Final ID: MP2195
Using Machine Learning Methods to Predict Adverse Events in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Cardiovascular risk models generally use standard statistical methods that limit their performance for common outcomes and don’t allow for prediction of rare outcomes. Machine learning methods may address these shortcomings. The objective of this study was to determine how performance would vary across methods for prediction of in-hospital clinical events in the NCDR Left Atrial Appendage Occlusion (LAAO) Registry.
Methods: Using data from the LAAO Registry, logistic regression (LR), LASSO, and XG Boost were used to predict the combined outcome of all major in-hospital adverse events (MAE), as well as 11 individual events for patients undergoing transcatheter LAAO. Randomly selected 70% development and 30% validation cohorts were used for model creation and to assess performance. Models were assessed using the 16 original variables used in the previously developed logistic regression risk model and with an expanded list of 51 total variables.
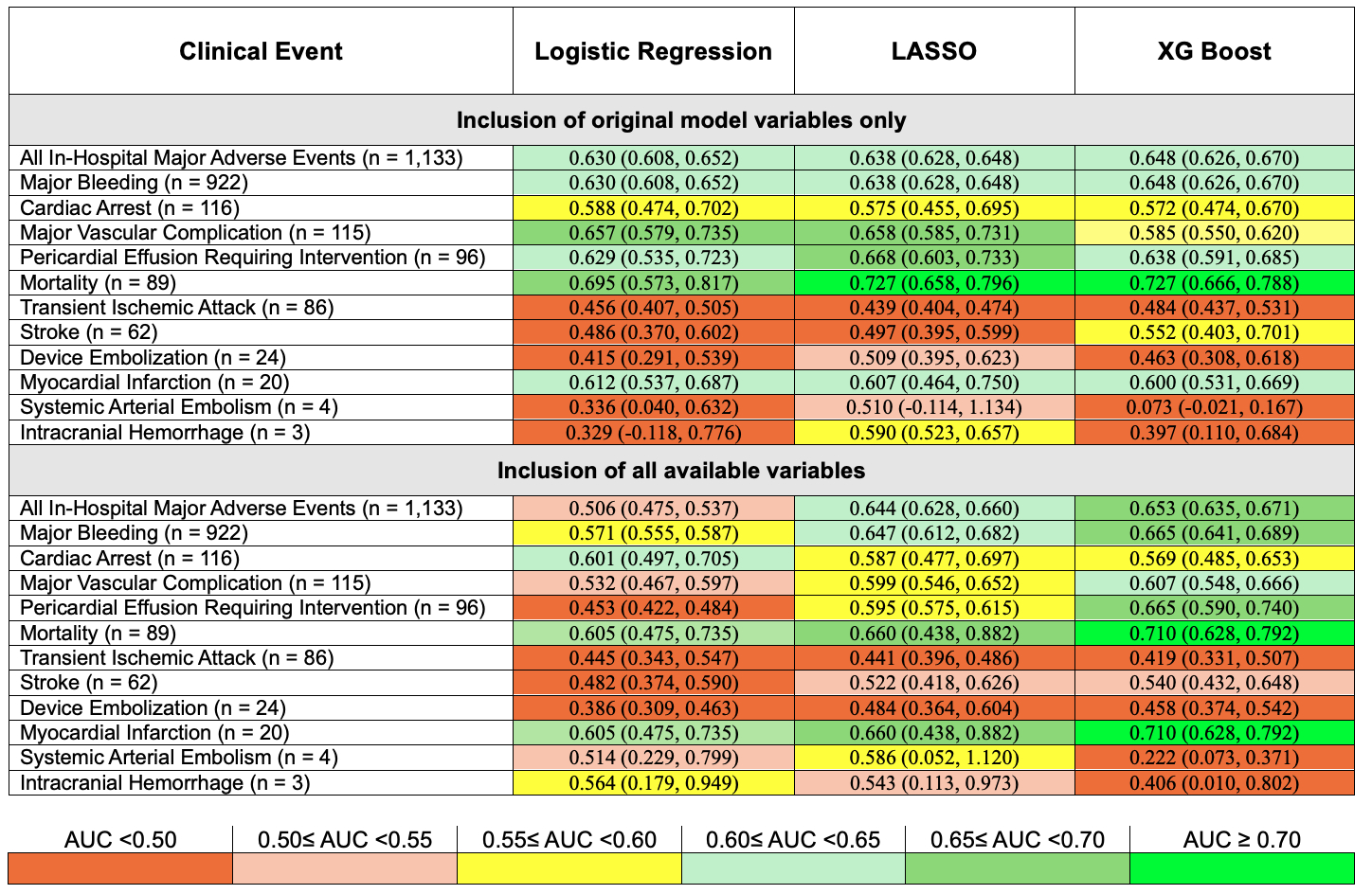
Results: The development cohort included data from 57,192 transcatheter LAAO procedures performed with the Watchman FLX device, and the validation cohort included 24,511 procedures. The overall incidence rate for the composite of all MAE was 1.39%, with rates for individual events ranging from <0.01% up to 1.13%. XG Boost had the best performance for combined MAE using original model variables in the validation cohort (AUC 0.648 [95% CI 0.626-0.670] vs. 0.630 [95% CI 0.608-0.642] for LR and 0.638 [95% CI 0.626-0.670] for LASSO). When an expanded list of candidate variables were included, XG Boost (AUC 0.653 [95% CI 0.635-0.671]) performed marginally better than LASSO (AUC 0.644 [95% CI 0.628-0.660]) for MAE in the validation cohort, whereas LR performed poorly (AUC 0.515 [95% CI 0.501-0.529]). Performance across all methods declined and was generally worse for most infrequent events (Figure). XG Boost generally outperformed the other model types and performed better with an expanded list of variables, but this was not consistently the case, particularly for very rare events. However, prediction of mortality using XG Boost was incrementally better.
Conclusions: In a nationwide registry cohort, the XG Boost machine learning method improved prediction of a composite of all MAE and several individual events over standard methods, particularly when using an expanded list of variables. Prediction of rare mortality events was also improved, although this was not consistently the case for other rare outcomes.
Methods: Using data from the LAAO Registry, logistic regression (LR), LASSO, and XG Boost were used to predict the combined outcome of all major in-hospital adverse events (MAE), as well as 11 individual events for patients undergoing transcatheter LAAO. Randomly selected 70% development and 30% validation cohorts were used for model creation and to assess performance. Models were assessed using the 16 original variables used in the previously developed logistic regression risk model and with an expanded list of 51 total variables.
Results: The development cohort included data from 57,192 transcatheter LAAO procedures performed with the Watchman FLX device, and the validation cohort included 24,511 procedures. The overall incidence rate for the composite of all MAE was 1.39%, with rates for individual events ranging from <0.01% up to 1.13%. XG Boost had the best performance for combined MAE using original model variables in the validation cohort (AUC 0.648 [95% CI 0.626-0.670] vs. 0.630 [95% CI 0.608-0.642] for LR and 0.638 [95% CI 0.626-0.670] for LASSO). When an expanded list of candidate variables were included, XG Boost (AUC 0.653 [95% CI 0.635-0.671]) performed marginally better than LASSO (AUC 0.644 [95% CI 0.628-0.660]) for MAE in the validation cohort, whereas LR performed poorly (AUC 0.515 [95% CI 0.501-0.529]). Performance across all methods declined and was generally worse for most infrequent events (Figure). XG Boost generally outperformed the other model types and performed better with an expanded list of variables, but this was not consistently the case, particularly for very rare events. However, prediction of mortality using XG Boost was incrementally better.
Conclusions: In a nationwide registry cohort, the XG Boost machine learning method improved prediction of a composite of all MAE and several individual events over standard methods, particularly when using an expanded list of variables. Prediction of rare mortality events was also improved, although this was not consistently the case for other rare outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Machine Learning-based Adverse Cardiovascular Events Risk Algorithm For Cancer Patients Treated With Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Wahi Shawn, Cross James, Mora Ruben, Im Yunju, Kwan Jennifer
A Two-year Longitudinal Investigation of Lipoprotein Particle Profile as Cardiometabolic Risk Biomarkers in Family Caregivers of Adult Patients with CancerLee Lena, Shamburek Robert, Son Elisa H, Wallen Gwenyth, Yang Li, Tuason Ralph, Gerrard Chantal, Tsai Thomas, Kim Youngmee