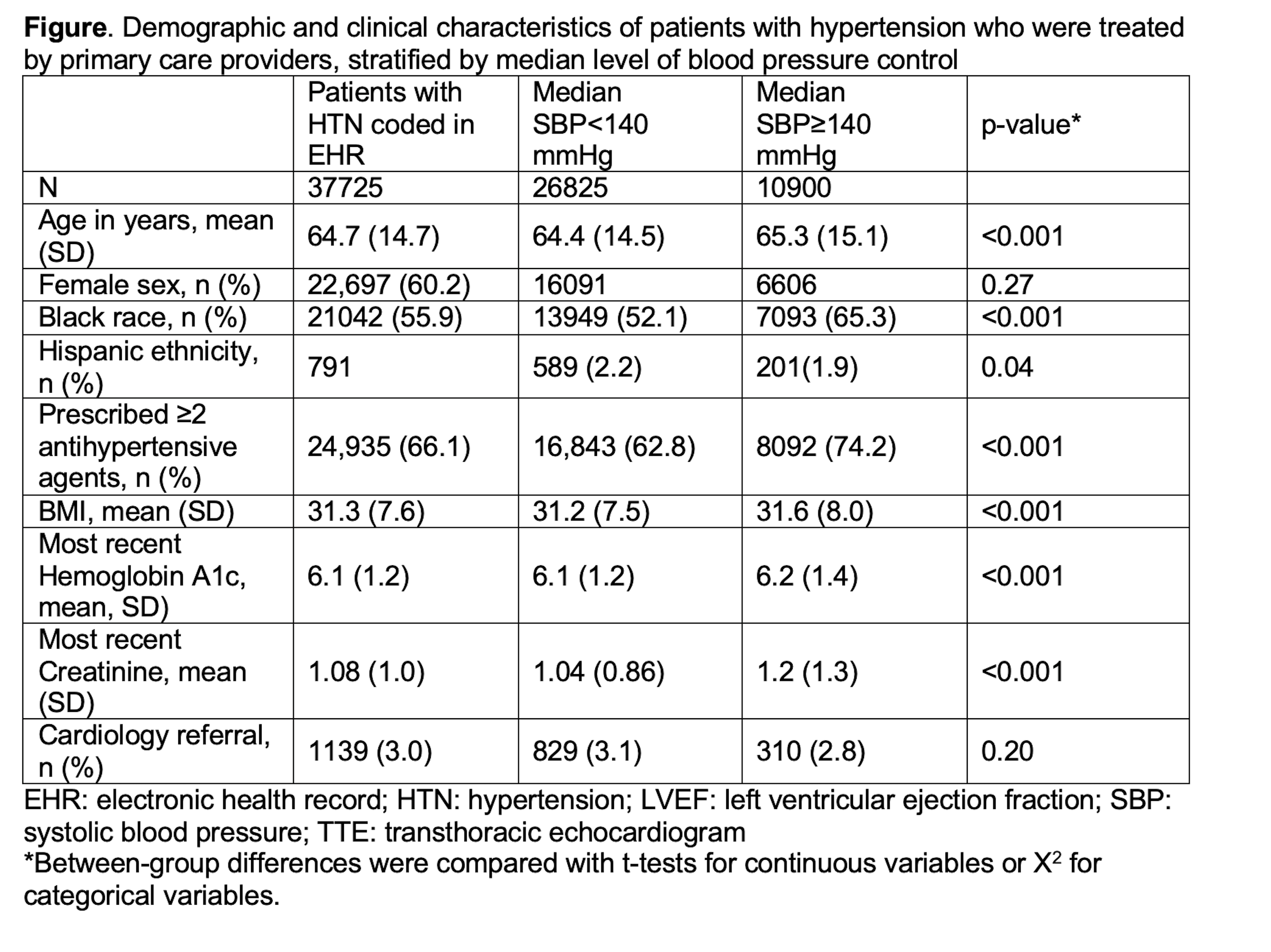
Results: Among our network of PCPs, there were 76039 patients with BP data and 37725 (49.6%) had a visit coded for HTN. Of those with HTN, 10900 (28.9%) had a median systolic BP≥140 mmHg and 3802 (10.1%) had SBP≥150 mmHg. The Figure provides our findings in detail. Calcium channel blockers and thiazides were the most prescribed drug classes. Only 1139 (3%) patients completed a cardiology referral during the study period, and BP was lower among those seen by cardiology (mean SBP at end of study period 126 vs 141 mmHg for those seen by cardiology versus not, p<0.001).
Conclusions: We used MDClone to assess HTN care among a PCP cohort. We found overall poor BP control and identified therapeutic opportunities to potentially reduce risk of renal and cardiovascular disease. After EHR interrogation with MDClone, we determined real time provider-level solutions to enhance the quality of care. Next steps will include providing data to each PCP. If scaled across a health system, such analytics could efficiently inform patient monitoring, medication titration, and multidisciplinary referral.
Objective: Use a novel data exploration platform to rapidly identify opportunities for improved BP management among PCPs at an academic health system.
MethodsIn this observational quality improvement analysis, we reviewed electronic health record (EHR) data using a cloud-based, machine-learning platform, MDClone ADAMS (2024) to assess outpatient HTN management at the University of Chicago (112 PCPs, 23 clinics). Between January 2022-March 2025, we identified hypertensive patients who had been clinically evaluated by PCPs. Patient-level variables were extracted from the EHR including current age; sex; race; systolic and diastolic BP during the study period; antihypertensive drug class and dose; serum creatinine; and referrals to specialists (cardiology, nephrology). Between-group differences were compared with t-tests or X2 using a 2-sided significance level of 0.05. The project was IRB exempt.
Results: Among our network of PCPs, there were 76039 patients with BP data and 37725 (49.6%) had a visit coded for HTN. Of those with HTN, 10900 (28.9%) had a median systolic BP≥140 mmHg and 3802 (10.1%) had SBP≥150 mmHg. The Figure provides our findings in detail. Calcium channel blockers and thiazides were the most prescribed drug classes. Only 1139 (3%) patients completed a cardiology referral during the study period, and BP was lower among those seen by cardiology (mean SBP at end of study period 126 vs 141 mmHg for those seen by cardiology versus not, p<0.001).
Conclusions: We used MDClone to assess HTN care among a PCP cohort. We found overall poor BP control and identified therapeutic opportunities to potentially reduce risk of renal and cardiovascular disease. After EHR interrogation with MDClone, we determined real time provider-level solutions to enhance the quality of care. Next steps will include providing data to each PCP. If scaled across a health system, such analytics could efficiently inform patient monitoring, medication titration, and multidisciplinary referral.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Hospital-Wide Multidimensional Approach to Pediatric In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest Review: Early Identification and Prevention
Loeb Daniel, Collins Kelly, Ortega Karina, Dewan Maya
A Delayed Diagnosis of Anti-HMG-CoA Reductase Immune-Mediated Necrotizing MyopathyJadhav Reshma, Shekar Arush, Westenhaver Zack, Skandhan Amith