Final ID: Su3026
Trends in Mortality of Ischemic Heart Disease and Cardiac Arrhythmias in the Adult Population: CDC Data Analysis (1999–2020)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD), primarily due to cardiac arrhythmias. An estimated 180,000–450,000 SCDs occur annually in the U.S. This study analyzes CDC data (1999–2020) to assess long-term mortality trends and disparities by demographics, sex, and region to inform public health strategies.
Methods:
CDC WONDER data for adults aged 25–85+ were analyzed. Deaths were identified using ICD-10 codes I20–I25 (IHD) and I47–I49 (Re-entry ventricular arrhythmias, atrial and ventricular fibrillation and flutter). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 were stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, census region, state, and urbanization. Trends were assessed using Joinpoint regression. Annual percentage changes (APC) were estimated via Monte Carlo permutation with 95% confidence intervals using the Parametric Method. Two-tailed t-tests tested significance.
Results:
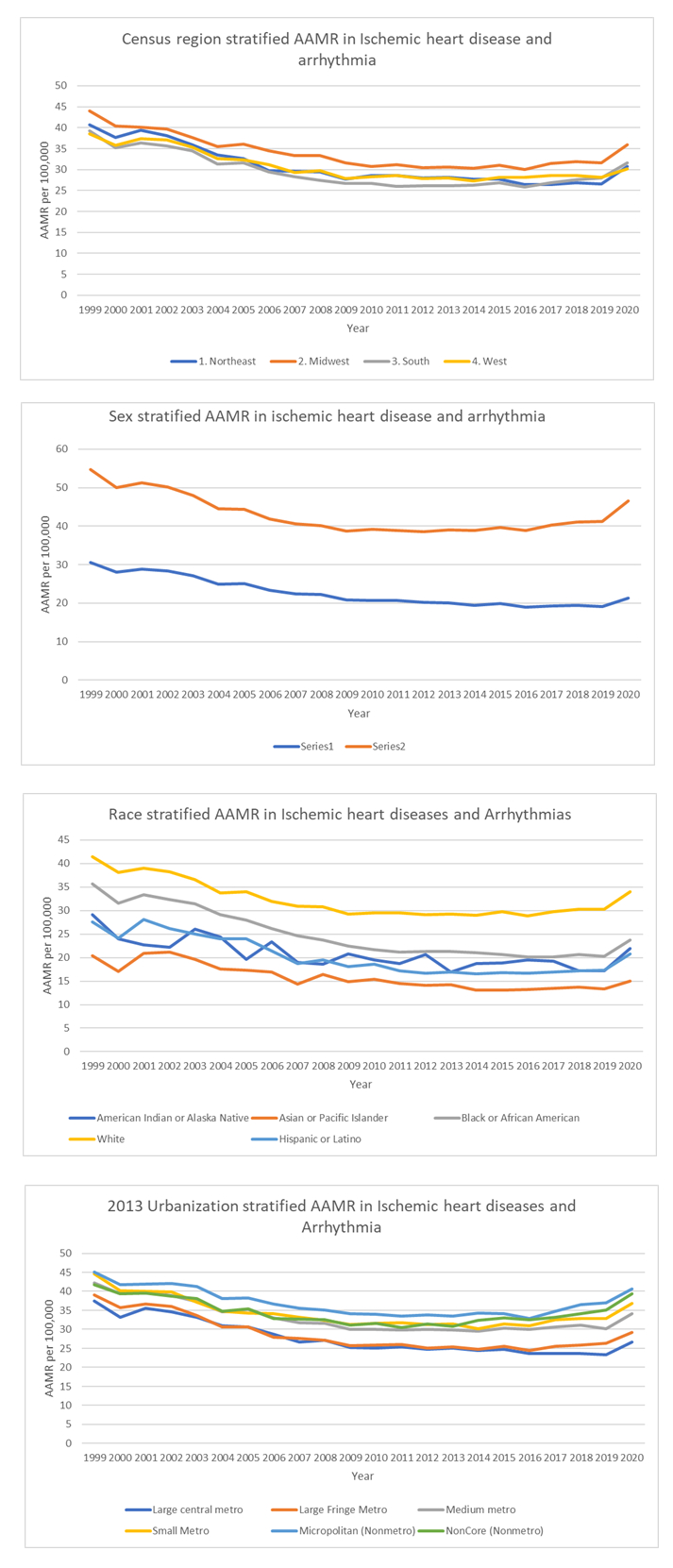
From 1999–2020, arrhythmia-related IHD mortality (ages 25–85+) showed fluctuations across demographics. Overall AAMR declined slightly from 39.58 in 1999 to 38.08 in 2020. In females, AAMR declined from 1999–2018 (APC = -3.52 to -1.02). In males, mortality dropped from 1999–2009 (APC = -3.35), then rose through 2018 (APC = 0.45). From 2018–2020, AAMR increased sharply—males (APC = 7.01), females (APC = 4.95). All racial groups showed varying trends, except American Indians, who had a consistent decline (APC = -1.40). The largest rise from 2018–2020 occurred among Black or African Americans (APC = 7.75), followed by Whites (APC = 6.54). Regionally, AAMRs declined in the West, Midwest, and South until 2010 (APC = -3.06, -2.99, -3.58), and in the Northeast through 2018 (APC = -4.11 to -1.09). From 2018–2020, the South saw the largest increase (APC = 7.73), and the West the smallest (APC = 0.48). Large metro areas experienced a steady decline, slowing after 2010 (APC = -3.65 to -0.18). Other regions saw increases in the second decade, with the highest in noncore (APC = 7.92) and large fringe metro areas (APC = 7.35) (2018-2020). State-level data showed highest AAMRs in Washington and North Dakota (35.18–47.21), and lowest in Arizona and Nevada (16.58–24.23).
Conclusion:
After 2018, arrhythmia-related IHD mortality rose across most groups. Males, Black individuals, Southern residents, and those in noncore/fringe metro areas were most affected. These trends highlight the need for targeted public health efforts to reduce disparities and improve outcomes.
Ischemic heart disease (IHD) is the leading cause of Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD), primarily due to cardiac arrhythmias. An estimated 180,000–450,000 SCDs occur annually in the U.S. This study analyzes CDC data (1999–2020) to assess long-term mortality trends and disparities by demographics, sex, and region to inform public health strategies.
Methods:
CDC WONDER data for adults aged 25–85+ were analyzed. Deaths were identified using ICD-10 codes I20–I25 (IHD) and I47–I49 (Re-entry ventricular arrhythmias, atrial and ventricular fibrillation and flutter). Age-adjusted mortality rates (AAMR) per 100,000 were stratified by sex, race/ethnicity, census region, state, and urbanization. Trends were assessed using Joinpoint regression. Annual percentage changes (APC) were estimated via Monte Carlo permutation with 95% confidence intervals using the Parametric Method. Two-tailed t-tests tested significance.
Results:
From 1999–2020, arrhythmia-related IHD mortality (ages 25–85+) showed fluctuations across demographics. Overall AAMR declined slightly from 39.58 in 1999 to 38.08 in 2020. In females, AAMR declined from 1999–2018 (APC = -3.52 to -1.02). In males, mortality dropped from 1999–2009 (APC = -3.35), then rose through 2018 (APC = 0.45). From 2018–2020, AAMR increased sharply—males (APC = 7.01), females (APC = 4.95). All racial groups showed varying trends, except American Indians, who had a consistent decline (APC = -1.40). The largest rise from 2018–2020 occurred among Black or African Americans (APC = 7.75), followed by Whites (APC = 6.54). Regionally, AAMRs declined in the West, Midwest, and South until 2010 (APC = -3.06, -2.99, -3.58), and in the Northeast through 2018 (APC = -4.11 to -1.09). From 2018–2020, the South saw the largest increase (APC = 7.73), and the West the smallest (APC = 0.48). Large metro areas experienced a steady decline, slowing after 2010 (APC = -3.65 to -0.18). Other regions saw increases in the second decade, with the highest in noncore (APC = 7.92) and large fringe metro areas (APC = 7.35) (2018-2020). State-level data showed highest AAMRs in Washington and North Dakota (35.18–47.21), and lowest in Arizona and Nevada (16.58–24.23).
Conclusion:
After 2018, arrhythmia-related IHD mortality rose across most groups. Males, Black individuals, Southern residents, and those in noncore/fringe metro areas were most affected. These trends highlight the need for targeted public health efforts to reduce disparities and improve outcomes.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Measurement Model of Socioeconomic Status and its Association with Cardiovascular Disease in the Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos
Cordero Christina, Llabre Maria, Romaker Emma, Kobayashi Marissa, Gianola Morgan, Gallo Linda, Isasi Carmen, Perreira Krista, Corsino Leonor, Zhou Laura
Automated Personalized Modulation of the Sympathetic “fight-or-flight” Reflex In Vivo Using Implantable Microdevices for Enhancing Neurocardiac Function and Reducing Mortality Risk.Kundu Dibyasankha, Hazra Debapriya, Mukherjee Shayani, Jones Steven, Dey Swati, Demazumder Deeptankar