Final ID: MDP1386
Effects of Influenza Vaccination Among Patients With Myocardial Ischemia and Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
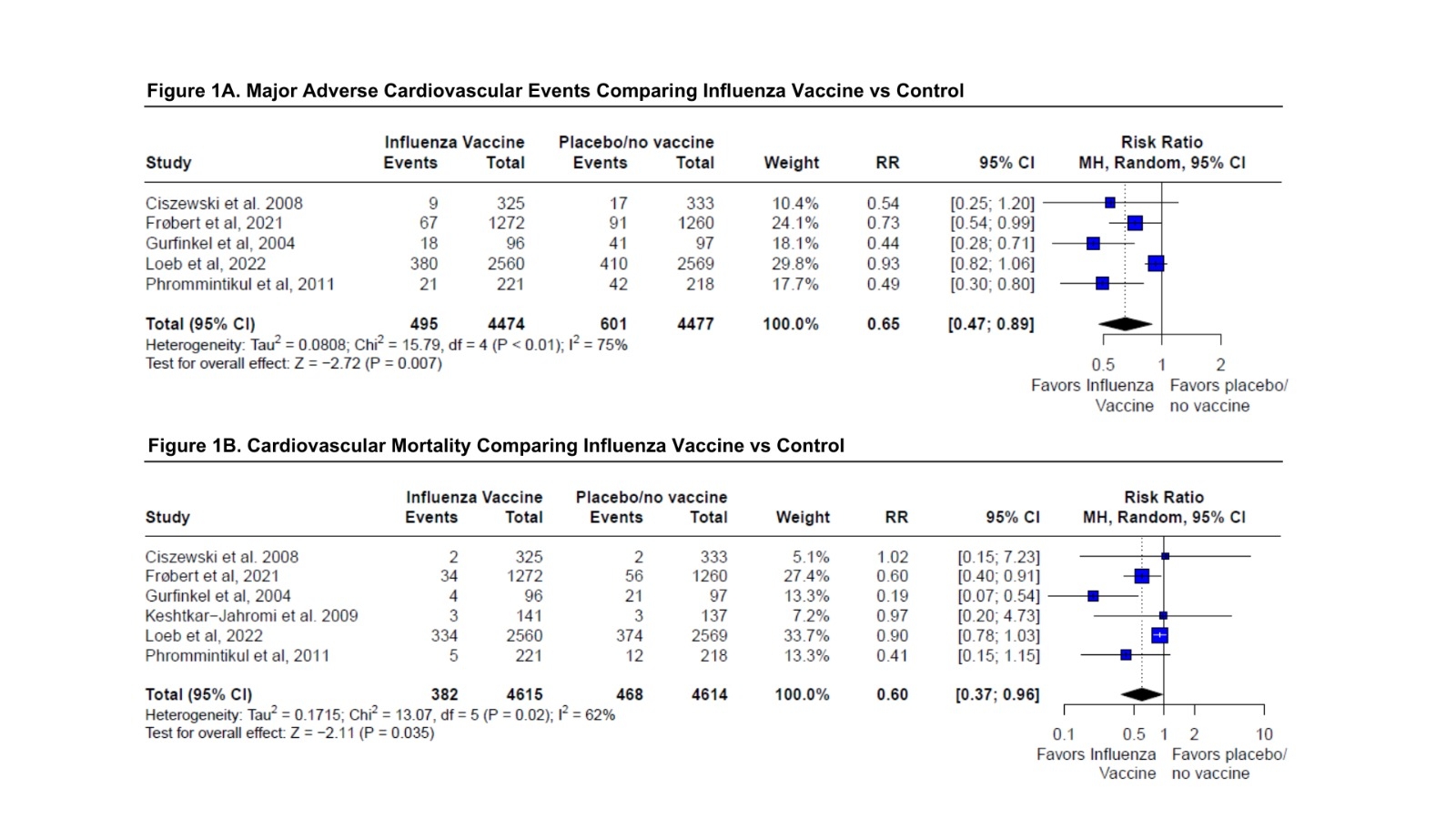
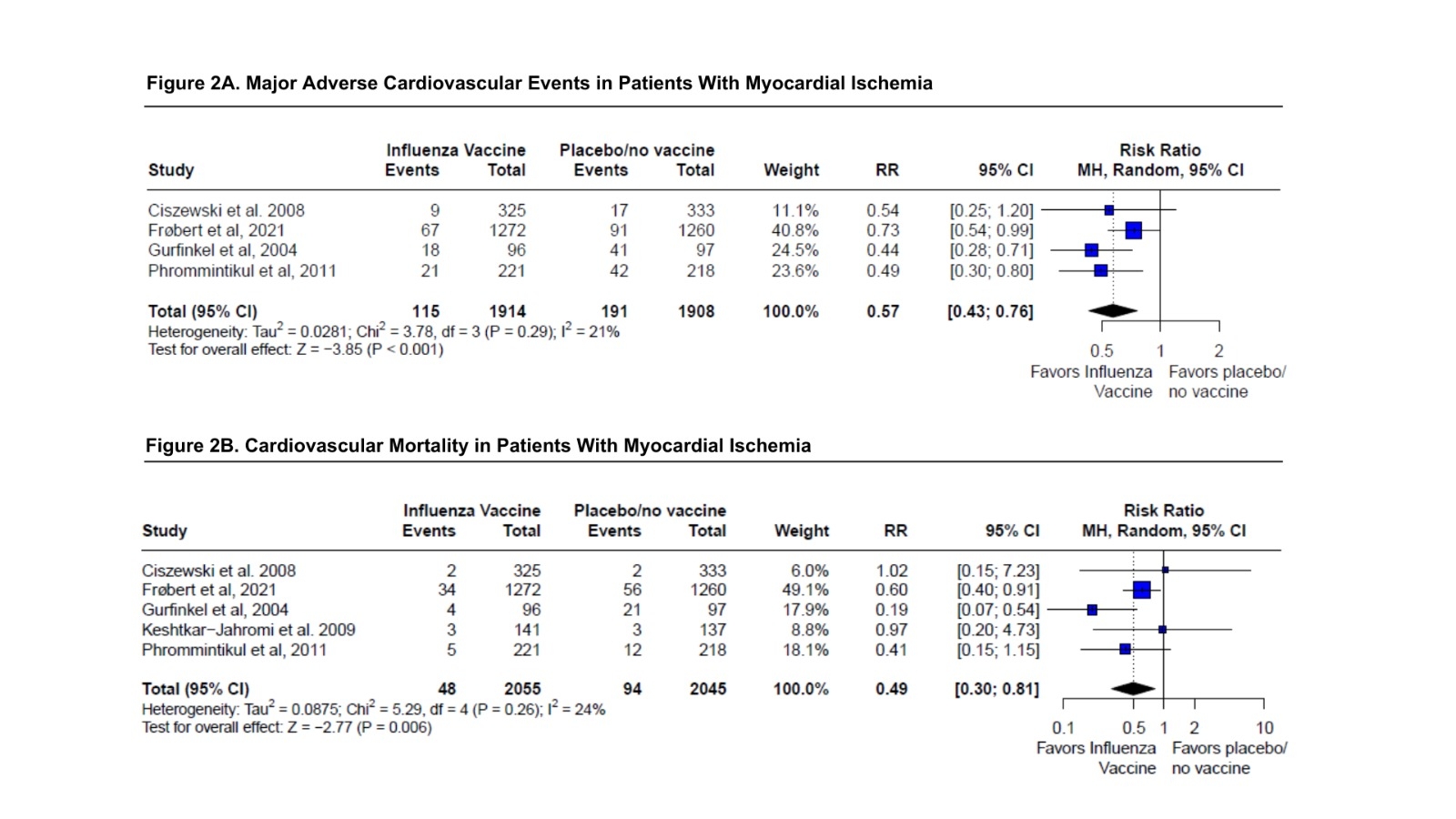
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Previous studies have shown that influenza vaccination (IV) may reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in patients with cardiovascular disease. In this meta-analysis, we aimed to clarify the effects of IV in patients with myocardial ischemia (MI) and heart failure (HF). Hypothesis: The influenza vaccine reduces the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events among patients with MI and HF. Methods: A comprehensive search was performed in PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Embase databases from inception up to march 2024. We included randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that assessed the effects of IV in patients with HF and MI, and reported outcomes of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), cardiovascular death, and all-cause death. Analyses were conducted using R software. Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic. A random-effects model was applied to calculate pooled Relative Risk (RR). A stratified analysis was performed to investigate ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) and non-STEMI subgroups. Sensitivity analysis was performed to explore heterogeneity. Confidence Interval (CI) was set at 95%. Results: We identified six RCTs comprising a total population of 9229 participants. Of these, 4100 were patients with MI, and 5129 were HF patients. Overall, MACE (RR 0.65; 95%CI 0.47-0.89; p=0.007; I2=75%) (Figure 1A) and cardiovascular death (RR 0.60; 95%CI 0.37-0.96; p=0.035; I2=62%) (Figure 1B) were significantly lower in group receiving IV compared to placebo/no treatment. No statistically significant difference was observed for all-cause death. In sensitivity analysis, after excluding HF patients, IV significantly decreased the risk of MACE (RR 0.57; 95%CI 0.43-0.76; p<0.001; I2=21%) (Figure 2A), cardiovascular death (RR 0.49; 95%CI 0.30-0.81; p=0.006; I2=24%) (Figure 2B), and all-cause death (RR 0.56; 95%CI 0.39-0.80; p=0.001; I2=0%). Consistent results were observed, with IV reducing the risk of MACE in the non-STEMI subgroup (RR 0.48; 95%CI 0.30-0.78; p=0.003; I2=24%). However, no significant difference was identified in the STEMI subgroup. Meta-regression showed impact of age and follow-up duration on treatment effect estimates. Conclusion: IV exhibited potential in reducing the risk of major cardiovascular events and cardiovascular mortality in patients with HF and MI. These findings reinforce the importance of the IV as a secondary prevention strategy for these populations.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Case Presentation of Severe Left Ventricular Dysfunction from Focal Myocarditis due to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor
Patel Romil, Hussain Kifah, Gordon Robert
Double Trouble: Impact of Viral Pneumonia on Mortality and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized with Pulmonary Embolism: A Nationwide Analysis (2016 – 2021)Towfig Muhanned Faisal, Sule-saa Samuel, Akella Sai Anusha, Ahmed Mugtaba, Muriuki Hiram, Adedayo Ajibola