Final ID: MDP420
Deep Learning Enabled Electrocardiogram Aimed to Detect Coronary Artery Disease to Predict Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Events in the Community
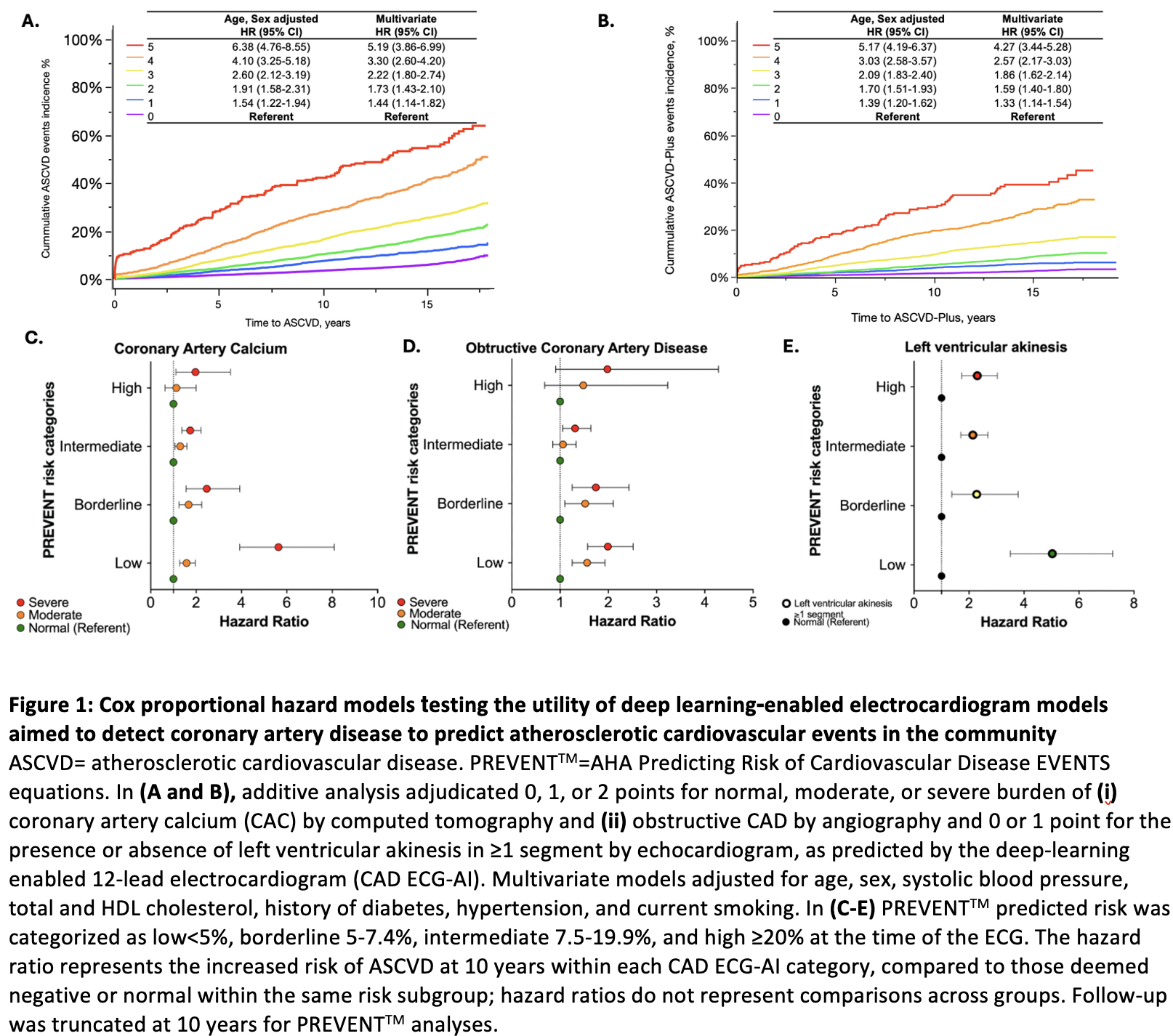
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: We previously developed deep-learning algorithms that identify coronary artery disease (CAD) risk based on (i) coronary artery calcium (CAC), (ii) obstructive CAD by angiography, and (iii) left ventricular akinesis in ≥1 segment by echocardiogram, using a 12-lead electrocardiogram (CAD ECG-AI). We tested the hypothesis that those with increased probability of CAD by CAD ECG-AI algorithms will have an increased risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) events and would refine the AHA Predicting Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Events (PREVENTTM) equations’ predictive capabilities.
Methods: We assessed a group of consecutive patients who sought primary care in Olmsted County, MN, between 1997 and 2003. Passive follow-up was conducted using the Rochester Epidemiology Project's record linkage system. Patients included met the same criteria of the original PREVENTTM equations. The probability output of each CAD ECG-AI algorithm was used to predict ASCVD (fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke) and ASCVD-Plus [further including percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and all-cause mortality]. Events were validated in duplicate. Cox proportional hazard models adjusted for age, sex, and risk factors while modeling each CAD ECG-AI algorithm as an individual and additive predictor (see footnote). PREVENTTM risk categories stratified analysis to evaluate the effect of the CAD ECG-AI models on predicted ASCVD risk.
Results: We included 21,193 patients, with mean ± SD age 51.6 ± 12.0, 54% women and 95% white. After 14.2±12.4 years follow-up, 1,351 (6.4%) developed ASCVD, and 2,808 (13.2%) had ASCVD-Plus. The risk of ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus increased with positivity for the CAD ECG-AI algorithms after adjustments for age, sex, and PREVENTTM equations factors, all p for trend <0.001 (data not shown). In additive analyses, the risk of ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus increased with increased CAD ECG-AI factors, all p for trend <0.001 (Fig. A-B). Furthermore, the CAD ECG-AI algorithm enhanced the predictive capabilities of PREVENTTM equations across most risk subgroups (Fig. C-E).
Conclusions: The deep-learning CAD ECG-AI algorithms displayed an independent and additive association
with long-term ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus events in the community and improved the PREVENTTM predicted ASCVD risk. The CAD ECG-AI algorithms could help identify individuals at risk in primary prevention of cardiovascular events.
Methods: We assessed a group of consecutive patients who sought primary care in Olmsted County, MN, between 1997 and 2003. Passive follow-up was conducted using the Rochester Epidemiology Project's record linkage system. Patients included met the same criteria of the original PREVENTTM equations. The probability output of each CAD ECG-AI algorithm was used to predict ASCVD (fatal and non-fatal myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke) and ASCVD-Plus [further including percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and all-cause mortality]. Events were validated in duplicate. Cox proportional hazard models adjusted for age, sex, and risk factors while modeling each CAD ECG-AI algorithm as an individual and additive predictor (see footnote). PREVENTTM risk categories stratified analysis to evaluate the effect of the CAD ECG-AI models on predicted ASCVD risk.
Results: We included 21,193 patients, with mean ± SD age 51.6 ± 12.0, 54% women and 95% white. After 14.2±12.4 years follow-up, 1,351 (6.4%) developed ASCVD, and 2,808 (13.2%) had ASCVD-Plus. The risk of ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus increased with positivity for the CAD ECG-AI algorithms after adjustments for age, sex, and PREVENTTM equations factors, all p for trend <0.001 (data not shown). In additive analyses, the risk of ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus increased with increased CAD ECG-AI factors, all p for trend <0.001 (Fig. A-B). Furthermore, the CAD ECG-AI algorithm enhanced the predictive capabilities of PREVENTTM equations across most risk subgroups (Fig. C-E).
Conclusions: The deep-learning CAD ECG-AI algorithms displayed an independent and additive association
with long-term ASCVD and ASCVD-Plus events in the community and improved the PREVENTTM predicted ASCVD risk. The CAD ECG-AI algorithms could help identify individuals at risk in primary prevention of cardiovascular events.
More abstracts on this topic:
Baseline Severity of Coronary Artery Calcium Among Patients Enrolled in the CorCal Trial Compared to those Enrolled in the MESA Study
Muhlestein Joseph, May Heidi, Winslow Tyler, Knight Stacey, Le Viet, Iverson Leslie, Bair Tami, Knowlton Kirk, Anderson Jeffrey
Abdominal Circumference and Coronary Calcium Score in a Healthy Nonobese Brazilian Cohort: ELSA-Brasil Cohort AnalysisCorrea Fabiano Ronaldo, Bittencourt Marcio, Bosco Mendes Thiago, Romero-nunez Carlos, Generoso Giuliano, Staniak Henrique, Foppa Murilo, Santos Raul, Lotufo Paulo, Bensenor Isabela