Final ID: Sa4133
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance Distribution in Pulmonary Hypertension Associated with Left Heart Disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is commonly considered to reflect opposition to lung blood flow caused by the arteries (PVRa), but downstream venous resistance (PVRv) may also contribute to pulmonary hypertension (PH) associated with left heart diseases (PH-LHD). In patients referred for right heart catheterization, we investigated PVR distribution and its pathophysiologic implications in PH-LHD and other forms of PH.
Methods
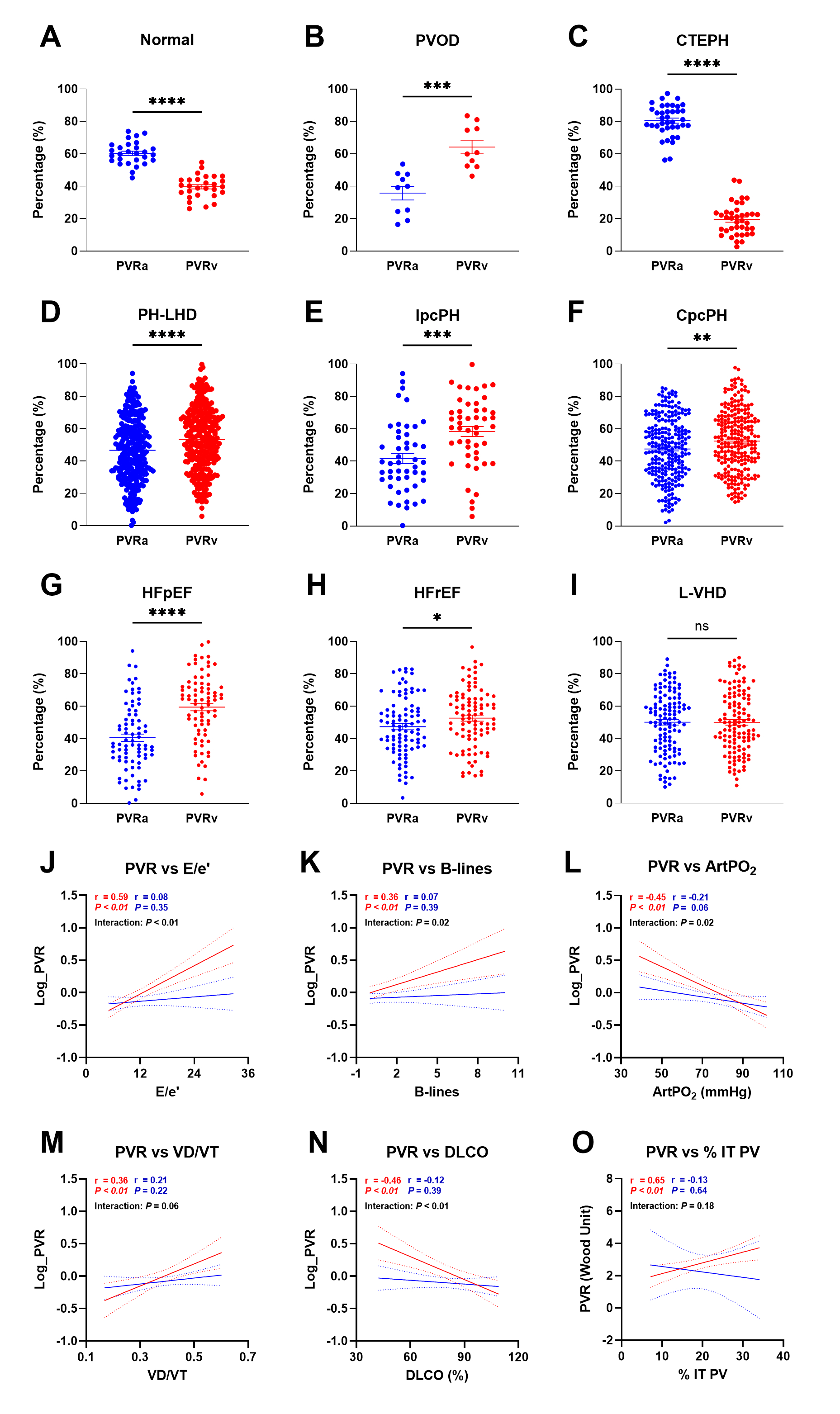
Patients with PH-LHD (n=292), pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD, n=10), chronic thromboembolic PH (CTEPH, n=36) and controls without PH (Ctrl, n=28) were included. Pulmonary capillary pressure (Pc) was calculated using the pulmonary artery occlusion technique. PVR was partitioned into PVRa ((mPAP-Pc)/CO) and PVRv ((Pc-PAWP)/CO) with each expressed as % of PVR. PH-LHD was divided into isolated post-capillary PH (IpcPH) and combined post- and pre-capillary PH (CpcPH). Further, PH-LHD was categorized as heart failure with preserved (HFpEF, EF≥50%) or reduced (HFrEF, EF<50%) ejection fraction or left valvular heart disease (L-VHD). In subsets, functional tests (n=71-81) and histological pulmonary venous (PV) remodeling (autopsy, n=15) were performed to investigate correlations with PVR distribution.
Results
PVR distribution showed an arterial predominance in Ctrl and CTEPH, and increasing venous contribution in PH-LHD (both IpcPH and CpcPH) and PVOD (Figure A-F). In PH-LHD, patients with HFpEF had proportionately greater venous contribution to PVR than HFrEF and L-VHD (Figure G-I), though not to the extent observed in PVOD. In subsets, PVRv was more strongly correlated with E/e’, extravascular lung water estimated by sonographic B-lines, arterial PO2, pulmonary dead space fraction (VD/VT), DLCO, and, among the autopsy series, PV intimal thickness as compared to PVRa (Figure J-O).
Conclusions
Pulmonary venous contributions to PVR are amplified in patients with PH-LHD, which is correlated with greater lung congestion, ventilatory and gas exchange abnormalities, and histological venous remodeling. Further study is required to determine the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutics of pulmonary venous disease in PH-LHD.
Pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) is commonly considered to reflect opposition to lung blood flow caused by the arteries (PVRa), but downstream venous resistance (PVRv) may also contribute to pulmonary hypertension (PH) associated with left heart diseases (PH-LHD). In patients referred for right heart catheterization, we investigated PVR distribution and its pathophysiologic implications in PH-LHD and other forms of PH.
Methods
Patients with PH-LHD (n=292), pulmonary veno-occlusive disease (PVOD, n=10), chronic thromboembolic PH (CTEPH, n=36) and controls without PH (Ctrl, n=28) were included. Pulmonary capillary pressure (Pc) was calculated using the pulmonary artery occlusion technique. PVR was partitioned into PVRa ((mPAP-Pc)/CO) and PVRv ((Pc-PAWP)/CO) with each expressed as % of PVR. PH-LHD was divided into isolated post-capillary PH (IpcPH) and combined post- and pre-capillary PH (CpcPH). Further, PH-LHD was categorized as heart failure with preserved (HFpEF, EF≥50%) or reduced (HFrEF, EF<50%) ejection fraction or left valvular heart disease (L-VHD). In subsets, functional tests (n=71-81) and histological pulmonary venous (PV) remodeling (autopsy, n=15) were performed to investigate correlations with PVR distribution.
Results
PVR distribution showed an arterial predominance in Ctrl and CTEPH, and increasing venous contribution in PH-LHD (both IpcPH and CpcPH) and PVOD (Figure A-F). In PH-LHD, patients with HFpEF had proportionately greater venous contribution to PVR than HFrEF and L-VHD (Figure G-I), though not to the extent observed in PVOD. In subsets, PVRv was more strongly correlated with E/e’, extravascular lung water estimated by sonographic B-lines, arterial PO2, pulmonary dead space fraction (VD/VT), DLCO, and, among the autopsy series, PV intimal thickness as compared to PVRa (Figure J-O).
Conclusions
Pulmonary venous contributions to PVR are amplified in patients with PH-LHD, which is correlated with greater lung congestion, ventilatory and gas exchange abnormalities, and histological venous remodeling. Further study is required to determine the molecular mechanism and novel therapeutics of pulmonary venous disease in PH-LHD.
More abstracts on this topic:
Active Left Atrial Ejection Fraction as a Non-Invasive Prognostic Marker in Left Heart Failure associated Pulmonary Hypertension
Zhou Di, Xin Li, Liu Zhihong, Lu Minjie
Multi-Venous Compression Syndromes Are Characterized by Preload Failure and DysautonomiaPandey Arvind, Abdou Magda, Gerhard-herman Marie, Menard Matthew, Systrom David