Final ID: MDP200
HFpEF in Space: The Influence of Weightlessness on Cardiac Filling Pressure in Obese Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) and obesity are often co-morbid, with obesity being associated with greater left ventricular (LV) filling pressures. Obesity may contribute to LV filling pressure by increasing external constraint due to the weight of the lungs and chest wall compressing the heart. The magnitude of the contribution of external constraint to LV filling pressure in HFpEF is unknown. We investigated the influence of chest weight on pulmonary artery systolic, diastolic, and mean pressures in two patients with obesity and HFpEF during acute exposure to weightlessness.
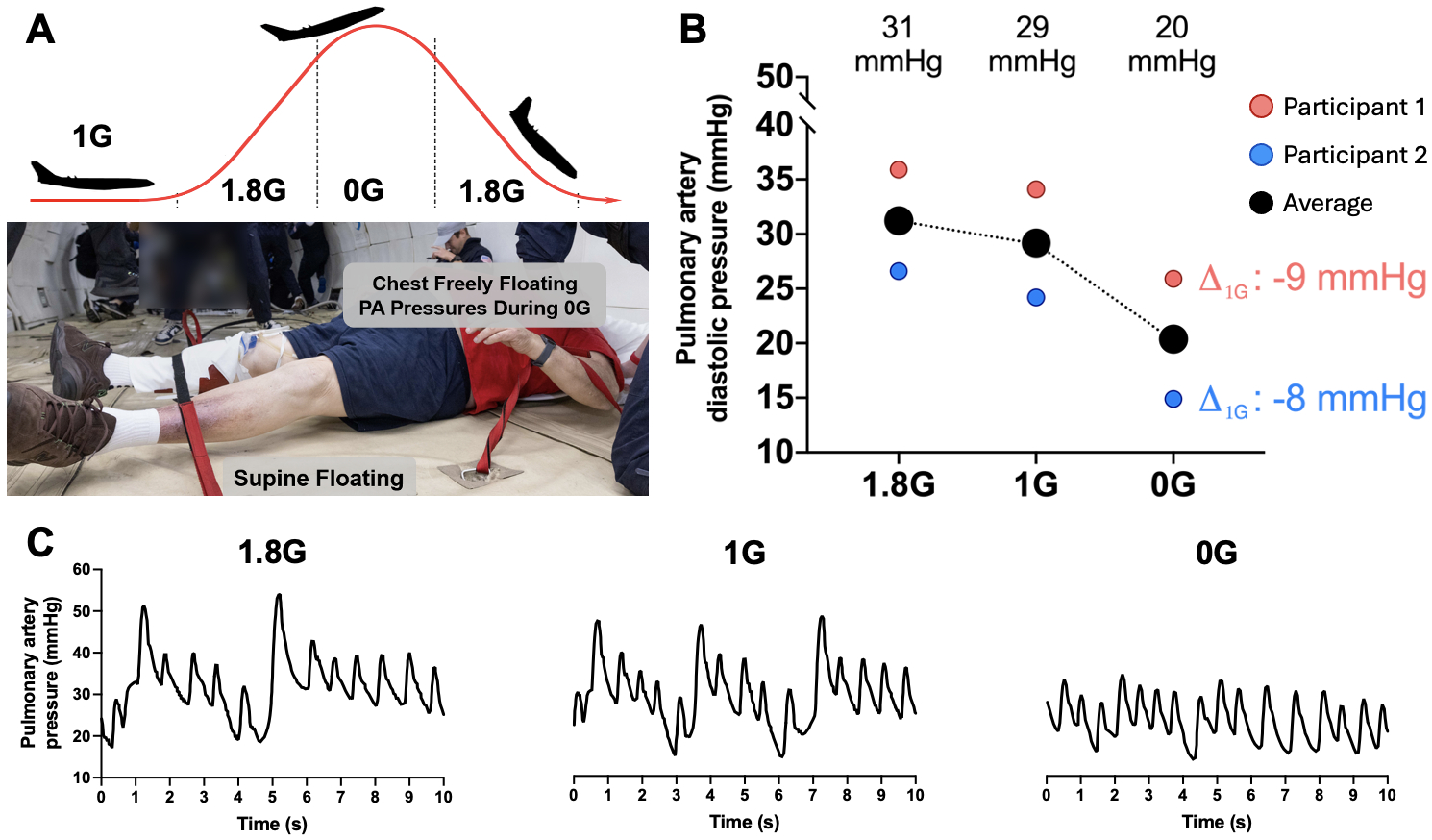
Methods: One female (participant 1; age: 62 years; BMI: 41.2 kg/m2) and one male (participant 2; age: 72 years; BMI: 46.8 kg/m2) patient with HFpEF, obesity, and previously placed CardioMEMS device (Abbott), completed a parabolic flight consisting of repeated parabolas with ~30 seconds of 0G, and ~30 seconds of 1.8G, with level flying (1G) between sets (Figure 1A). Pulmonary artery systolic, diastolic and mean pressures were measured using a CardioMEMS console in the supine position and 10-second waveforms were recorded for analysis (Figure 1C). Spontaneous end-expiratory pressures were corrected for barometric pressure.
Results: Pulmonary diastolic pressures during flight are shown in Figure 1B and 1C. Removal of gravity immediately and significantly decreased pulmonary pressures in both participant 1 (1.8G: 61/36 (46), 1G: 59±4/34±3 (45±3), 0G: 52±3/26±1 (37±2) mmHg) and participant 2 (1.8G: 41/27 (32), 1G: 38/24 (30), 0G: 29±1/15±1 (21±1) mmHg). The absolute change in pulmonary artery diastolic pressure from 1G to 0G was -8 mmHg and -9 mmHg, while between 1.8G and 0G was -10 mmHg and -12 mmHg for participant 1 and 2, respectively.
Conclusion: Acute exposure to weightlessness profoundly reduced pulmonary artery pressures in patients with the obese phenotype of HFpEF. The magnitude of the decrease was greater than nitrates and left atrial shunt devices. Our results suggest that the weight of the lungs and chest wall contribute mechanically to LV filling pressures in HFpEF, and that weight loss may lower LV filling pressures by reducing external constraint.
Methods: One female (participant 1; age: 62 years; BMI: 41.2 kg/m2) and one male (participant 2; age: 72 years; BMI: 46.8 kg/m2) patient with HFpEF, obesity, and previously placed CardioMEMS device (Abbott), completed a parabolic flight consisting of repeated parabolas with ~30 seconds of 0G, and ~30 seconds of 1.8G, with level flying (1G) between sets (Figure 1A). Pulmonary artery systolic, diastolic and mean pressures were measured using a CardioMEMS console in the supine position and 10-second waveforms were recorded for analysis (Figure 1C). Spontaneous end-expiratory pressures were corrected for barometric pressure.
Results: Pulmonary diastolic pressures during flight are shown in Figure 1B and 1C. Removal of gravity immediately and significantly decreased pulmonary pressures in both participant 1 (1.8G: 61/36 (46), 1G: 59±4/34±3 (45±3), 0G: 52±3/26±1 (37±2) mmHg) and participant 2 (1.8G: 41/27 (32), 1G: 38/24 (30), 0G: 29±1/15±1 (21±1) mmHg). The absolute change in pulmonary artery diastolic pressure from 1G to 0G was -8 mmHg and -9 mmHg, while between 1.8G and 0G was -10 mmHg and -12 mmHg for participant 1 and 2, respectively.
Conclusion: Acute exposure to weightlessness profoundly reduced pulmonary artery pressures in patients with the obese phenotype of HFpEF. The magnitude of the decrease was greater than nitrates and left atrial shunt devices. Our results suggest that the weight of the lungs and chest wall contribute mechanically to LV filling pressures in HFpEF, and that weight loss may lower LV filling pressures by reducing external constraint.
More abstracts on this topic:
3-Mercaptopyruvate Sulfurtransferase is a Critical Regulator of Branched-Chain Amino Acid Catabolism in Cardiometabolic HFpEF
Li Zhen, Doiron Jake, Xia Huijing, Lapenna Kyle, Sharp Thomas, Yu Xiaoman, Nagahara Noriyuki, Goodchild Traci, Lefer David
A Two-Hit HFpEF-like Mouse Model with Accelerated Disease OnsetNehra Sarita, Selvam Sabariya, Anand Amit, Luettgen Joseph, Gulia Jyoti, Dokania Manoj, Gupta Ankit, Garcia Ricardo, Dudhgaonkar Shailesh, Mazumder Tagore Debarati, Ck Neethu, Wagh Somnath, Kale Prajakta