Final ID: Mo2009
Complex Pathogenesis and Clinical Presentations of Pediatric Infectious Endocarditis in the Modern Era
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Infective endocarditis (IE) can induce serious acute and chronic impacts on the cardiovascular system in children. Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a common predisposing factor, but IE can occur without CHD, suggesting its complex pathogenesis.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed for patients with an admission diagnosis of IE. Demographic data, clinical manifestations, isolated organisms, treatment, and outcomes were studied.
Results
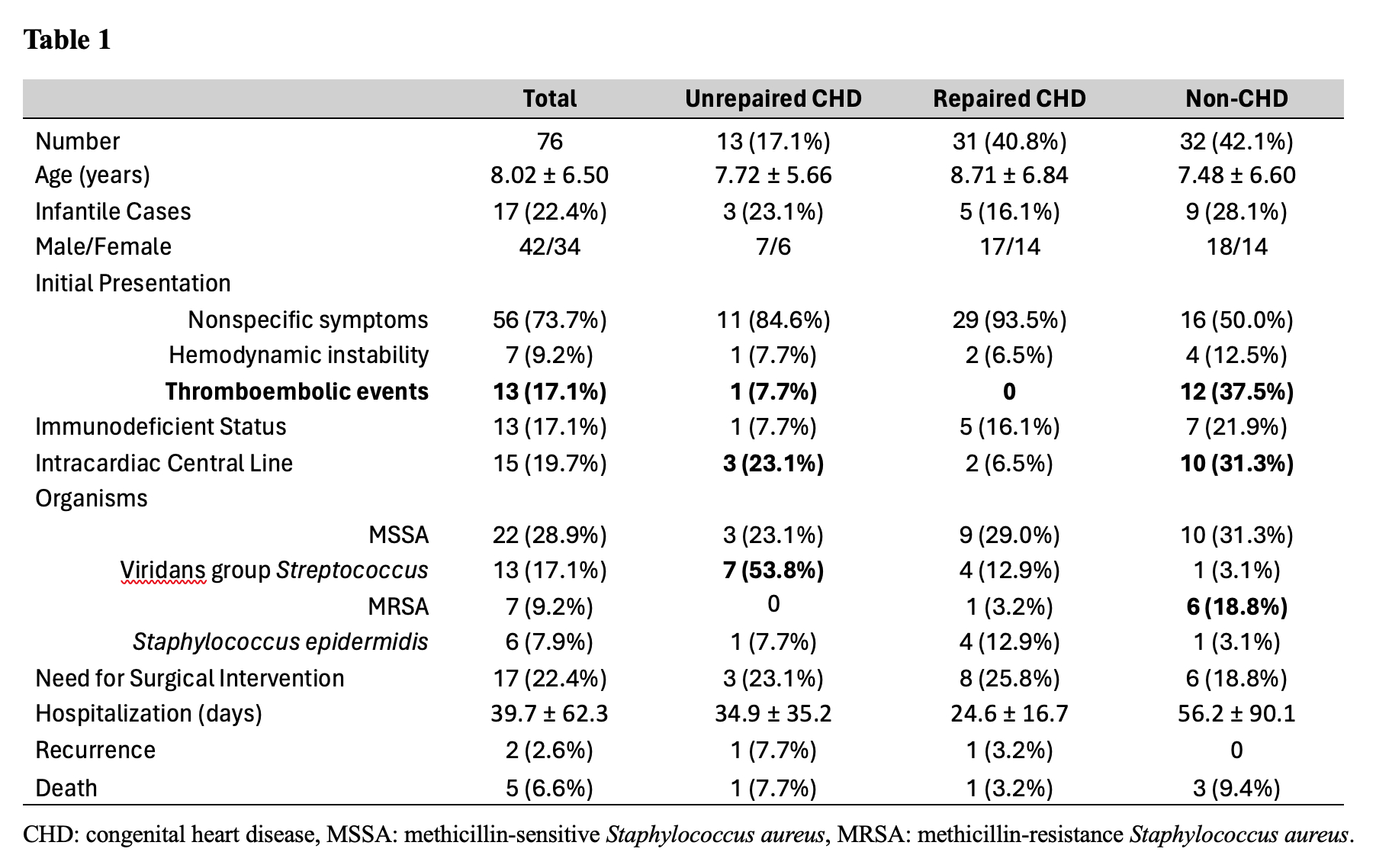
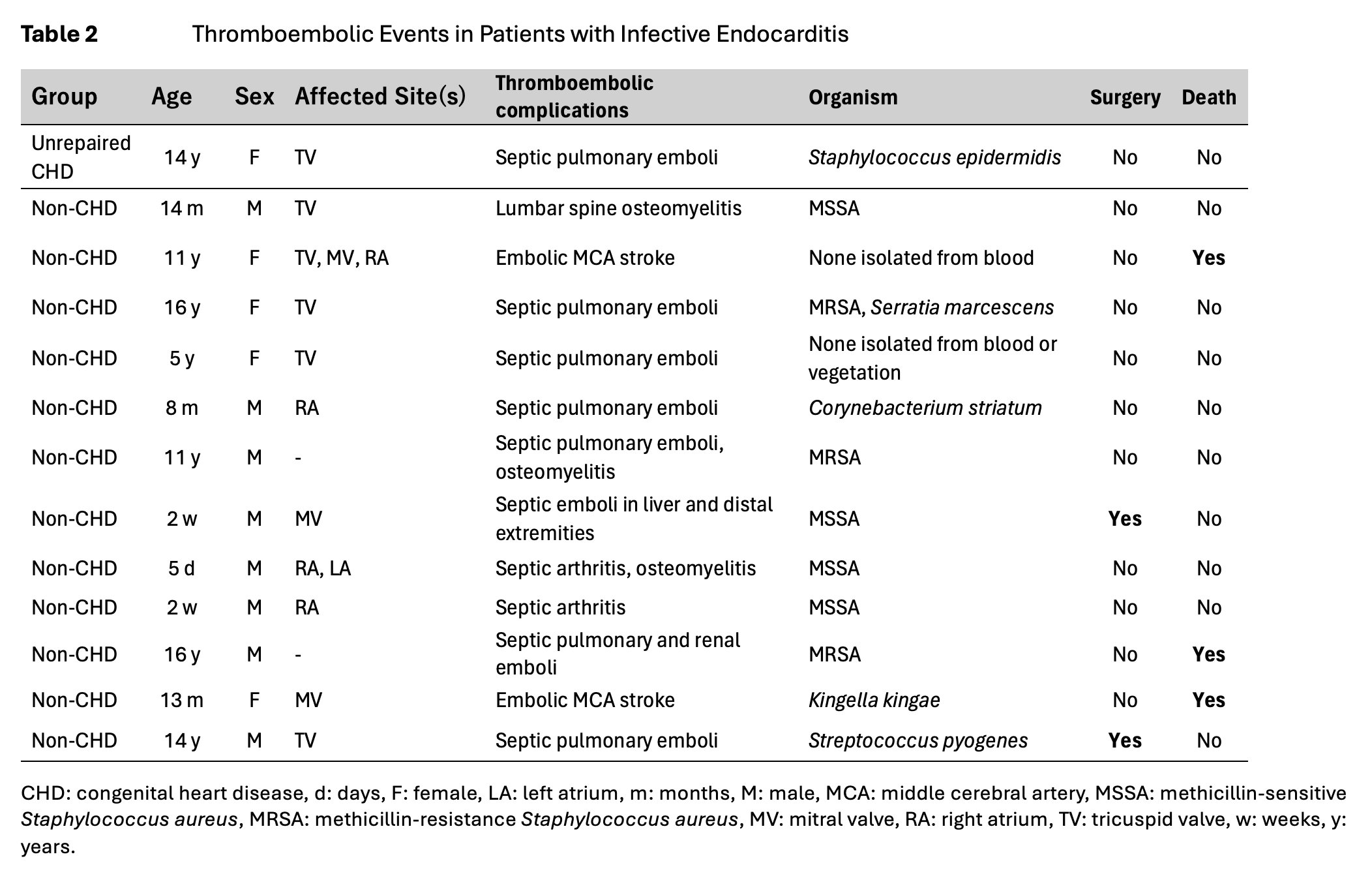
A total of 76 IE cases were divided into unrepaired CHD (13), repaired CHD (31), and non-CHD (32) (Table 1). There was no significant difference in age or sex between the three groups. Although a majority of the patients presented with nonspecific symptoms, a high incidence of thromboembolic events was noted in the Non-CHD group. Five patients with repaired CHD had DiGeorge syndrome. Overall, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was the most common organism; a high incidence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus was noted only in the Non-CHD group. Surgical intervention and hospitalization days were comparable between the groups. Recurrence was noted only in 2 cases. In 13 patients with thromboembolic events at presentation, vegetations were identified in the right (7), left (2), and both (2) sides of the heart (Table 2). Embolic events were noted as pulmonary embolism (5), arthritis/osteomyelitis (5), stroke (2), liver abscess (1), and renal embolism (1). Two patients developed an embolism in both pulmonary and systemic circulation. There were 5 total deaths, 3 of which occurred in the Non-CHD group. Two of these deaths in the Non-CHD group were directly attributable to embolic strokes from IE.
Conclusions
Distinct clinical pictures of IE were identified with and without underlying CHD. The IE without CHD was characterized by a high incidence of thromboembolic events and mortality rate. The pathogenesis and clinical presentation of IE has become more diverse due to more advanced and comprehensive medical treatment.
Infective endocarditis (IE) can induce serious acute and chronic impacts on the cardiovascular system in children. Congenital heart disease (CHD) is a common predisposing factor, but IE can occur without CHD, suggesting its complex pathogenesis.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed for patients with an admission diagnosis of IE. Demographic data, clinical manifestations, isolated organisms, treatment, and outcomes were studied.
Results
A total of 76 IE cases were divided into unrepaired CHD (13), repaired CHD (31), and non-CHD (32) (Table 1). There was no significant difference in age or sex between the three groups. Although a majority of the patients presented with nonspecific symptoms, a high incidence of thromboembolic events was noted in the Non-CHD group. Five patients with repaired CHD had DiGeorge syndrome. Overall, Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) was the most common organism; a high incidence of methicillin-resistant S. aureus was noted only in the Non-CHD group. Surgical intervention and hospitalization days were comparable between the groups. Recurrence was noted only in 2 cases. In 13 patients with thromboembolic events at presentation, vegetations were identified in the right (7), left (2), and both (2) sides of the heart (Table 2). Embolic events were noted as pulmonary embolism (5), arthritis/osteomyelitis (5), stroke (2), liver abscess (1), and renal embolism (1). Two patients developed an embolism in both pulmonary and systemic circulation. There were 5 total deaths, 3 of which occurred in the Non-CHD group. Two of these deaths in the Non-CHD group were directly attributable to embolic strokes from IE.
Conclusions
Distinct clinical pictures of IE were identified with and without underlying CHD. The IE without CHD was characterized by a high incidence of thromboembolic events and mortality rate. The pathogenesis and clinical presentation of IE has become more diverse due to more advanced and comprehensive medical treatment.
More abstracts on this topic:
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Gene Polymorphisms (ACE-I/D) Do Not Predict Exercise-Induced Cardiac Remodeling or Performance in Adolescent Male Athletes
Becker Kristian, Hardie William, Gubanich Paul, Hill Garick, Logan Kelsey, Martin Lisa, Powell Adam
4D Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Identifies Differences in Regional Strain Patterns Among Pediatric Heart Transplant Patients with Acute Rejection or Cardiac Allograft VasculopathyHenderson Christopher, Starnes Joseph, Samyn Margaret, Damon Bruce, Hernandez Lazaro, Goergen Craig, Soslow Jonathan, Prado Marco Aurélio, Earl Conner, Georgedurrett Kristen, Lee Simon, Nandi Deipanjan, Chan Kak-chen, Shugh Svetlana, Kikano Sandra