Final ID: MDP1154
PAROXYSMAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION PATIENTS ON ANTICOAGULATION PRESENTING WITH EMBOLIC STROKE: A NATIONWIDE ANALYSIS
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here):
Introduction/ Background
Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation is a clinical condition that increases the risk for embolic stroke. Current guidelines suggest anticoagulating patients with atrial fibrillation when the chadvasc score is > 2 to decrease the risk of embolic stroke.
Aim/ Research Questions
Analyze comorbid conditions that holds significant associations with occurence of embolic stroke in paroxsymal atrial fibrillation admissions while being on long term anticoagulation.
Methods/Approach
We used National inpatient Sample (2019) to identify admissions for embolic pattern stroke, with documented history of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (p AFib) on chronic anticoagulation (AC) (Age group > 18 years).Prevalence of comorbid conditions in the cohort was analyzed. Associations of the comorbid conditions with occurrence of embolic stroke in the admission cohort was analyzed using multivariate linear regression. A two tailed p value < 0.05 was used to define significance in all the calculations.
Results/Data (descriptive and inferential statistics)
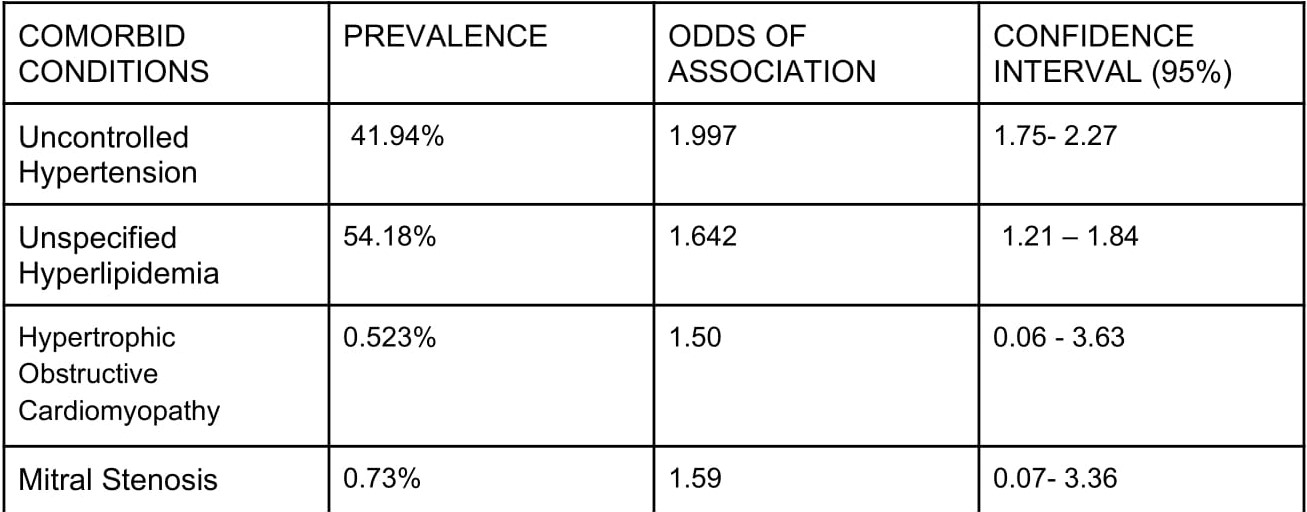
Of 4780 admissions for embolic stroke with comorbid Pafib on chronic AC were identified. Mean age of the admission cohort was 76.94. Of the admissions, 38.192% had congestive heart failure, 25.83% had chronic kidney disease, 41.94% had uncontrolled hypertension, 54.18% had diagnosis of unspecified hyperlipidemia, 0.523% had Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, 0.73% had rheumatic/non rheumatic mitral stenosis listed as their comorbidities. Statistically significant association was seen between uncontrolled hypertension and occurence of embolic stroke OR: 1.997. 95%: 1.756- 2.27. Documented diagnosis of unspecified hyperlipidemia had statistically significant association with admissions for embolic stroke in the patient cohort: OR: 1.642, 95% CI: 1.214 – 1.845). Presence of coexisting HOCM and Mitral stenosis had positive ODDs but did not reach statistical significance {HOCM: OR :1.50, 95% :0.062 - 3.63 and Mitral stenosis: OR: 1.59, 95%: 0.075- 3.36). (Table 1) There was no statistically significant association between CHF, CKD, smoking or with presence of prosthetic valve with embolic stroke.
(HOCM: hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy) (OR: Odds Ratio)
Conclusion(s)
Based on our analysis, presence of uncontrolled hypertension and hyperlipidemia had significant association with the occurrence of embolic stroke in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation population who were on long term anticoagulation.
Introduction/ Background
Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation is a clinical condition that increases the risk for embolic stroke. Current guidelines suggest anticoagulating patients with atrial fibrillation when the chadvasc score is > 2 to decrease the risk of embolic stroke.
Aim/ Research Questions
Analyze comorbid conditions that holds significant associations with occurence of embolic stroke in paroxsymal atrial fibrillation admissions while being on long term anticoagulation.
Methods/Approach
We used National inpatient Sample (2019) to identify admissions for embolic pattern stroke, with documented history of Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation (p AFib) on chronic anticoagulation (AC) (Age group > 18 years).Prevalence of comorbid conditions in the cohort was analyzed. Associations of the comorbid conditions with occurrence of embolic stroke in the admission cohort was analyzed using multivariate linear regression. A two tailed p value < 0.05 was used to define significance in all the calculations.
Results/Data (descriptive and inferential statistics)
Of 4780 admissions for embolic stroke with comorbid Pafib on chronic AC were identified. Mean age of the admission cohort was 76.94. Of the admissions, 38.192% had congestive heart failure, 25.83% had chronic kidney disease, 41.94% had uncontrolled hypertension, 54.18% had diagnosis of unspecified hyperlipidemia, 0.523% had Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy, 0.73% had rheumatic/non rheumatic mitral stenosis listed as their comorbidities. Statistically significant association was seen between uncontrolled hypertension and occurence of embolic stroke OR: 1.997. 95%: 1.756- 2.27. Documented diagnosis of unspecified hyperlipidemia had statistically significant association with admissions for embolic stroke in the patient cohort: OR: 1.642, 95% CI: 1.214 – 1.845). Presence of coexisting HOCM and Mitral stenosis had positive ODDs but did not reach statistical significance {HOCM: OR :1.50, 95% :0.062 - 3.63 and Mitral stenosis: OR: 1.59, 95%: 0.075- 3.36). (Table 1) There was no statistically significant association between CHF, CKD, smoking or with presence of prosthetic valve with embolic stroke.
(HOCM: hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy) (OR: Odds Ratio)
Conclusion(s)
Based on our analysis, presence of uncontrolled hypertension and hyperlipidemia had significant association with the occurrence of embolic stroke in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation population who were on long term anticoagulation.
More abstracts on this topic:
4-5 Years Outcomes of Left Atrial Appendage Closure vs. Oral Anticoagulants in Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis:
Khan Muhammad Aslam, Haider Taimoor, Bhattarai Shraddha, Afzal Hafsa, Khan Bilal, Muhammad Anza, Shafique Nouman, Bhatia Hitesh, Aafreen Asna, Adil Abid Nawaz Khan, Akbar Usman, Khan Alamzaib, Haider Muhammad Adnan
Anticoagulation For Patients On Hemodialysis And Atrial FibrillationEbrahimi Ramin, Alvarez Carlos, Dennis Paul