Final ID: MP1870
Plasma Protein N-Glycosylation Profiles Are Associated with Future Cardiovascular Events: Analyses from the JUPITER and TNT Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Glycosylation—a key post-translational modification—plays a critical role in biological pathways of atherosclerosis. We previously demonstrated associations between N-glycosylation of immunoglobulin G and cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, the relationship between N-glycosylation of other plasma proteins and CVD remains largely unexplored.
Methods: We analyzed N-glycosylation of baseline plasma proteins using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography in two nested case-control studies of incident CVD: JUPITER (NCT00239681; 513 pairs; primary prevention) and TNT (NCT00327691; 436 pairs; secondary prevention). We used conditional logistic regression to evaluate associations between 39 measured chromatographic N-glycan peaks (GP1-39) and incident CVD. The fully adjusted model accounted for age, sex, race, LDL, HDL, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, hs-CRP, BMI, aspirin use, and treatment assignment. We then performed a fixed-effects meta-analysis to combine effect estimates across cohorts. Using stepwise regression, we derived a glycan score in JUPITER and validated it in TNT. We also performed Spearman correlations between N-glycans and clinical biomarkers.
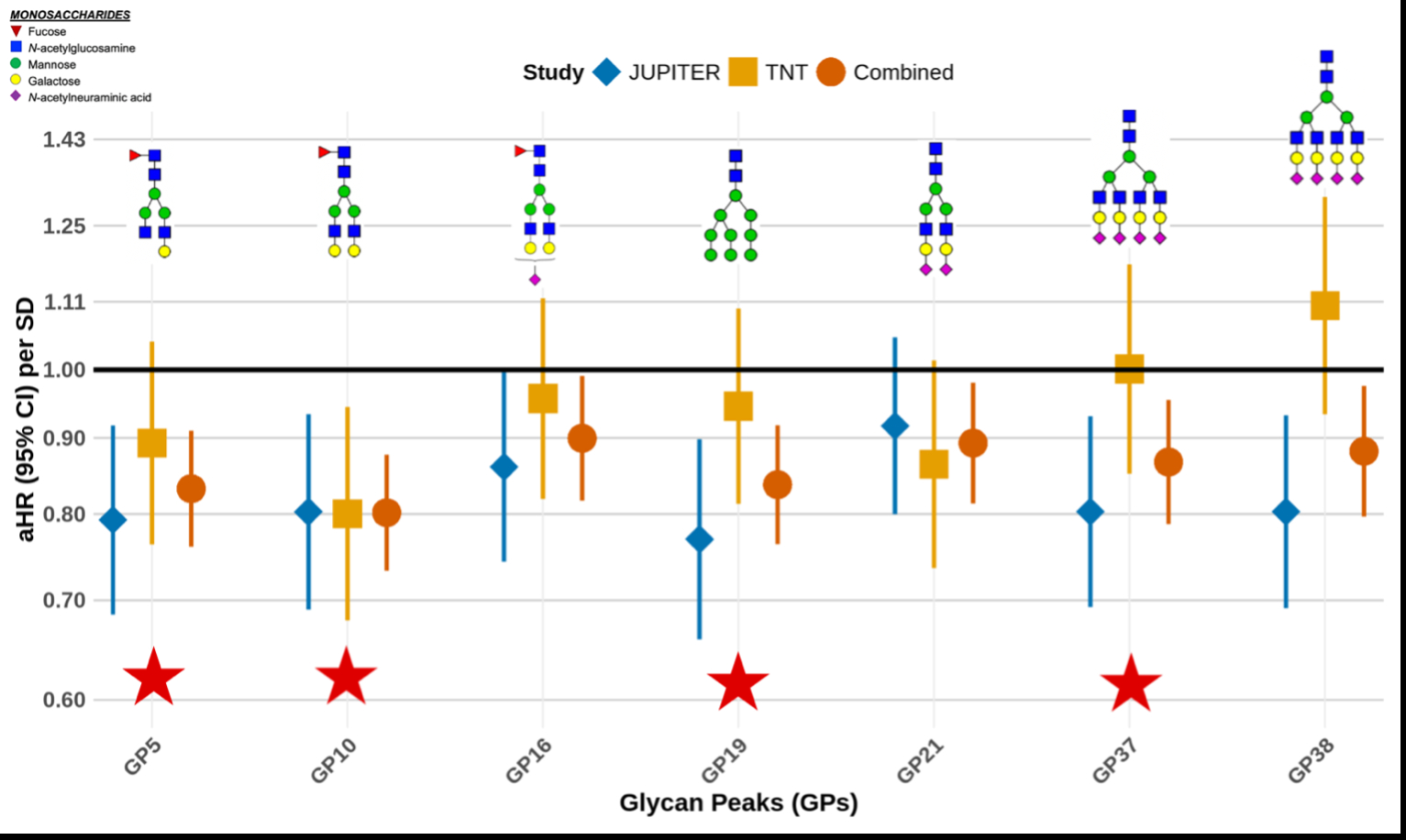
Results: The meta-analysis identified specific N-glycosylation patterns independently associated with CVD. These included mono- and digalactosylated glycans with core fucose (GP5,10), a tetragalactosylated tetrasialylated glycan (GP37), and an oligomannose glycan (GP19), all inversely associated with CVD in the fully adjusted model (aHR per SD:0.80–0.90; FDR<0.05) (Figure 1).
In contrast, antennary fucosylated glycans (GP27,33,39) were positively associated with CVD in the baseline model accounted for age, sex, and treatment assignment (FDR<0.05), but these associations lost significance after adjusting for inflammatory covariates. Notably, all three antennary fucosylated structures were positively correlated with hs-CRP in both cohorts (FDR<0.05), suggesting a potential link to inflammation-mediated CVD risk.
A glycan score of seven GPs was associated with increased CVD risk in JUPITER (aHR per SD:1.91; 95%CI:1.59–2.30; P<0.001), independent of other risk factors, and validated in TNT (P=0.03). It improved the AUC from 0.73 to 0.76 in JUPITER (P<0.001) and from 0.66 to 0.67 in TNT (P=0.03).
Conclusion: Specific N-glycosylation profiles of plasma proteins are associated with future CVD events. Furthermore, a composite glycan score enhanced CVD risk prediction beyond established risk factors.
Methods: We analyzed N-glycosylation of baseline plasma proteins using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography in two nested case-control studies of incident CVD: JUPITER (NCT00239681; 513 pairs; primary prevention) and TNT (NCT00327691; 436 pairs; secondary prevention). We used conditional logistic regression to evaluate associations between 39 measured chromatographic N-glycan peaks (GP1-39) and incident CVD. The fully adjusted model accounted for age, sex, race, LDL, HDL, hypertension, diabetes, smoking, hs-CRP, BMI, aspirin use, and treatment assignment. We then performed a fixed-effects meta-analysis to combine effect estimates across cohorts. Using stepwise regression, we derived a glycan score in JUPITER and validated it in TNT. We also performed Spearman correlations between N-glycans and clinical biomarkers.
Results: The meta-analysis identified specific N-glycosylation patterns independently associated with CVD. These included mono- and digalactosylated glycans with core fucose (GP5,10), a tetragalactosylated tetrasialylated glycan (GP37), and an oligomannose glycan (GP19), all inversely associated with CVD in the fully adjusted model (aHR per SD:0.80–0.90; FDR<0.05) (Figure 1).
In contrast, antennary fucosylated glycans (GP27,33,39) were positively associated with CVD in the baseline model accounted for age, sex, and treatment assignment (FDR<0.05), but these associations lost significance after adjusting for inflammatory covariates. Notably, all three antennary fucosylated structures were positively correlated with hs-CRP in both cohorts (FDR<0.05), suggesting a potential link to inflammation-mediated CVD risk.
A glycan score of seven GPs was associated with increased CVD risk in JUPITER (aHR per SD:1.91; 95%CI:1.59–2.30; P<0.001), independent of other risk factors, and validated in TNT (P=0.03). It improved the AUC from 0.73 to 0.76 in JUPITER (P<0.001) and from 0.66 to 0.67 in TNT (P=0.03).
Conclusion: Specific N-glycosylation profiles of plasma proteins are associated with future CVD events. Furthermore, a composite glycan score enhanced CVD risk prediction beyond established risk factors.
More abstracts on this topic:
A DHX38 Spliceosomal Mutation Impairs MYC Signaling, Cardiac Transcriptome Splicing, and Leads to Diastolic Dysfunction
Iwanski Jessika, Sarvagalla Sailu, Methawasin Mei, Van Den Berg Marloes, Churko Jared
Apolipoprotein A-I Proteoforms, Cardiometabolic Status, and Coronary Heart Disease: Insights from the Dallas Heart StudyGangwar Anamika, Des Soye Benjamin, Saldanha Suzanne, Jaiswal Shailesh, Patel Parthvi Bharatkumar, Shah Amil, Pandey Ambarish, Wilkins John, Rohatgi Anand