Final ID: Su3022
Air pollution exposure and effect of finerenone treatment in patients with chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes: A FIDELITY analysis
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background
Finerenone significantly reduced the risk of CV and adverse kidney outcomes vs placebo in patients with CKD and T2D in FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of the phase III FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials. Exposure to particulate matter air pollution ≤2.5 microns (PM2.5) is established as the world’s leading environmental risk factor and is implicated in CV and kidney events. This FIDELITY post-hoc subanalysis aimed to examine the effect of finerenone across varying levels of PM2.5 exposure.
Methods
Patients in FIDELITY were on optimized renin–angiotensin system inhibition and randomized 1:1 to finerenone or placebo. Key outcomes included composite CV (CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure), composite kidney (kidney failure, sustained ≥57% decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline over at least 4 weeks, or kidney-related death), and combined composite CV and kidney. Participants were assigned to antecedent PM2.5 exposure using site location at the time of enrollment (annual PM2.5 using an integrated exposure model). The effect of finerenone vs placebo was assessed on outcomes across strata of PM2.5 exposure (quartiles, ≤ vs > median) and as a continuous variable.
Results
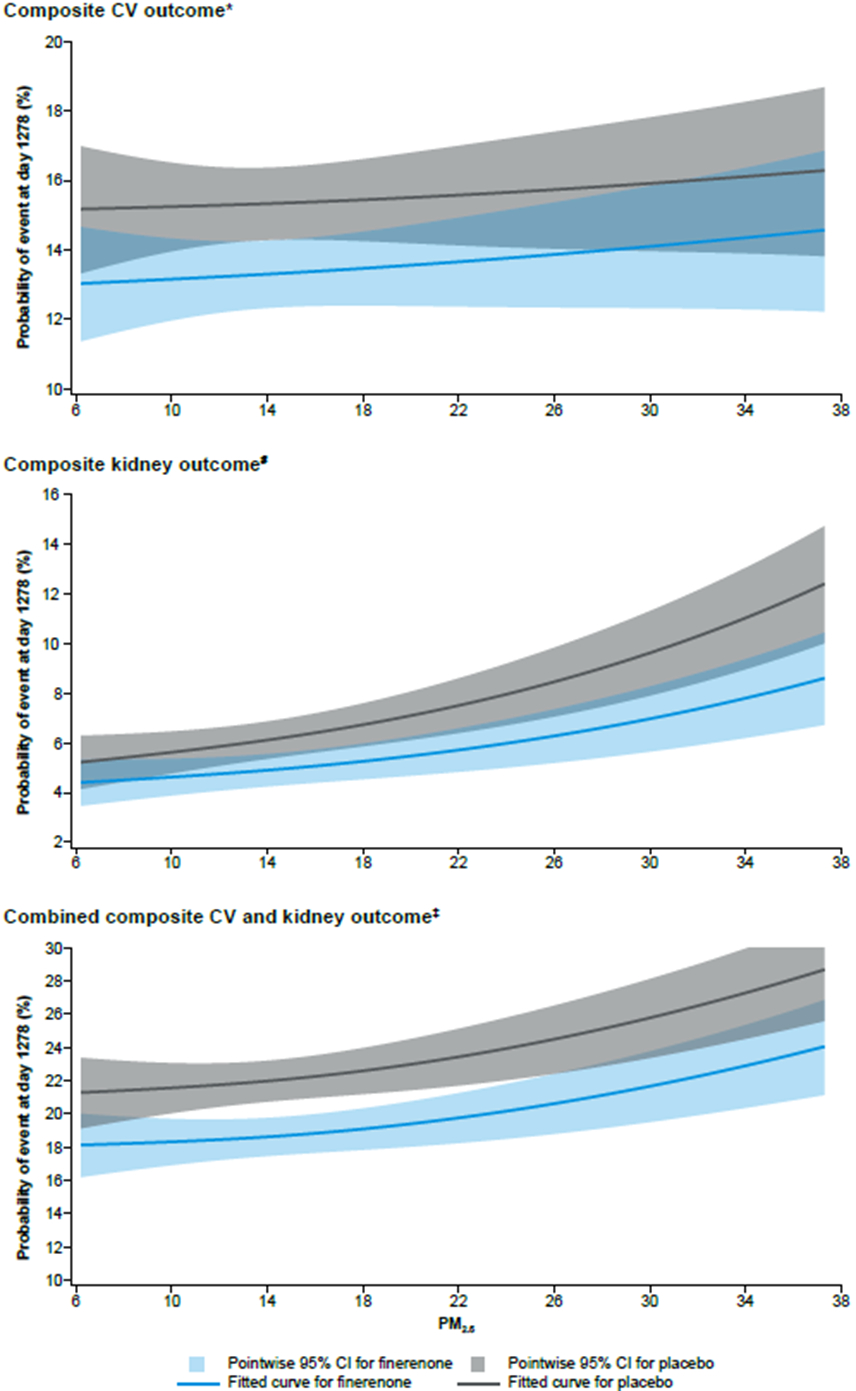
A total of 12,990 participants were included. Median PM2.5 exposure was 15.5 (IQR 9.8–21.0) µg/m3. PM2.5 exposure was associated with higher CV and kidney event rates (Fig 1). Although finerenone had a similar beneficial impact on composite CV and renal outcomes across strata of PM2.5 exposure (Pinteraction=NS), the numbers needed to treat to prevent one composite CV/kidney event were 34 and 29 for participants at low (≤ median) and high (> median) PM2.5 exposure, respectively. The finerenone safety profile was generally similar across PM2.5 quartiles.
Conclusions
In FIDELITY, finerenone lowered the risks of CV and kidney outcomes vs placebo in patients with CKD and T2D irrespective of PM2.5 exposure levels. Given the association between PM2.5 and risk of CV and kidney events, finerenone may be particularly beneficial in those exposed to higher air pollution levels.
Finerenone significantly reduced the risk of CV and adverse kidney outcomes vs placebo in patients with CKD and T2D in FIDELITY, a prespecified pooled analysis of the phase III FIDELIO-DKD and FIGARO-DKD trials. Exposure to particulate matter air pollution ≤2.5 microns (PM2.5) is established as the world’s leading environmental risk factor and is implicated in CV and kidney events. This FIDELITY post-hoc subanalysis aimed to examine the effect of finerenone across varying levels of PM2.5 exposure.
Methods
Patients in FIDELITY were on optimized renin–angiotensin system inhibition and randomized 1:1 to finerenone or placebo. Key outcomes included composite CV (CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, nonfatal stroke, or hospitalization for heart failure), composite kidney (kidney failure, sustained ≥57% decrease in estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline over at least 4 weeks, or kidney-related death), and combined composite CV and kidney. Participants were assigned to antecedent PM2.5 exposure using site location at the time of enrollment (annual PM2.5 using an integrated exposure model). The effect of finerenone vs placebo was assessed on outcomes across strata of PM2.5 exposure (quartiles, ≤ vs > median) and as a continuous variable.
Results
A total of 12,990 participants were included. Median PM2.5 exposure was 15.5 (IQR 9.8–21.0) µg/m3. PM2.5 exposure was associated with higher CV and kidney event rates (Fig 1). Although finerenone had a similar beneficial impact on composite CV and renal outcomes across strata of PM2.5 exposure (Pinteraction=NS), the numbers needed to treat to prevent one composite CV/kidney event were 34 and 29 for participants at low (≤ median) and high (> median) PM2.5 exposure, respectively. The finerenone safety profile was generally similar across PM2.5 quartiles.
Conclusions
In FIDELITY, finerenone lowered the risks of CV and kidney outcomes vs placebo in patients with CKD and T2D irrespective of PM2.5 exposure levels. Given the association between PM2.5 and risk of CV and kidney events, finerenone may be particularly beneficial in those exposed to higher air pollution levels.
More abstracts on this topic:
A major effect of aprocitentan on albuminuria in patients with resistant hypertension
Schlaich Markus, Bakris George, Flack John, Gimona Alberto, Narkiewicz Krzysztof, Sassi-sayadi Mouna, Wang Jiguang, Weber Michael
Age-standardized trends in Incidence Rates of Noncommunicable diseases among Adults Aged 30 to 79 in Senegal from 2000 to 2019Gaye Ngone, Ka Mame, Kyem Damaris, Jobe Modou, Sattler Elisabeth, Gary-webb Tiffany, Gaye Bamba