Final ID: MDP11
Pharmacological Targeting of FAS Attenuates Macrophage-Derived Foam Cell Formation
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Introduction: Fatty acid synthase (FAS), a key enzyme in de novo lipogenesis, may contribute to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Notably, the circulating form of FAS (cFAS) is a potential biomarker for peripheral arterial disease and carotid artery stenosis, particularly in patients with diabetes. Within the atherosclerotic lesion, macrophage-derived foam cells (MDFc) play a crucial role in disease pathogenesis.
Research question: This study addressed the role of cFAS in macrophage-derived foam cell formation and the efficacy of FAS inhibitors in mitigating this process.
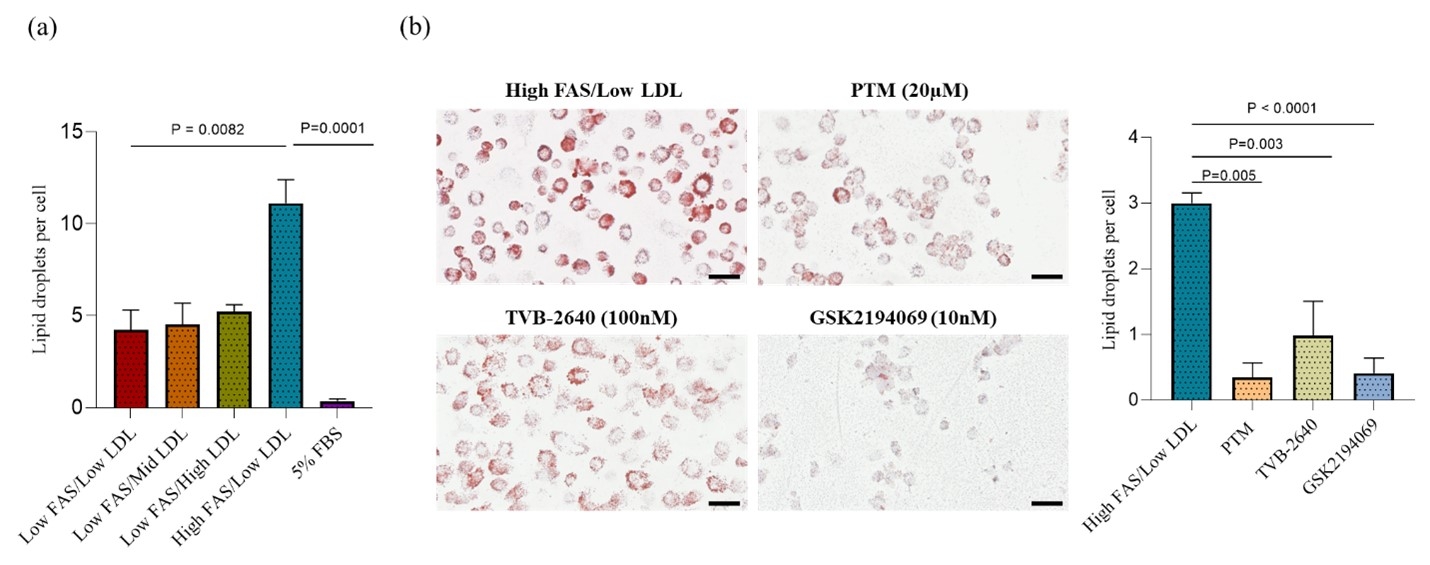
Methods: Cell culture: U937 monocytes were differentiated into macrophages using PMA (200ng/mL) for 24h. Foam Cell Assay: Differentiated macrophages were cultured under various conditions. The RPMI1640 media supplemented with 5% FBS used as a negative control. To induce MDFc, some cultures used 5% human serum containing high FAS/low LDL levels as a positive control. Other cultures combined human serum containing low FAS with high, medium, or low LDL levels. Additionally, the effects of FAS inhibitors were tested by adding PTM (20μM), TVB-2640 (100nM), or GSK2194069 (10nM) to the media for 48h, both with and without high FAS/low LDL levels. Oil-O-Red Staining: Lipid droplets were quantified after neutral lipid staining with Oil-O-Red.
Results: Our findings reveal a notable increase in the formation of MDFc when macrophages were cultured with high FAS/low LDL levels as compared to the low FAS/low LDL condition (P=0.00082) and as compared to the negative control using 5% FBS (P=0.0001). Furthermore, we observed a significant reduction in lipid droplets within MDFc following treatment with FAS inhibitors. Both the selective FAS inhibitors TVB2640 and GSK2194069 led to significant reductions in MDFc (P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Our findings underscore the potential role of FAS in promoting the formation of MDFc. Pharmacological inhibition of FAS can mitigate foam cell formation, which represents a potential novel avenue for clinical management of atherosclerosis. Further exploration of the mechanism of action of pharmacological targeting of extracellular cFAS versus intracellular FAS in pre-clinical in vivo models is warranted.
Research question: This study addressed the role of cFAS in macrophage-derived foam cell formation and the efficacy of FAS inhibitors in mitigating this process.
Methods: Cell culture: U937 monocytes were differentiated into macrophages using PMA (200ng/mL) for 24h. Foam Cell Assay: Differentiated macrophages were cultured under various conditions. The RPMI1640 media supplemented with 5% FBS used as a negative control. To induce MDFc, some cultures used 5% human serum containing high FAS/low LDL levels as a positive control. Other cultures combined human serum containing low FAS with high, medium, or low LDL levels. Additionally, the effects of FAS inhibitors were tested by adding PTM (20μM), TVB-2640 (100nM), or GSK2194069 (10nM) to the media for 48h, both with and without high FAS/low LDL levels. Oil-O-Red Staining: Lipid droplets were quantified after neutral lipid staining with Oil-O-Red.
Results: Our findings reveal a notable increase in the formation of MDFc when macrophages were cultured with high FAS/low LDL levels as compared to the low FAS/low LDL condition (P=0.00082) and as compared to the negative control using 5% FBS (P=0.0001). Furthermore, we observed a significant reduction in lipid droplets within MDFc following treatment with FAS inhibitors. Both the selective FAS inhibitors TVB2640 and GSK2194069 led to significant reductions in MDFc (P<0.0001).
Conclusion: Our findings underscore the potential role of FAS in promoting the formation of MDFc. Pharmacological inhibition of FAS can mitigate foam cell formation, which represents a potential novel avenue for clinical management of atherosclerosis. Further exploration of the mechanism of action of pharmacological targeting of extracellular cFAS versus intracellular FAS in pre-clinical in vivo models is warranted.
More abstracts on this topic:
Abdominal Aortic Perivascular Adipose Tissue Lipolysis Is Activated In Hypertensive Dahl SS Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet
Chirivi Miguel, Rendon Javier, Lauver Adam, Fink Gregory, Watts Stephanie, Contreras Andres
A Loss of Function Polymorphism in the Propeptide of Lysyl Oxidase Exacerbates AtherosclerosisJung In-hyuk, Amrute Junedh, Luna Sophia, Wagoner Ryan, Lee Paul, Burks Kendall, Holloway Karyn, Alisio Arturo, Stitziel Nathan