Final ID: MDP1677
Analysing the Global Landscape of Hypertension-Related Aortic Aneurysm Mortality: Insights from 31-Year Analysis of Global Burden Of Disease 2021
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Aortic aneurysm, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by weakness of the aortic wall, poses a significant health risk, especially when concurrent with high systolic blood pressure. In an aging population experiencing the effects of smoking and atherosclerotic disease, it is imperative to explore the burden associated with hypertension-related aortic aneurysm mortality.
Methods: The Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) study was used to extract data for high systolic blood pressure-related aortic aneurysm from 1990-2021. Dataset was stratified globally, continent wise, and by World Bank income levels. Age-standardized death rates (ASDRs), disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years of life lost (YLL) were examined. Jointpoint regression was used to quantify these estimates and calculate average annual percentage changes (AAPCs).
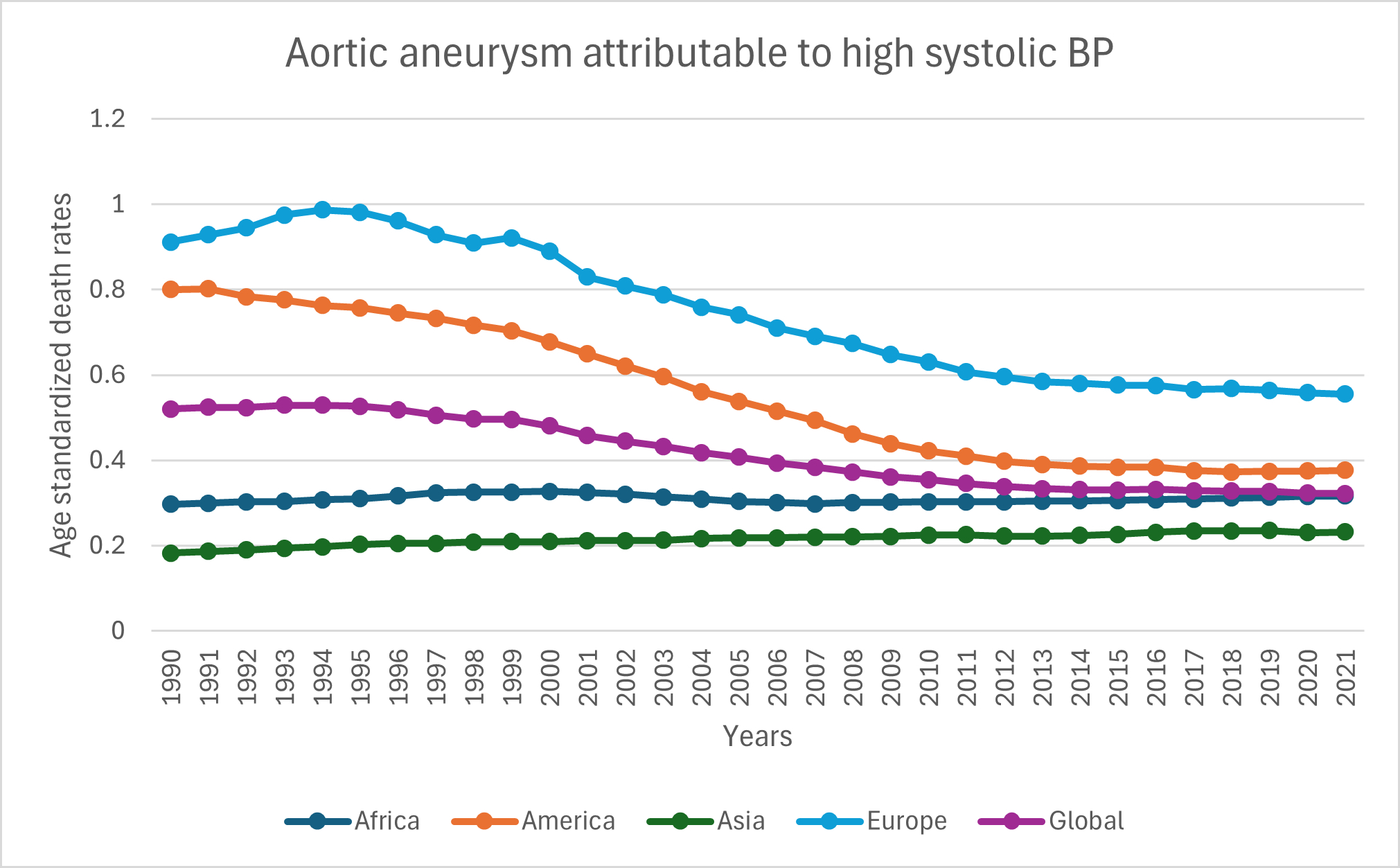
Results: Globally, the age standardized death rates (ASDR) for hypertension-related aortic aneurysm rupture had a declining trend from 1990-2021. In 1990, the ASDR was 0.52 (95% UI 0.39-0.65), which declined to 0.32 in 2021 (AAPC=-1.53; 95% CI -1.57 to -1.48). The disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) were 9.55 in 1990 and decreased to 6.19 in 2021 (AAPC=-1.38; 95% CI -1.42 to -1.33). The age standardized years of life lost (YLL) also showed a uniform drop over the same period (AAPC=-1.38; 95% CI -1.42 to -1.33). In continent wise analysis, North America and Europe exhibited significant decline [(AAPC=-2.44; 95% CI -2.48 to -2.40) and (AAPC=-1.58; 95% CI -1.64 to -1.51) respectively], while Africa showed minimal variation. Importantly, however, Asia was the only continent with a rising mortality during this period (AAPC=0.77; 95% CI 0.73-0.81). According to World Bank income levels, high income countries had continuous decline in death rates while lower-middle income countries had increasing deaths rates. Upper-middle and low-income countries both had minimal variation in death rates during this period.
Conclusion: Global efforts to reduce hypertension-related aortic aneurysm mortality have yielded positive results, but regional disparities persist. Continued research, prevention, and healthcare interventions are crucial to further mitigate this health risk.
Methods: The Global Burden of Diseases (GBD) study was used to extract data for high systolic blood pressure-related aortic aneurysm from 1990-2021. Dataset was stratified globally, continent wise, and by World Bank income levels. Age-standardized death rates (ASDRs), disability-adjusted life years (DALYs), and years of life lost (YLL) were examined. Jointpoint regression was used to quantify these estimates and calculate average annual percentage changes (AAPCs).
Results: Globally, the age standardized death rates (ASDR) for hypertension-related aortic aneurysm rupture had a declining trend from 1990-2021. In 1990, the ASDR was 0.52 (95% UI 0.39-0.65), which declined to 0.32 in 2021 (AAPC=-1.53; 95% CI -1.57 to -1.48). The disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) were 9.55 in 1990 and decreased to 6.19 in 2021 (AAPC=-1.38; 95% CI -1.42 to -1.33). The age standardized years of life lost (YLL) also showed a uniform drop over the same period (AAPC=-1.38; 95% CI -1.42 to -1.33). In continent wise analysis, North America and Europe exhibited significant decline [(AAPC=-2.44; 95% CI -2.48 to -2.40) and (AAPC=-1.58; 95% CI -1.64 to -1.51) respectively], while Africa showed minimal variation. Importantly, however, Asia was the only continent with a rising mortality during this period (AAPC=0.77; 95% CI 0.73-0.81). According to World Bank income levels, high income countries had continuous decline in death rates while lower-middle income countries had increasing deaths rates. Upper-middle and low-income countries both had minimal variation in death rates during this period.
Conclusion: Global efforts to reduce hypertension-related aortic aneurysm mortality have yielded positive results, but regional disparities persist. Continued research, prevention, and healthcare interventions are crucial to further mitigate this health risk.
More abstracts on this topic:
Achieving Guidelines within a 24-Hour Movement Paradigm and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease and All-Cause Mortality in United States Adults
Boudreaux Benjamin, Xu Chang, Dooley Erin, Hornikel Bjoern, Munson Alexandra, Shechter Ari, Palta Priya, Gabriel Kelley, Diaz Keith
A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies Comparing Short and Longterm Outcomes of Trans-Catheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Patient with and without Cancer:Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Adnan, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Khan Bilal, Lamichhane Bikal, Shafique Nouman, Rahman Hammad, Aafreen Asna, Muhammad Anza, Bhatia Hitesh, Khan Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib