Final ID: MP1584
Early Versus Late Initiation of Oral Anticoagulants After Ischemic Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is present in approximately 20% of ischemic stroke patients. While oral anticoagulants (OACs) are effective in reducing stroke risk, the optimal timing for initiating OACs after acute ischemic stroke remains uncertain, with varying recommendations across guidelines.
Hypothesis:
Early initiation of OACs following ischemic stroke in patients with AF is as safe and effective as late initiation in preventing recurrent ischemic events.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing early versus late OAC initiation in adults with AF and recent ischemic stroke. A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL was performed through October 2024. The primary outcome was recurrent ischemic stroke. Secondary outcomes included major extracranial bleeding, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), non-major bleeding, systemic embolism, and all-cause mortality. Risk ratios (RRs) were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results:
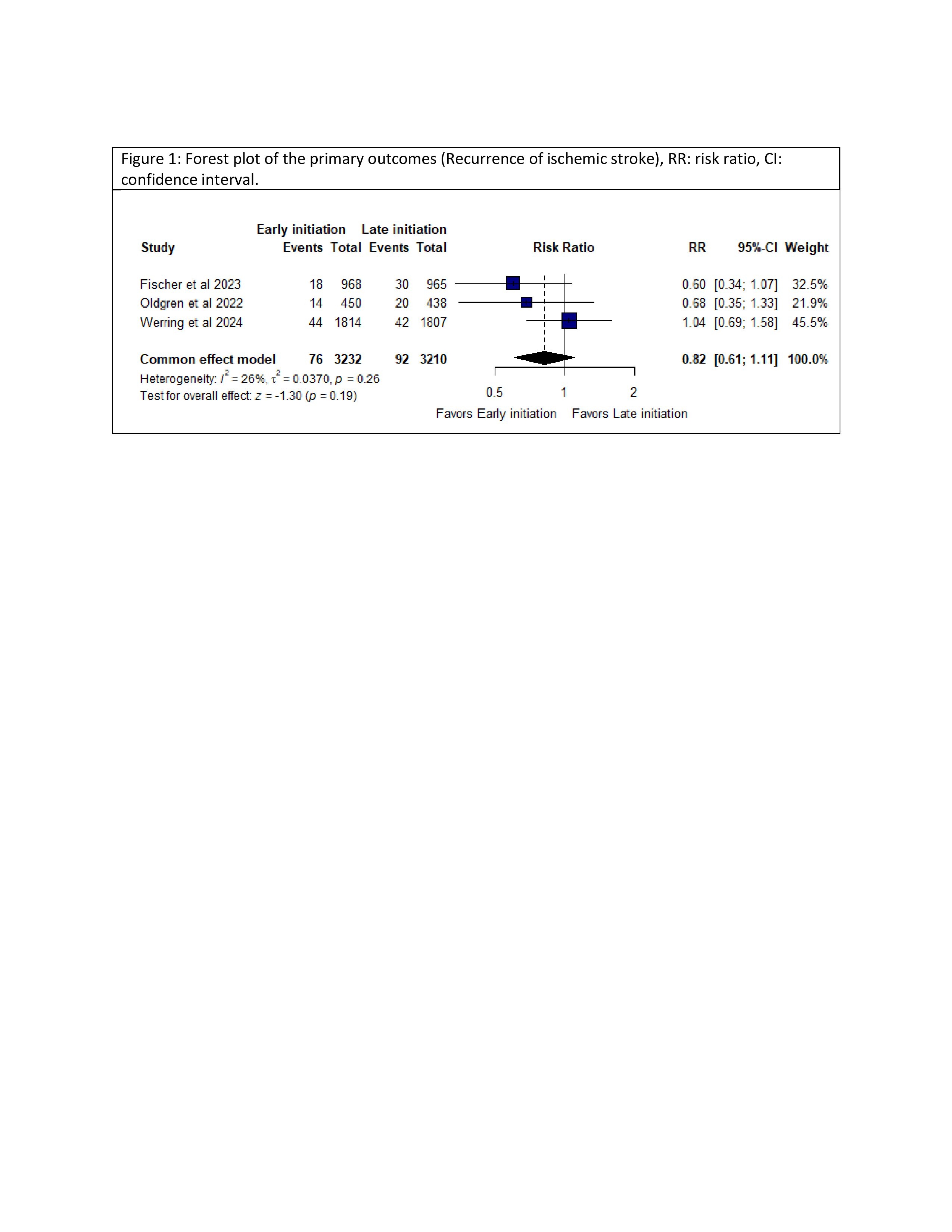
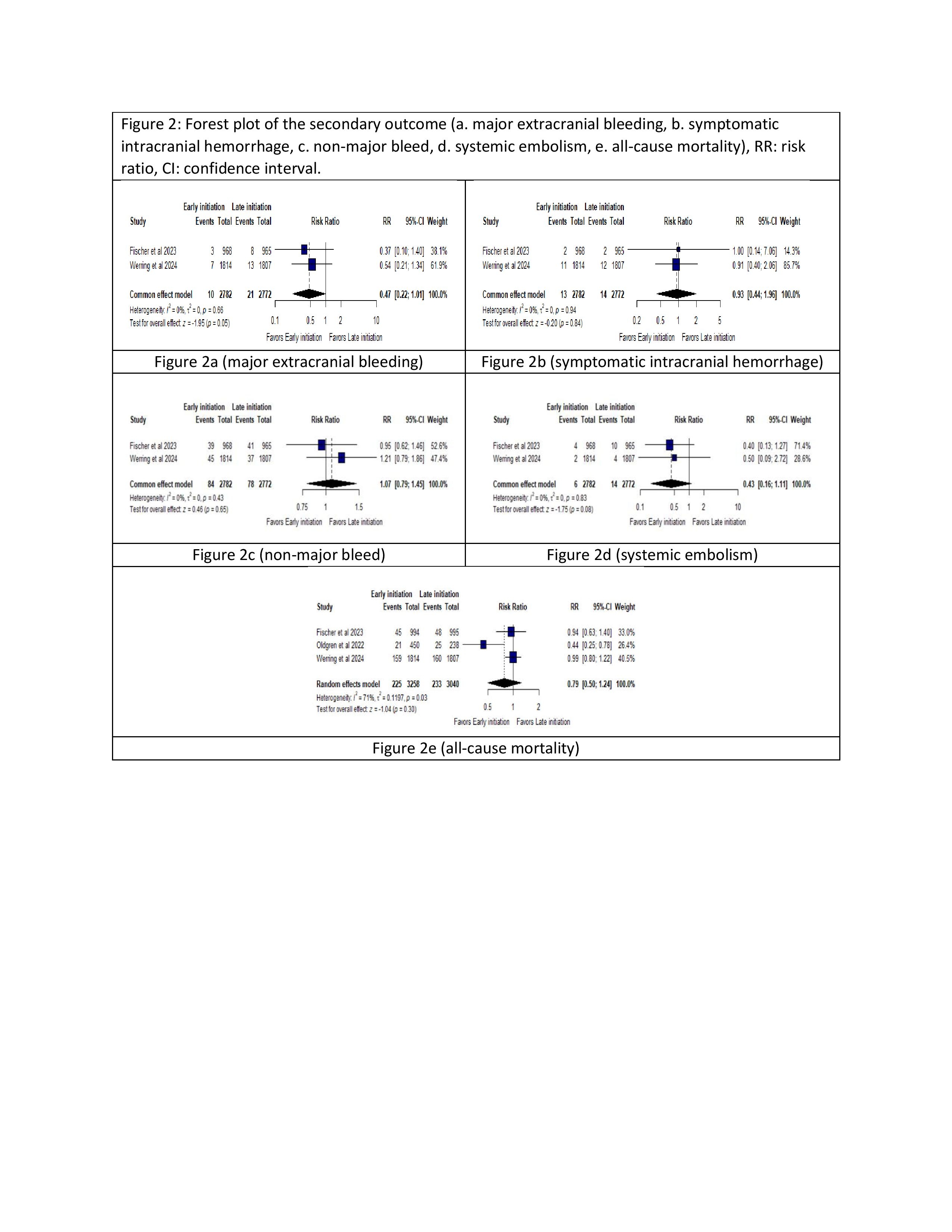
Three RCTs involving 6,522 patients were included. No significant difference was observed in recurrent ischemic stroke between early and late OAC initiation (RR: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.61–1.11; P=0.19). Similarly, no significant differences were seen in major extracranial bleeding (RR: 0.47; 95% CI: 0.22–1.01; P=0.05), sICH (RR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.44–1.96; P=0.84), non-major bleeding (RR: 1.07; 95% CI: 0.79–1.45; P=0.65), systemic embolism (RR: 0.43; 95% CI: 0.16–1.11; P=0.08), or all-cause mortality (RR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.50–1.24; P=0.30).
Conclusion:
Early initiation of OACs after ischemic stroke in patients with AF appears to be as safe as delayed initiation, with no increased risk of bleeding or mortality. Although the difference in efficacy was not statistically significant, the trend toward reduced stroke recurrence with early therapy supports further investigation. These findings may inform individualized decision-making in the acute stroke setting.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is present in approximately 20% of ischemic stroke patients. While oral anticoagulants (OACs) are effective in reducing stroke risk, the optimal timing for initiating OACs after acute ischemic stroke remains uncertain, with varying recommendations across guidelines.
Hypothesis:
Early initiation of OACs following ischemic stroke in patients with AF is as safe and effective as late initiation in preventing recurrent ischemic events.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing early versus late OAC initiation in adults with AF and recent ischemic stroke. A comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, EMBASE, and Cochrane CENTRAL was performed through October 2024. The primary outcome was recurrent ischemic stroke. Secondary outcomes included major extracranial bleeding, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH), non-major bleeding, systemic embolism, and all-cause mortality. Risk ratios (RRs) were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results:
Three RCTs involving 6,522 patients were included. No significant difference was observed in recurrent ischemic stroke between early and late OAC initiation (RR: 0.82; 95% CI: 0.61–1.11; P=0.19). Similarly, no significant differences were seen in major extracranial bleeding (RR: 0.47; 95% CI: 0.22–1.01; P=0.05), sICH (RR: 0.93; 95% CI: 0.44–1.96; P=0.84), non-major bleeding (RR: 1.07; 95% CI: 0.79–1.45; P=0.65), systemic embolism (RR: 0.43; 95% CI: 0.16–1.11; P=0.08), or all-cause mortality (RR: 0.79; 95% CI: 0.50–1.24; P=0.30).
Conclusion:
Early initiation of OACs after ischemic stroke in patients with AF appears to be as safe as delayed initiation, with no increased risk of bleeding or mortality. Although the difference in efficacy was not statistically significant, the trend toward reduced stroke recurrence with early therapy supports further investigation. These findings may inform individualized decision-making in the acute stroke setting.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Multi-Center Clinic Site Comparison of Patient-level factors Affecting Oral Anticoagulation Prescription for Atrial Fibrillation
Iqbal Fatima, Hoang Kenneth, Chiadika Simbo
Antithrombotic Strategies for Stroke Prevention in Elderly Patients with Atrial Fibrillation: A Meta-Analysis of Contemporary EvidenceFarooq Talha, Pandit Maleeha, Ali Mohammad Eisa, Ahsan Muhammad, Khan Abdul Moiz, Qasim Muhammad, Qayyum Mahhum, Akram Anusha, Kamel Mohammed, Naseem Ali