Final ID: Sa1028
Association Between Lipoprotein A Levels and Vulnerable Atherosclerotic Plaques: Meta-Analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction:
Lipoprotein A (LpA), an inherited, soluble protein formed in the liver, may be useful as a risk stratification tool for atherosclerosis. Asymptomatic atherosclerosis with a high tendency to rupture is known as vulnerable plaques, which can be defined with common morphologies such as thin-cap fibro-atheroma with a thin layer of depleted smooth muscles (TCFA) or a lipid-rich (LR) plaque.
Hypothesis:
A high LpA level is associated with an increased risk of vulnerable plaques, defined as TCFA or LR plaque.
Methods:
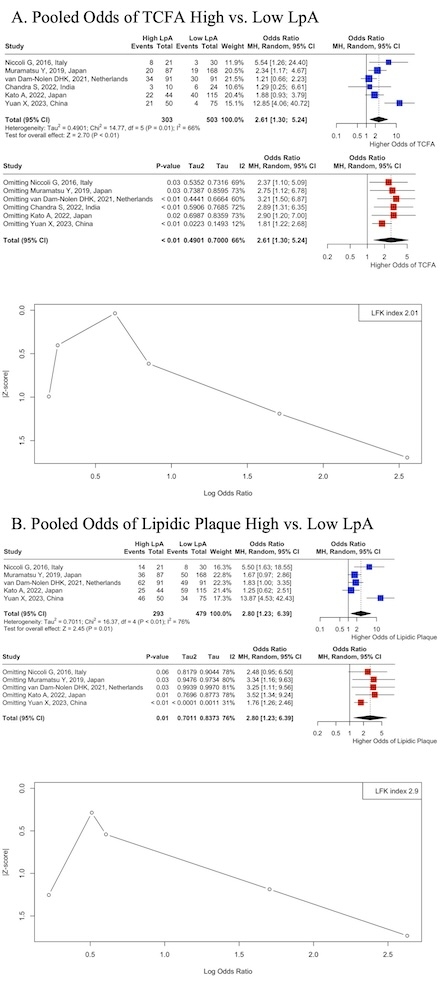
A systematic search of PubMed, SCOPUS, and Embase databases was conducted to find and include relevant observational studies that compared LpA levels with two primary outcomes of plaque vulnerability, TCFA or lipid-rich plaques. A total of 196 studies were identified, 67 underwent initial screening, and 15 were assessed for full-text eligibility. The random effects model was used to pool binary outcomes as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), and the results were presented on forest plots. Sensitivity analysis was performed using the leave-one-out method, and heterogeneity was identified using I2 statistics. Publication bias was assessed using the Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index.
Results:
A total of 6 studies were included in our analysis, comprising three retrospective cohort studies and three prospective cohort studies involving 806 patients, out of which 503 were defined as low LpA and 303 as high LpA. Our analysis revealed that high LpA levels were associated with greater odds for both TCFA (OR 2.61 95% CI:1.30-5.24, p<0.01) and LR plaques (OR 2.80 95% CI: 1.23-6.39, p=0.01). Leave-one sensitivity analysis confirmed the stability of our analysis. High heterogeneity values of I2=66% for TCFA and I2=76% for lipid-rich plaques (p<0.01) were observed. However, the LFK index suggested major asymmetry for both outcomes (TCFA: 2.01 and LR plaque: 2.9), indicating the potential of publication bias to confound our results.
Conclusions:
Our analysis, the first of its kind, reveals an association between higher LpA levels and plaque vulnerability.
Introduction:
Lipoprotein A (LpA), an inherited, soluble protein formed in the liver, may be useful as a risk stratification tool for atherosclerosis. Asymptomatic atherosclerosis with a high tendency to rupture is known as vulnerable plaques, which can be defined with common morphologies such as thin-cap fibro-atheroma with a thin layer of depleted smooth muscles (TCFA) or a lipid-rich (LR) plaque.
Hypothesis:
A high LpA level is associated with an increased risk of vulnerable plaques, defined as TCFA or LR plaque.
Methods:
A systematic search of PubMed, SCOPUS, and Embase databases was conducted to find and include relevant observational studies that compared LpA levels with two primary outcomes of plaque vulnerability, TCFA or lipid-rich plaques. A total of 196 studies were identified, 67 underwent initial screening, and 15 were assessed for full-text eligibility. The random effects model was used to pool binary outcomes as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI), and the results were presented on forest plots. Sensitivity analysis was performed using the leave-one-out method, and heterogeneity was identified using I2 statistics. Publication bias was assessed using the Luis Furuya-Kanamori (LFK) index.
Results:
A total of 6 studies were included in our analysis, comprising three retrospective cohort studies and three prospective cohort studies involving 806 patients, out of which 503 were defined as low LpA and 303 as high LpA. Our analysis revealed that high LpA levels were associated with greater odds for both TCFA (OR 2.61 95% CI:1.30-5.24, p<0.01) and LR plaques (OR 2.80 95% CI: 1.23-6.39, p=0.01). Leave-one sensitivity analysis confirmed the stability of our analysis. High heterogeneity values of I2=66% for TCFA and I2=76% for lipid-rich plaques (p<0.01) were observed. However, the LFK index suggested major asymmetry for both outcomes (TCFA: 2.01 and LR plaque: 2.9), indicating the potential of publication bias to confound our results.
Conclusions:
Our analysis, the first of its kind, reveals an association between higher LpA levels and plaque vulnerability.
More abstracts on this topic:
A Novel Tool for Evaluating Endothelial Function: Plethysmographic Flow-mediated Vasodilation (pFMD)
Kishimoto Shinji, Itarashiki Tomomasa, Higashi Yukihito, Maruhashi Tatsuya, Kajikawa Masato, Mizobuchi Aya, Harada Takahiro, Yamaji Takayuki, Nakano Yukiko, Mohamad Yusoff Farina, Yada Tomohiko
Atherosclerotic Plaque Progresses Over Time in Healthy Individuals Without MACE, Risk Factors, or InterventionsAldana Jairo, Kinninger April, Krishnan Srikanth, Ichikawa Keishi, Budoff Matthew, Karlsberg Ronald