Final ID: MP806
Iron Deficiency And Quality Of Life In Patients With Chronic Heart Failure Treated With Liposomal Bivalent Stabilized Iron Sulfate
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): INTRODUCTION. Iron deficiency (ID), affecting up to 50% of Chronic Heart Failure (CHF) patients, is associated with higher mortality, worse symptoms, poorer quality of life and impaired exercise capacity.
Chronic inflammation in CHF promotes functional ID through elevated hepcidin levels, impairing iron availability and worsening anemia.
The stabilized bivalent liposomal iron (SBLI) bypasses the absorption channel blocked by hepcidin and is directly absorbed by enterocyte cells, allowing immediate and high bioavailability.
In previous trials, oral iron therapy has never demonstrated, unlike intravenous administration, an improvement in functional capacity and quality of life in these patients.
The aim of our study was to evaluate the efficacy of SBLI in increasing the availability of circulating iron, in patients with CHF, as well as its effects on quality of life.
METHODS. 59 patients (mean age 68±12 years) with CHF and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fraction and confirmed ID were enrolled in the study. ID was defined as ferritin levels <100 μg/L or ferritin levels of 100 to 299 μg/L along with Transferrin Saturation (TSAT)<20%.
Patients were randomized in a double-blind manner to receive SBLI (30 mg twice daily for 1 month, then once daily for an additional 2 months) or placebo. Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) scores were acquired at baseline and after three months of therapy.
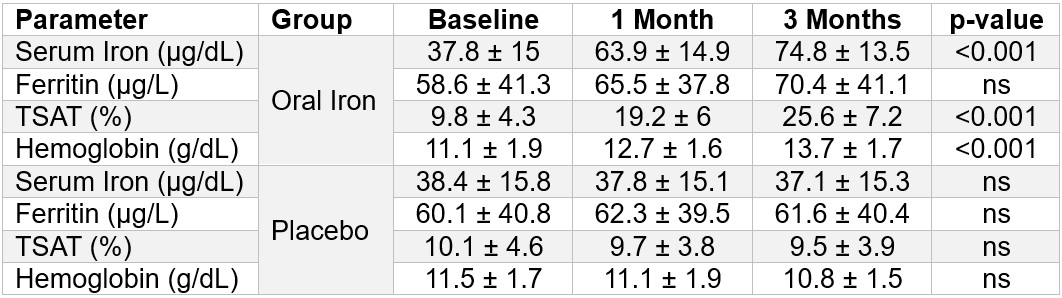
RESULTS. Baseline characteristics and blood parameters were similar in both groups and all patients were on optimal medical therapy. Blood parameters are reported in Table 1.
KCCQ Overall Summary Score significantly improved, in the treatment arm, from 48.9±18.50 to 62.1±13.8 (p<0.001), but not in the placebo arm (from 48.1±16.9 to 50.2±12.2, p=0.06).
CONCLUSIONS. The positive impact of oral SBLI on iron balance and quality of life underscores its potential as a therapeutic intervention for CHF patients with ID.
Its ability to bypass the hepcidin-mediated absorption block allows for a more effective increase in iron balance compared to other formulations. It increases iron bioavailability instead than quick iron storage, avoiding elevated risk of oxidative stress, membrane damage and ferroptotic cell death. It also represents an excellent therapeutic choice in terms of cost-effectiveness.
This clinical trial is the first to show that oral SBLI therapy improves quality of life in CHF patients as well as iron bioavailability. Future research can validate these findings.
Chronic inflammation in CHF promotes functional ID through elevated hepcidin levels, impairing iron availability and worsening anemia.
The stabilized bivalent liposomal iron (SBLI) bypasses the absorption channel blocked by hepcidin and is directly absorbed by enterocyte cells, allowing immediate and high bioavailability.
In previous trials, oral iron therapy has never demonstrated, unlike intravenous administration, an improvement in functional capacity and quality of life in these patients.
The aim of our study was to evaluate the efficacy of SBLI in increasing the availability of circulating iron, in patients with CHF, as well as its effects on quality of life.
METHODS. 59 patients (mean age 68±12 years) with CHF and reduced or mildly reduced ejection fraction and confirmed ID were enrolled in the study. ID was defined as ferritin levels <100 μg/L or ferritin levels of 100 to 299 μg/L along with Transferrin Saturation (TSAT)<20%.
Patients were randomized in a double-blind manner to receive SBLI (30 mg twice daily for 1 month, then once daily for an additional 2 months) or placebo. Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) scores were acquired at baseline and after three months of therapy.
RESULTS. Baseline characteristics and blood parameters were similar in both groups and all patients were on optimal medical therapy. Blood parameters are reported in Table 1.
KCCQ Overall Summary Score significantly improved, in the treatment arm, from 48.9±18.50 to 62.1±13.8 (p<0.001), but not in the placebo arm (from 48.1±16.9 to 50.2±12.2, p=0.06).
CONCLUSIONS. The positive impact of oral SBLI on iron balance and quality of life underscores its potential as a therapeutic intervention for CHF patients with ID.
Its ability to bypass the hepcidin-mediated absorption block allows for a more effective increase in iron balance compared to other formulations. It increases iron bioavailability instead than quick iron storage, avoiding elevated risk of oxidative stress, membrane damage and ferroptotic cell death. It also represents an excellent therapeutic choice in terms of cost-effectiveness.
This clinical trial is the first to show that oral SBLI therapy improves quality of life in CHF patients as well as iron bioavailability. Future research can validate these findings.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case of Concomitant Wild-Type Transthyretin and Systemic Light Chain Amyloidosis Involving Separate Organs
Chiu Leonard, Afrough Aimaz, Nadeem Urooba, Jebakumar Deborah, Grodin Justin
Cardiac RBFOX1 Deficiency Enhances Glucose and Ketone Metabolism and Provides Tolerance Against Ischemia Reperfusion InjuryTejay Saymon, Michelakis Evangelos, Hannington Patrick, Ussher John, Sutendra Gopinath, Chan Jordan, Wagg Cory, Nanoa Joseph, Lorenzana Maria Areli, Liu Yongsheng, Zhao Yuan Yuan, Hambrook Jacob, Bowhay Christina