Final ID: MDP1690
Social Support and Blood Pressure Control Among Older US Adults (1999-2008)
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Blood Pressure (BP) control is less likely among older adults compared to other age groups in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Lack of social support is a growing epidemic among older adults and is associated with a higher prevalence of hypertension. It is unclear whether BP control among older adults with and without social support has changed over time.
Aim: To determine if BP control among older adults with and without social support has changed from 1999 to 2008.
Methods: We conducted weighted cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data from 1999 through 2008 (5 cycles). BP control was defined as BP <140/<90 mmHg. Having social support was assessed during 5 cycles. The proportion of adults with controlled BP was calculated for adults with and without social support and by demographics.
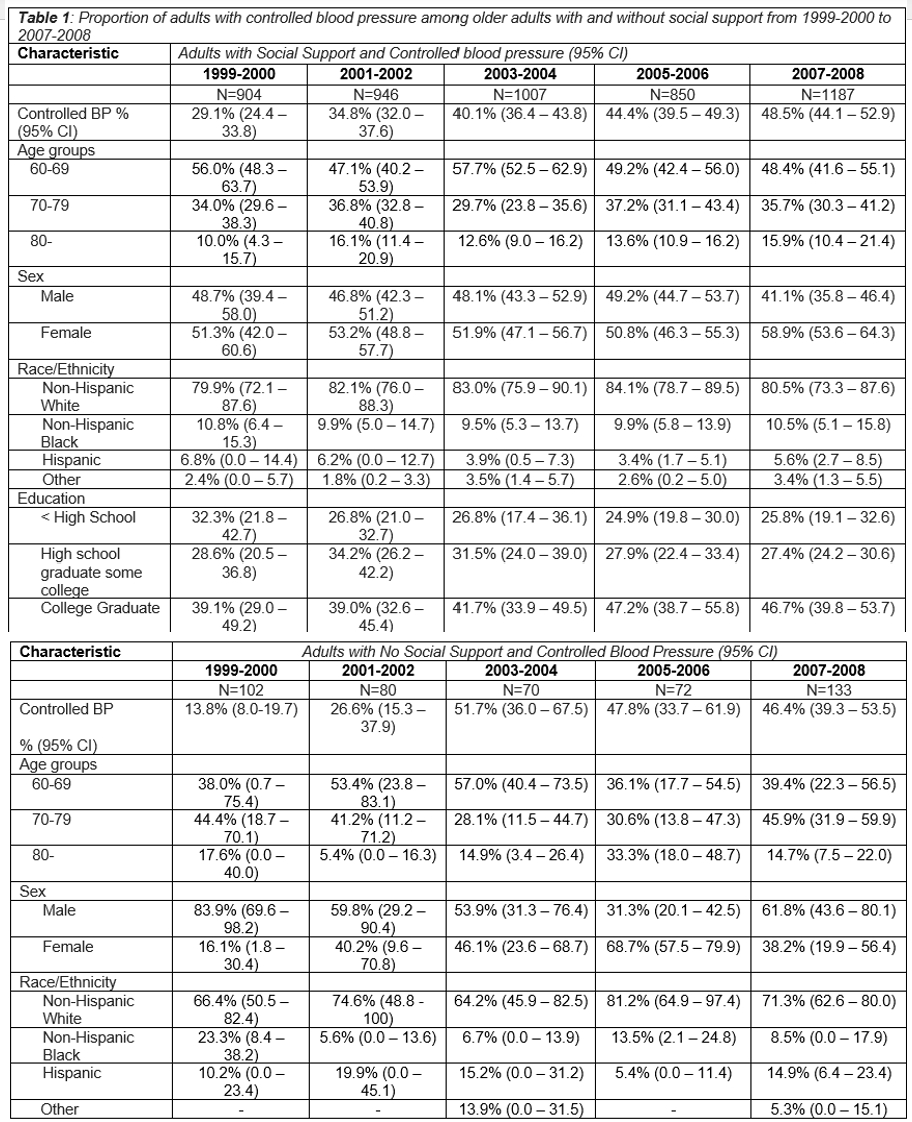
Results: The analysis included 5,351 adults ≥60 years with systolic/diastolic BP ≥140/≥90 mmHg on antihypertensive medication; 45.1% were 60-69 years old, 19.4% were >80 years, 58.8% were female, 80.6% were non-Hispanic White adults. Among adults with social support, the proportion with controlled BP increased from 29.1% (95% CI, 24.3-33.8%) in 1999-2000 to 48.5% (95% CI, 44.1-52.9%) in 2007-2008 (p<.0001 for trend). Among adults without social support, the proportion with controlled BP increased from 13.5% in 1999-2000 and was 51.7% in 2003-2004 and then declined to 46.4% in 2007-2008 (p<.0001 for trend; Table 1). For those with social support, women, non-Hispanic White adults, and college graduates had consistently higher BP control rates compared to their counterparts. For those without social support, men had higher BP control compared to women except in 2005-2006. Non-Hispanic White adults had high BP control rates consistently. The proportion with controlled BP was highest for adults with
Aim: To determine if BP control among older adults with and without social support has changed from 1999 to 2008.
Methods: We conducted weighted cross-sectional analysis of NHANES data from 1999 through 2008 (5 cycles). BP control was defined as BP <140/<90 mmHg. Having social support was assessed during 5 cycles. The proportion of adults with controlled BP was calculated for adults with and without social support and by demographics.
Results: The analysis included 5,351 adults ≥60 years with systolic/diastolic BP ≥140/≥90 mmHg on antihypertensive medication; 45.1% were 60-69 years old, 19.4% were >80 years, 58.8% were female, 80.6% were non-Hispanic White adults. Among adults with social support, the proportion with controlled BP increased from 29.1% (95% CI, 24.3-33.8%) in 1999-2000 to 48.5% (95% CI, 44.1-52.9%) in 2007-2008 (p<.0001 for trend). Among adults without social support, the proportion with controlled BP increased from 13.5% in 1999-2000 and was 51.7% in 2003-2004 and then declined to 46.4% in 2007-2008 (p<.0001 for trend; Table 1). For those with social support, women, non-Hispanic White adults, and college graduates had consistently higher BP control rates compared to their counterparts. For those without social support, men had higher BP control compared to women except in 2005-2006. Non-Hispanic White adults had high BP control rates consistently. The proportion with controlled BP was highest for adults with
More abstracts on this topic:
A Study Using Team Based Hypertension Care Focused on Black Patients to Inform a Future Randomized Trial
Manandhar Srista, Taylor Yhenneko, Bosworth Hayden, Pokharel Yashashwi, Chhetri Sunit, Sutton Danielle, Saha Animita, Kaur Suneet, Brown Josh, Moore Justin, Callahan Kate, Williamson Jeff
A New Analytical Approach for Noninvasive Reconstruction of the Entire Left Ventricular Pressure Waveform in Myocardial Ischemia and InfarctionBilgi Coskun, Li Jiajun, Alavi Rashid, Dai Wangde, Matthews Ray, Kloner Robert, Pahlevan Niema