Final ID: MDP134
Coronary atheroma burden and structural vascular dysfunction in women with suspected ischemia and no obstructive coronary artery disease.
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Different mechanisms have been proposed to explain abnormal coronary flow reserve (CFR), with authors describing structural vs functional endotypes of coronary microvascular dysfunction (CMD). Epicardial coronary atheroma burden (AB) index is a marker of vascular remodeling confirmed by intravascular ultrasound and is estimated by the measurement of coronary artery tapering. Atheroma burden index is inversely related to CFR in women with suspected ischemia and no obstructive coronary artery disease (INOCA). We hypothesized that AB could help better understand the pathophysiology of these CMD endotypes.
Purpose: To evaluate the association between epicardial AB, baseline average peak velocity (APV), and resting coronary blood flow (CBF) to better understand endotypes (structural vs functional) of vascular dysfunction.
Methods: Women with suspected INOCA (n=180) enrolled in two prospective cohort studies (NCT02582021, NCT03876223) who underwent clinically indicated invasive coronary function testing with a Doppler wire measuring CFR, baseline APV and resting CBF, were included in this analysis. Epicardial AB was measured by core laboratory and was derived for the left main and anterior descending coronary segments. The association of AB with CBF and APV was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
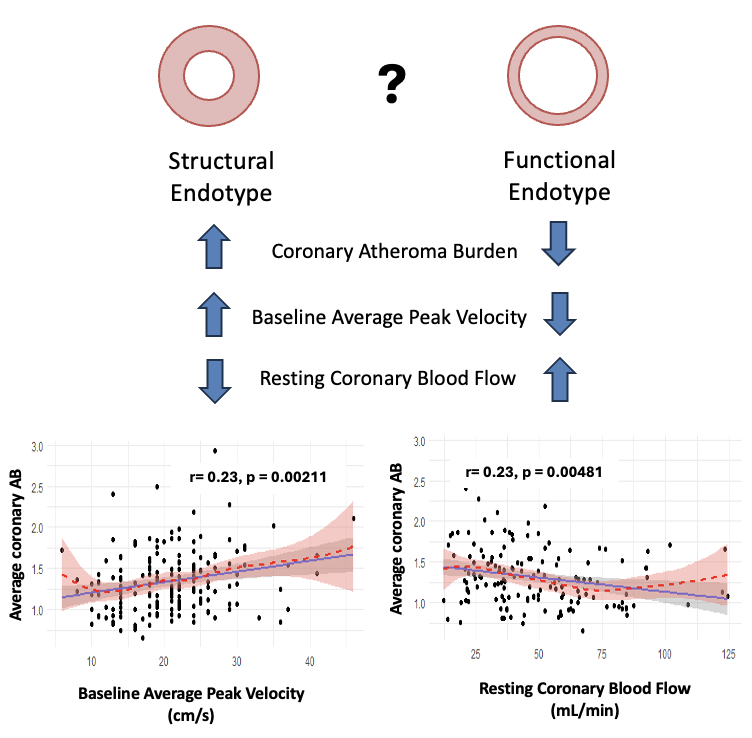
Results: Mean age was 55±10 years, body mass index 27.5±5.9 kg/m2, 33% had hypertension, 12% diabetes, 18% dyslipidemia and 27% were former smokers. Mean average AB was 1.33±0.37, mean maximal AB was 2.02±0.54 and mean CFR was 3.23±2.35. Both average and maximal AB negatively correlated with resting CBF (r=-0.23, p=0.005; and r=-0.20, p=0.015, respectively) and positively correlated with baseline APV (r=0.23, p=0.002; and r=0.18, p=0.015, respectively). (Figure)
Conclusions: These results suggest that the findings of a low resting CBF and high baseline APV, among women with suspected INOCA, is associated with a higher epicardial coronary AB. The use of baseline APV and resting CBF could help identify those who are affected by a structural endotype of coronary vascular dysfunction.
Purpose: To evaluate the association between epicardial AB, baseline average peak velocity (APV), and resting coronary blood flow (CBF) to better understand endotypes (structural vs functional) of vascular dysfunction.
Methods: Women with suspected INOCA (n=180) enrolled in two prospective cohort studies (NCT02582021, NCT03876223) who underwent clinically indicated invasive coronary function testing with a Doppler wire measuring CFR, baseline APV and resting CBF, were included in this analysis. Epicardial AB was measured by core laboratory and was derived for the left main and anterior descending coronary segments. The association of AB with CBF and APV was assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
Results: Mean age was 55±10 years, body mass index 27.5±5.9 kg/m2, 33% had hypertension, 12% diabetes, 18% dyslipidemia and 27% were former smokers. Mean average AB was 1.33±0.37, mean maximal AB was 2.02±0.54 and mean CFR was 3.23±2.35. Both average and maximal AB negatively correlated with resting CBF (r=-0.23, p=0.005; and r=-0.20, p=0.015, respectively) and positively correlated with baseline APV (r=0.23, p=0.002; and r=0.18, p=0.015, respectively). (Figure)
Conclusions: These results suggest that the findings of a low resting CBF and high baseline APV, among women with suspected INOCA, is associated with a higher epicardial coronary AB. The use of baseline APV and resting CBF could help identify those who are affected by a structural endotype of coronary vascular dysfunction.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Site-by-Site Comparison of CT Attenuation, Effective Atomic Numbers, and Electron Densities of Focal Pericoronary Adipose Tissue and Its Relationship to Adjacent Coronary Plaques on Contrast Enhanced Spectral CT
Kaneko Aya, Sakaguchi Yamato, Funabashi Nobusada
A Diagnostic Challenge: Wild-Type Transthyretin Cardiac Amyloidosis in a Patient With Systemic Lupus and Ischemic CardiomyopathyAbdallah Ala, Khalid Arbab, Dicaro Michael, Lei Kachon, Ahsan Chowdhury