Final ID: Mo2076
Relationships Between Degree of Obesity, Transthoracic Impedance, and Cardioversion Efficacy
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background:
In our recent multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of single versus dual direct current cardioversion (DCCV) in patients with significant obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥35 kg/m2) undergoing DCCV for atrial fibrillation (AF), we found higher success rates using dual-DCCV. In addition to total energy applied, another important parameter is transthoracic impedance (TTI), as it impacts myocardial current density. Higher TTI is associated with DCCV failure. Previous studies found a positive correlation between BMI and TTI among normal-BMI patients (B=1.9 Ω/[kg/m2]). Whether there is a significant relationship between BMI and TTI in obese patients is unknown.
Objective:
In this post-hoc analysis of the dual-DCCV study, we investigated whether further increase in BMI above 35 kg/m2 correlates with increasing TTI, and whether TTI impacts procedural success in obese patients.
Methods:
Of the 200 patients included in the primary study, impedance data were available for 112. The relationship between BMI and TTI was compared using linear regression, and t-tests were used to assess whether DCCV efficacy varied significantly with BMI or TTI.
Results:
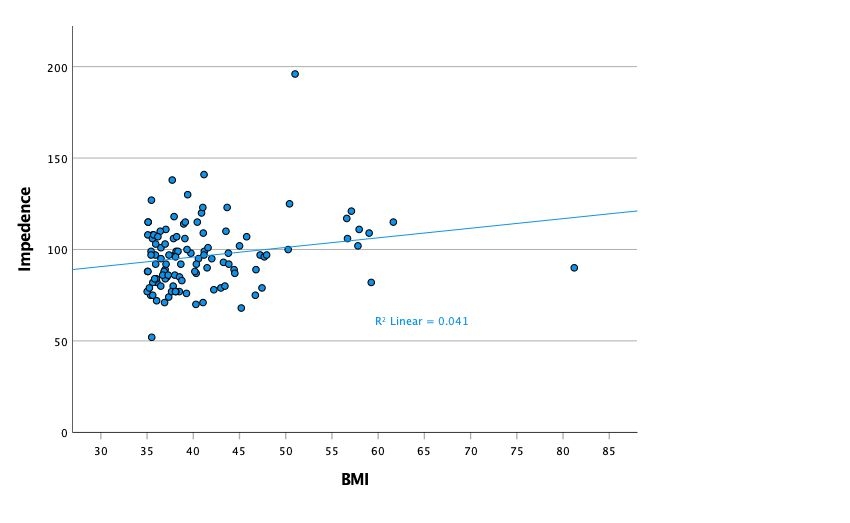
Among these 112 patients (age 65±11 years, BMI 41±7 kg/m2, 36 [32%] female, 17 [15%] Black), increasing BMI was weakly associated with a small, though statistically significant, increase in TTI (R2=0.04, B=0.53, p=0.03). There was no difference between patients with successful cardioversion (n=101) vs. failure (n=11) in terms of BMI (41±6 vs. 44±14 kg/m2, p=0.16) or TTI (96±19 vs. 98±18 Ω, p=0.81). These relationships were also true when the analysis was limited to participants receiving single-DCCV (n=57; with success in 48 [84%]): 41±6 vs. 45±15 kg/m2, p=0.21; and 98±15 vs. 102±17 Ω, p=0.48.
Conclusion:
In patients with Class 2 or higher obesity undergoing DCCV, there is a weaker association between further increase in BMI and TTI than previously found among patients with BMI <35 kg/m2. Further, in this high BMI population, there is no difference in TTI or BMI based on success or failure of DCCV.
In our recent multicenter randomized clinical trial comparing the efficacy of single versus dual direct current cardioversion (DCCV) in patients with significant obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥35 kg/m2) undergoing DCCV for atrial fibrillation (AF), we found higher success rates using dual-DCCV. In addition to total energy applied, another important parameter is transthoracic impedance (TTI), as it impacts myocardial current density. Higher TTI is associated with DCCV failure. Previous studies found a positive correlation between BMI and TTI among normal-BMI patients (B=1.9 Ω/[kg/m2]). Whether there is a significant relationship between BMI and TTI in obese patients is unknown.
Objective:
In this post-hoc analysis of the dual-DCCV study, we investigated whether further increase in BMI above 35 kg/m2 correlates with increasing TTI, and whether TTI impacts procedural success in obese patients.
Methods:
Of the 200 patients included in the primary study, impedance data were available for 112. The relationship between BMI and TTI was compared using linear regression, and t-tests were used to assess whether DCCV efficacy varied significantly with BMI or TTI.
Results:
Among these 112 patients (age 65±11 years, BMI 41±7 kg/m2, 36 [32%] female, 17 [15%] Black), increasing BMI was weakly associated with a small, though statistically significant, increase in TTI (R2=0.04, B=0.53, p=0.03). There was no difference between patients with successful cardioversion (n=101) vs. failure (n=11) in terms of BMI (41±6 vs. 44±14 kg/m2, p=0.16) or TTI (96±19 vs. 98±18 Ω, p=0.81). These relationships were also true when the analysis was limited to participants receiving single-DCCV (n=57; with success in 48 [84%]): 41±6 vs. 45±15 kg/m2, p=0.21; and 98±15 vs. 102±17 Ω, p=0.48.
Conclusion:
In patients with Class 2 or higher obesity undergoing DCCV, there is a weaker association between further increase in BMI and TTI than previously found among patients with BMI <35 kg/m2. Further, in this high BMI population, there is no difference in TTI or BMI based on success or failure of DCCV.
More abstracts on this topic:
A novel risk score predicts the prevalence of left atrial low-voltage areas and rhythm outcome in patients undergoing long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation ablation
Ooka Hirotaka, Nakao Sho, Kusuda Masaya, Ariyasu Wataru, Kudo Satoshi, Fujii Subaru, Mano Toshiaki, Matsuda Yasuhiro, Masuda Masaharu, Okamoto Shin, Ishihara Takayuki, Nanto Kiyonori, Tsujimura Takuya, Hata Yosuke, Uematsu Hiroyuki
A Multimodal Artificial Intelligence Signature of Advanced Cardiac and Vascular Aging Defines Elevated Risk of Cardiovascular DiseasePerera Sudheesha, Biswas Dhruva, Dhingra Lovedeep, Aminorroaya Arya, Coppi Andreas, Khera Rohan