Final ID: MDP1170
Integrating Multi-Omics, Phenotypic, and Social Determinants for Stroke Prediction in Atrial Fibrillation: Advancing Precision Health Using Machine Learning
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is linked to an elevated risk of ischemic stroke (IS) and mortality. However, the performance of existing clinical scoring systems in assessing these outcomes is at best moderate. The blood proteome serves as a vital indicator of biological processes related to complex disorders. Consequently, there exists an opportunity to enhance the predictive accuracy of such risk scores by incorporating blood proteomic data.
Purpose
In this study, we aim to evaluate the combined influence of genomics, proteomics, biomarkers, phenotypic, and social determinants of health (SDOH) on AF outcomes to better understand a precision health framework in managing AF.
Methods
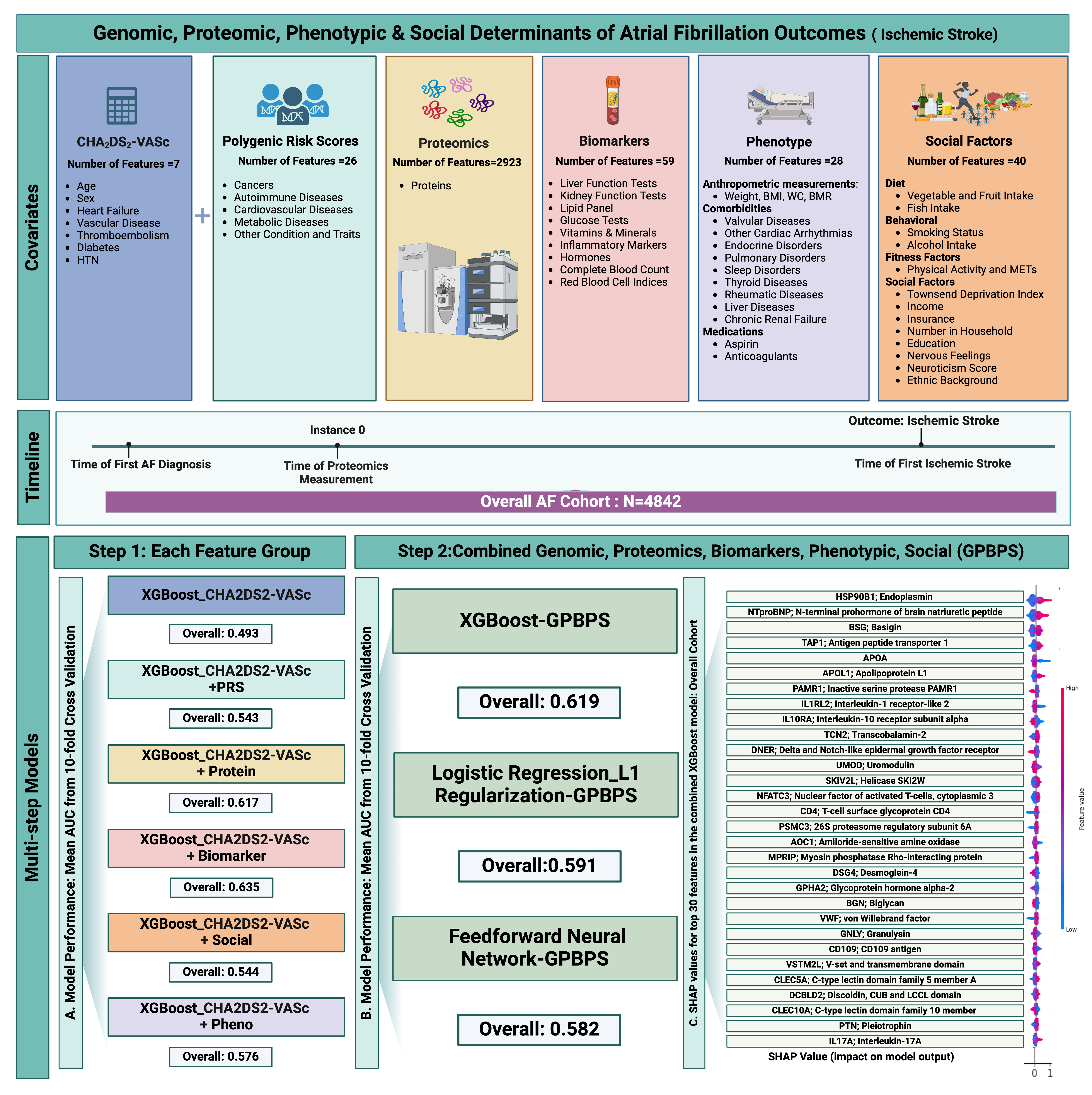
We analyzed patients with AF in the UK Biobank cohort who underwent proteomics measurements using the Olink Proximity Extension Assay. The primary endpoint was the incidence of IS.We assessed the intersection of multi-omics,comorbidities,SDOH and traditional CHA2DS2-VASc score to identify the most important factors associated with IS.We employed multi-step machine learning algorithms to evaluate 3,083 features, including Step1,which involved separate models for each feature type,followed by Step 2,where a combined model was used to assess the complex relationship between these features.The area under the curve (AUC) was used to compare the discriminative ability of the model with the addition of each feature group for predicting IS.Grid search and 10-fold cross-validation were performed to identify the best hyperparameters,and we calculated the mean AUC for the final models.SHAP values were reported for the top 30 features in the final XGBoost model (Figure1).
Results
Among 4,842 patients with AF(mean age 67.2±9.5 years,61.8% female),5.2% experienced an IS within 9.9±7.5 years after AF diagnosis.The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 2.3±1.4, with 60.14% on anticoagulation therapy.The AUC for the CHA2DS2-VASc score at baseline was 0.493.Adding SDOH, polygenic scores, phenotypic data, proteomics, and biomarkers improved the model's discriminative ability (Figure 1.A), with a combined model AUC of 0.619 (95% CI: 0.592-0.645)(Figure 1.B).The top 30 features in the final model, primarily proteins, are shown in Figure 1C.
Conclusion
A small number of plasma proteins can substantially enhance risk prediction of IS in the setting of AF. Further validation could enable a single-source,personalized assessment of stroke risk in patients with AF as a gateway to personalized risk reduction therapy.
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is linked to an elevated risk of ischemic stroke (IS) and mortality. However, the performance of existing clinical scoring systems in assessing these outcomes is at best moderate. The blood proteome serves as a vital indicator of biological processes related to complex disorders. Consequently, there exists an opportunity to enhance the predictive accuracy of such risk scores by incorporating blood proteomic data.
Purpose
In this study, we aim to evaluate the combined influence of genomics, proteomics, biomarkers, phenotypic, and social determinants of health (SDOH) on AF outcomes to better understand a precision health framework in managing AF.
Methods
We analyzed patients with AF in the UK Biobank cohort who underwent proteomics measurements using the Olink Proximity Extension Assay. The primary endpoint was the incidence of IS.We assessed the intersection of multi-omics,comorbidities,SDOH and traditional CHA2DS2-VASc score to identify the most important factors associated with IS.We employed multi-step machine learning algorithms to evaluate 3,083 features, including Step1,which involved separate models for each feature type,followed by Step 2,where a combined model was used to assess the complex relationship between these features.The area under the curve (AUC) was used to compare the discriminative ability of the model with the addition of each feature group for predicting IS.Grid search and 10-fold cross-validation were performed to identify the best hyperparameters,and we calculated the mean AUC for the final models.SHAP values were reported for the top 30 features in the final XGBoost model (Figure1).
Results
Among 4,842 patients with AF(mean age 67.2±9.5 years,61.8% female),5.2% experienced an IS within 9.9±7.5 years after AF diagnosis.The mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 2.3±1.4, with 60.14% on anticoagulation therapy.The AUC for the CHA2DS2-VASc score at baseline was 0.493.Adding SDOH, polygenic scores, phenotypic data, proteomics, and biomarkers improved the model's discriminative ability (Figure 1.A), with a combined model AUC of 0.619 (95% CI: 0.592-0.645)(Figure 1.B).The top 30 features in the final model, primarily proteins, are shown in Figure 1C.
Conclusion
A small number of plasma proteins can substantially enhance risk prediction of IS in the setting of AF. Further validation could enable a single-source,personalized assessment of stroke risk in patients with AF as a gateway to personalized risk reduction therapy.
More abstracts on this topic:
A-band titin-truncating variant promotes the development of arrhythmia-induced cardiomyopathy in a novel genetically-engineered porcine model
Lee Kwonjae, Del Rio Carlos, Mcnally Elizabeth, Pfenniger Anna, Bhatnagar Ashita, Glinton Kristofor, Burrell Amy, Ober Rebecca, Mcluckie Alicia, Bishop Brian, Rogers Christopher, Geist Gail
A Cross-scale Causal Machine Learning Framework Pinpoints Mgl2+ Macrophage Orchestrators of Balanced Arterial GrowthHan Jonghyeuk, Kong Dasom, Schwarz Erica, Takaesu Felipe, Humphrey Jay, Park Hyun-ji, Davis Michael E