Final ID: VD3
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 contributes to abdominal aortic aneurysm through accelerating smooth muscle cell metabolic reprogramming and NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a severe aortic disease, with a significantly high mortality rate if ruptured. Understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying disease progression is crucial to optimize therapeutic strategies. Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4 (PDK4) is an important mitochondrial matrix enzyme in cellular metabolism. We explored the role of PDK4 in AAA development, focusing on its effects on vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs).
Methods: We reanalyzed single-cell RNA sequencing datasets of multiple tissues and cell types to determine the PDK4 expression abundance in human AAA tissues and measured PDK4 expression in human and mouse AAA tissues. The role of PDK4 in AAA development was evaluated in VSMC-specific PDK4 knockout mice using an AAV-PCSK9DY/Ang II-induced AAA model. Seahorse analysis was used to assess oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis levels. RNA sequencing and mitochondrial functional analyses were performed to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying PDK4 action.
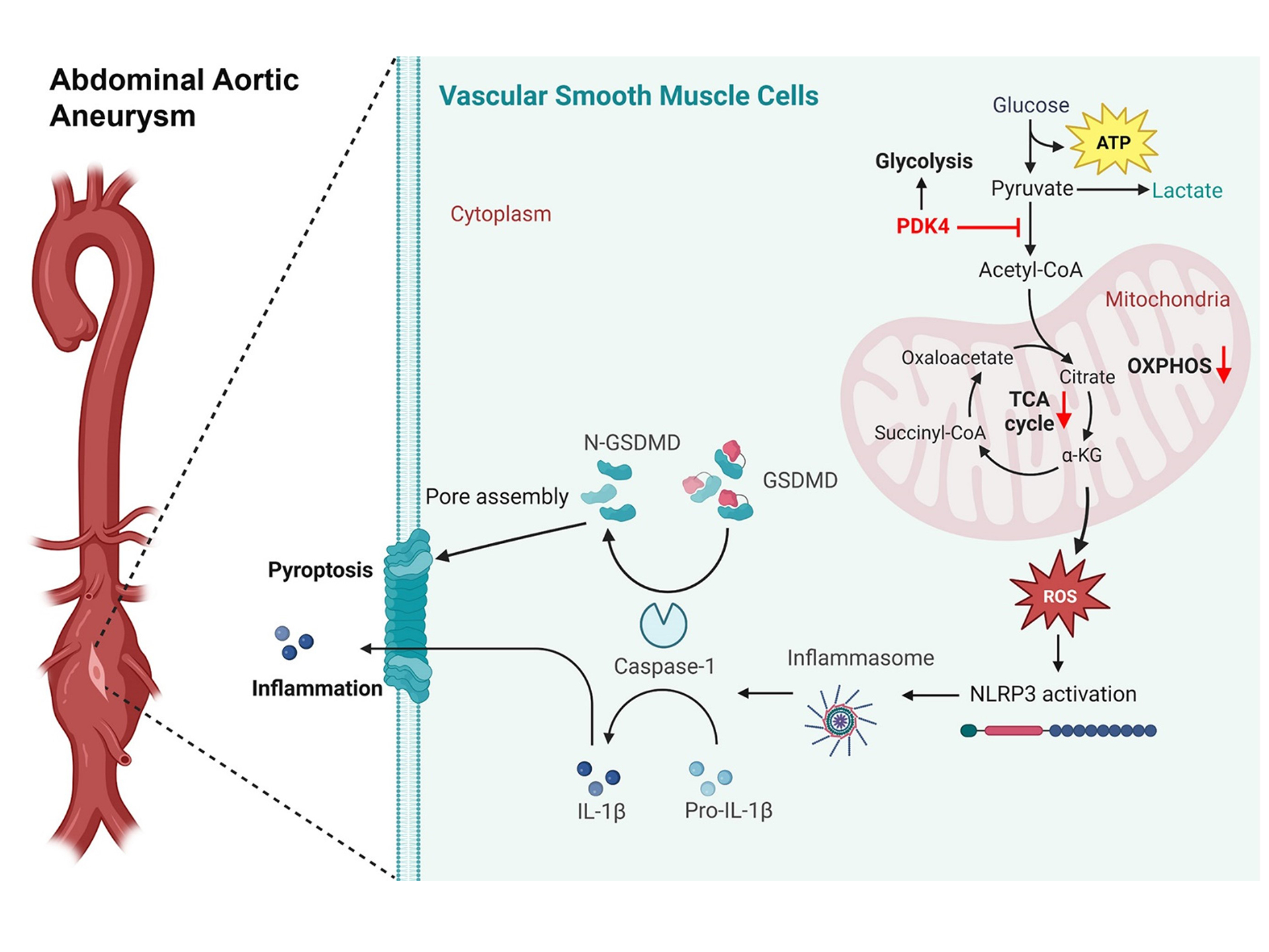
Results: Increased VSMC-PDK4 expression was observed in human AAA tissues and those from an AAV-PCSK9DY/Ang II-induced AAA mouse model. PDK4 deficiency in VSMCs significantly inhibited AAA formation, whereas PDK4 overexpression promoted AAA development. VSMC-specific PDK4 deletion ameliorated the contractile-to-synthetic phenotype switch in VSMCs. Moreover, PDK4 promoted metabolic reprogramming and activated the nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome by impairing mitochondrial function, contributing to VSMC pyroptosis and triggering an inflammatory response. Mitochondria-targeted reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavengers and the NLRP3 inhibitor, MCC950, effectively attenuated PDK4-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Furthermore, MCC950 supplementation ameliorated AAA progression in mice with PDK4 overexpression.
Conclusion: PDK4 promoted VSMC metabolic reprogramming and NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis, contributing to AAA development. Targeting PDK4 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for AAA prevention and treatment.
Methods: We reanalyzed single-cell RNA sequencing datasets of multiple tissues and cell types to determine the PDK4 expression abundance in human AAA tissues and measured PDK4 expression in human and mouse AAA tissues. The role of PDK4 in AAA development was evaluated in VSMC-specific PDK4 knockout mice using an AAV-PCSK9DY/Ang II-induced AAA model. Seahorse analysis was used to assess oxidative phosphorylation and glycolysis levels. RNA sequencing and mitochondrial functional analyses were performed to explore the molecular mechanisms underlying PDK4 action.
Results: Increased VSMC-PDK4 expression was observed in human AAA tissues and those from an AAV-PCSK9DY/Ang II-induced AAA mouse model. PDK4 deficiency in VSMCs significantly inhibited AAA formation, whereas PDK4 overexpression promoted AAA development. VSMC-specific PDK4 deletion ameliorated the contractile-to-synthetic phenotype switch in VSMCs. Moreover, PDK4 promoted metabolic reprogramming and activated the nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome by impairing mitochondrial function, contributing to VSMC pyroptosis and triggering an inflammatory response. Mitochondria-targeted reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavengers and the NLRP3 inhibitor, MCC950, effectively attenuated PDK4-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis. Furthermore, MCC950 supplementation ameliorated AAA progression in mice with PDK4 overexpression.
Conclusion: PDK4 promoted VSMC metabolic reprogramming and NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis, contributing to AAA development. Targeting PDK4 may be a promising therapeutic strategy for AAA prevention and treatment.
More abstracts on this topic:
A human cardiomyocyte model of CD36 haploinsufficiency uncovers fatty acid oxidation deficits driving dilated cardiomyopathy
Al Sayed Zeina, Klattenhoff Carla, Aragam Krishna, Ellinor Patrick, Willcox Jon, Zheng Alice, Koledova Vera, Srivastava Salil, Yin Xiaofei, Chaffin Mark, Rigaud Vagner, Kovacs-bogdan Erika
18F-NaF and 18F-FDG and calcification predict the development of abdominal aortic aneurysms and is attenuated by drug therapyNakahara Takehiro, Miyazawa Raita, Iwabuchi Yu, Tonda Kai, Narula Nupoor, Strauss Harry, Narula Jagat, Jinzaki Masahiro