Final ID: Su3025
Sex differences in cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic health for degenerative valvular heart disease
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background: Despite the increasing prevalence of degenerative valvular heart disease (VHD), recommended preventive interventions are notably lacking. The cardiovascular-kidney-metabolic (CKM) health approach advocates for multidisciplinary early-stage disease prevention. We aimed to explore sex differences in CKM risk factors associated with VHD.
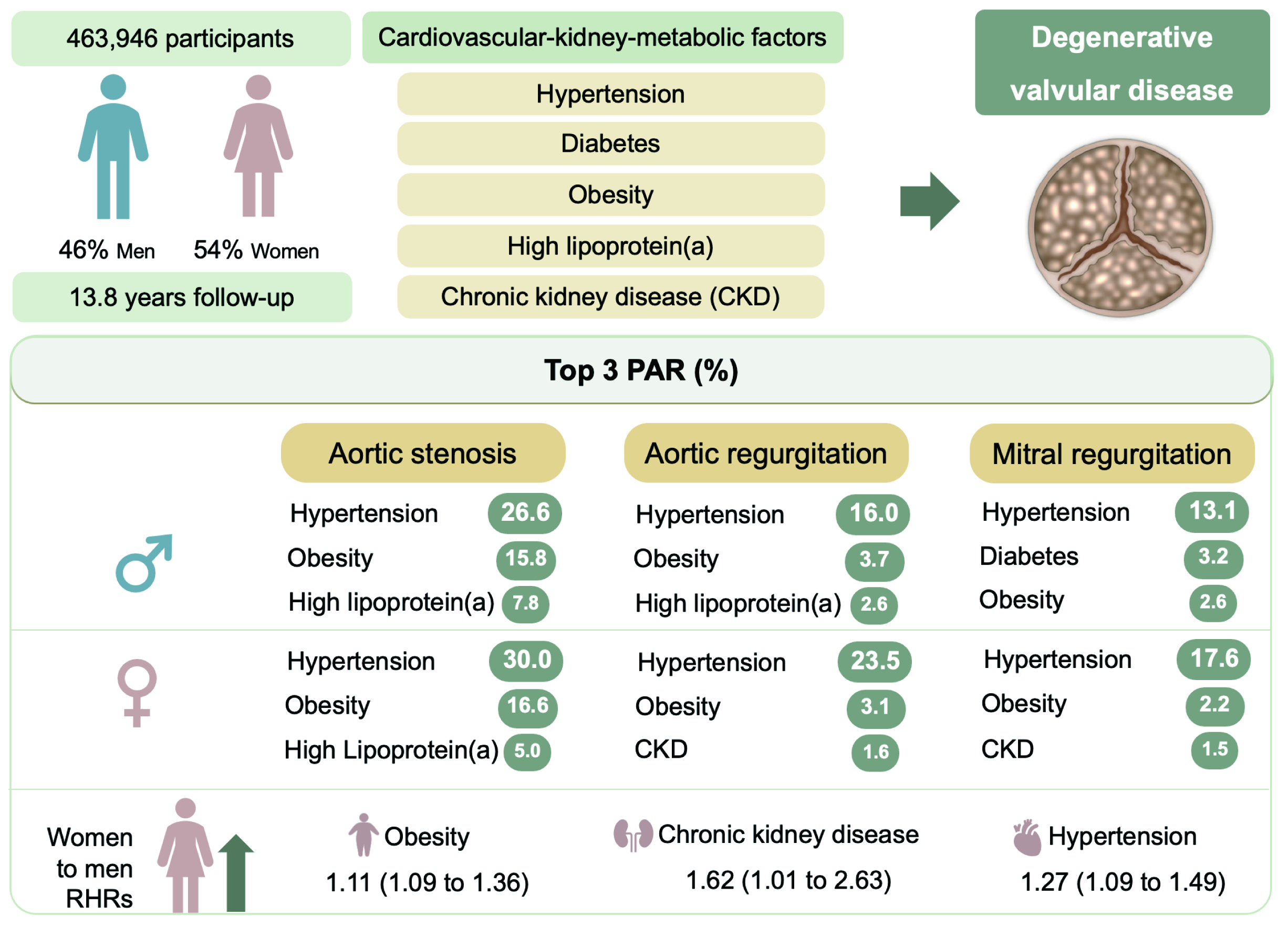
Methods: Using data from UK Biobank, participants without a history of VHD or heart failure at baseline were included. We assessed the sex differences in hazard ratios (HRs) and population-attributable risk (PAR) for incident aortic valve stenosis (AS), aortic valve regurgitation (AR), and mitral valve regurgitation (MR) associated with five CKM risk factors: hypertension, diabetes, obesity, high lipoprotein(a), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Results: Among 463,496 participants (54.4% women), AS, AR, and MR cases were observed at incidence of 1.05 and 0.52, 0.37 and 0.22, 1.04 and 0.70 events per 1000 person-years for men and women, respectively. Hypertension consistently accounted for the largest attributable risk factor for incident VHD in both sexes, with PARs of 29.96% and 26.61% for AS, 23.51% and 16.02% for AR, and 17.56% and 13.09% for MR in women and men, respectively. Compared to men, obesity, CKD, and hypertension were associated with higher risks of AS, AR, and MR in women (women-to-men ratios of HRs: 1.11[1.09–1.36], 1.62[1.01–2.63], and 1.27[1.09–1.49], respectively).
Conclusions: This study offers comprehensive insights into the profiles of CKM risk factors for degenerative VHD among middle-aged individuals. Tailoring the prioritization of risk factors based on gender has the potential to improve the precision and effectiveness of VHD prevention strategies.
Methods: Using data from UK Biobank, participants without a history of VHD or heart failure at baseline were included. We assessed the sex differences in hazard ratios (HRs) and population-attributable risk (PAR) for incident aortic valve stenosis (AS), aortic valve regurgitation (AR), and mitral valve regurgitation (MR) associated with five CKM risk factors: hypertension, diabetes, obesity, high lipoprotein(a), and chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Results: Among 463,496 participants (54.4% women), AS, AR, and MR cases were observed at incidence of 1.05 and 0.52, 0.37 and 0.22, 1.04 and 0.70 events per 1000 person-years for men and women, respectively. Hypertension consistently accounted for the largest attributable risk factor for incident VHD in both sexes, with PARs of 29.96% and 26.61% for AS, 23.51% and 16.02% for AR, and 17.56% and 13.09% for MR in women and men, respectively. Compared to men, obesity, CKD, and hypertension were associated with higher risks of AS, AR, and MR in women (women-to-men ratios of HRs: 1.11[1.09–1.36], 1.62[1.01–2.63], and 1.27[1.09–1.49], respectively).
Conclusions: This study offers comprehensive insights into the profiles of CKM risk factors for degenerative VHD among middle-aged individuals. Tailoring the prioritization of risk factors based on gender has the potential to improve the precision and effectiveness of VHD prevention strategies.
More abstracts on this topic:
Air pollutants, road traffic noise, and risk of valvular heart disease: a UK Biobank-based prospective study
Song Yanjun, Lin Zhangyu, Zheng Zhihao, Chen Xinyue, Bian Xiaohui
A peptoid derivative of alpha-calcitonin gene related peptide improves cardiac function in pressure-overload heart failure miceKumar Ambrish, Deloach Sarah, Dipette Donald, Potts Jay