Final ID: MDP842
Machine Learning-Based Clinical Predictive Models for Early Readmission in Patients with Cardiogenic Shock
Abstract Body (Do not enter title and authors here): Background/Purpose: Cardiogenic shock (CS) affects up to 50,000 people annually in the United States, with high in-hospital mortality rates of 40%-67%. About 18.6% of CS survivors are re-admitted. This study aims to predict 7-day and 30-day readmissions in CS patients using machine learning (ML) algorithms to guide targeted interventions and improve healthcare outcomes.
Methods: This retrospective study used the 2019 National Readmissions Database (NRD). CS hospitalizations were identified using ICD-10 code R57.0. Welch’s t-test compared continuous variables. The dataset was split into training and testing sets with a 7:3 ratio. Commonly used ML models, including XGBoost, Adaboost, decision tree, and random forest, were compared with logistic regression (LR). The primary outcome was CS readmission within 7 or 30 days of discharge. The area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used for performance measurement.
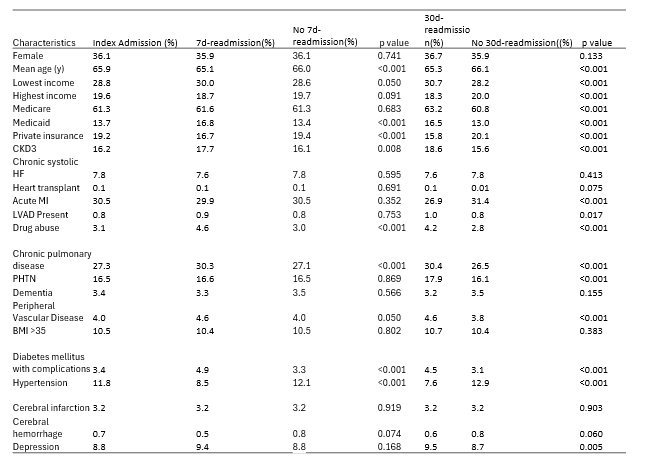
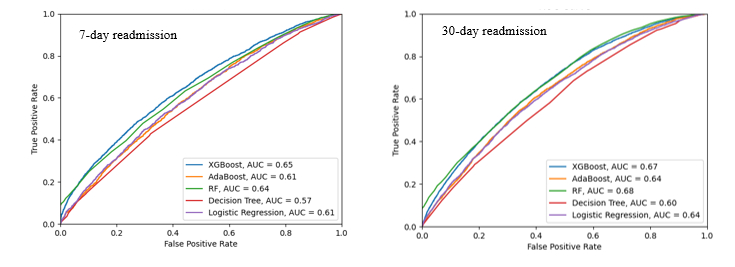
Results: Among 97,653 CS patients, 32,881 (33.7%) died during their initial hospitalization. Index hospitalizations were 51,976. We excluded hospitalizations where patients died during their initial stay, as these cases would not contribute to readmission data. Additionally, we only considered hospitalizations from January to November, excluding December hospitalizations since their 30-day readmissions would occur in the following year. The 7-day readmission rate was 4,317 (8.3%), and the 30-day readmission rate was 10,927 (21.02%). Significant predictors for both readmission periods (p value <0.05) included lower mean age, lower income, higher Medicaid coverage, lower private insurance coverage, higher rates of CKD3, chronic pulmonary disease, drug abuse, and diabetes with complications as shown in Table 1. Figure 1 shows the performance of various ML models, with XGBoost being the best model in both tasks, achieving an AUC of 0.65 for 7-day and 0.67 for 30-day readmissions, indicating less than a 70% chance of accurately predicting readmission. This performance was similar to that of LR (AUC of 0.61 and 0.67).
Conclusion: ML models have poor capacity for early CR readmission prediction and perform similarly to logistic regression (LR) when developed using large administrative datasets. To enhance future model development, incorporating electronic health records (EHRs) with more detailed and clinically relevant data should be considered.
Methods: This retrospective study used the 2019 National Readmissions Database (NRD). CS hospitalizations were identified using ICD-10 code R57.0. Welch’s t-test compared continuous variables. The dataset was split into training and testing sets with a 7:3 ratio. Commonly used ML models, including XGBoost, Adaboost, decision tree, and random forest, were compared with logistic regression (LR). The primary outcome was CS readmission within 7 or 30 days of discharge. The area under the curve (AUC) of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was used for performance measurement.
Results: Among 97,653 CS patients, 32,881 (33.7%) died during their initial hospitalization. Index hospitalizations were 51,976. We excluded hospitalizations where patients died during their initial stay, as these cases would not contribute to readmission data. Additionally, we only considered hospitalizations from January to November, excluding December hospitalizations since their 30-day readmissions would occur in the following year. The 7-day readmission rate was 4,317 (8.3%), and the 30-day readmission rate was 10,927 (21.02%). Significant predictors for both readmission periods (p value <0.05) included lower mean age, lower income, higher Medicaid coverage, lower private insurance coverage, higher rates of CKD3, chronic pulmonary disease, drug abuse, and diabetes with complications as shown in Table 1. Figure 1 shows the performance of various ML models, with XGBoost being the best model in both tasks, achieving an AUC of 0.65 for 7-day and 0.67 for 30-day readmissions, indicating less than a 70% chance of accurately predicting readmission. This performance was similar to that of LR (AUC of 0.61 and 0.67).
Conclusion: ML models have poor capacity for early CR readmission prediction and perform similarly to logistic regression (LR) when developed using large administrative datasets. To enhance future model development, incorporating electronic health records (EHRs) with more detailed and clinically relevant data should be considered.
More abstracts on this topic:
Assessing Prevalence of Cardiac Amyloidosis at the Time of Spinal Laminectomy for Spinal Stenosis
Sul Lidiya, Cotta Claudiu, Nakashima Megan, Steinmetz Michael, Kilpatrick Scott, Reith John, Hanna Mazen, Ives Lauren, Schlenk Richard, Kalfas Iain, Mroz Thomas, Orr Doug, Benzel Edward, Krishnaney Ajit, Pelle Dominic
A large-scale multi-view deep learning-based assessment of left ventricular ejection fraction in echocardiographyJing Linyuan, Metser Gil, Mawson Thomas, Tat Emily, Jiang Nona, Duffy Eamon, Hahn Rebecca, Homma Shunichi, Haggerty Christopher, Poterucha Timothy, Elias Pierre, Long Aaron, Vanmaanen David, Rocha Daniel, Hartzel Dustin, Kelsey Christopher, Ruhl Jeffrey, Beecy Ashley, Elnabawi Youssef